La pleuritis Pleuritis Pleuritis, also known as pleurisy, is an inflammation of the visceral and parietal layers of the pleural membranes of the lungs. The condition can be primary or secondary and results in sudden, sharp, and intense chest pain on inhalation and exhalation. Pleuritis, también conocida como pleuresía, es la inflamación de las capas visceral y parietal Parietal One of a pair of irregularly shaped quadrilateral bones situated between the frontal bone and occipital bone, which together form the sides of the cranium. Skull: Anatomy de las membranas pleurales de los LOS Neisseria pulmones. La afección puede ser primaria o secundaria y provoca dolor Dolor Inflammation torácico repentino, agudo e intenso que empeora con la inspiración. Las etiologías incluyen infección, traumatismo, embolia pulmonar y cáncer de pulmón. La causa infecciosa primaria más común es una infección viral, y las infecciones pulmonares subyacentes representan la mayoría de las causas infecciosas secundarias. El tratamiento consiste en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el control del dolor Dolor Inflammation y el tratamiento de la enfermedad subyacente.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
| Transudado | Exudado | |
|---|---|---|
| Proteína (pleural/sérica) | ≤ 0,5 | > 0,5 |
| LDH LDH Osteosarcoma (pleural/sérica) | ≤ 0,6 | > 0,6 |
| LDH LDH Osteosarcoma pleural ≤ dos-tercios del límite superior de la LDH LDH Osteosarcoma sérica normal | LDH LDH Osteosarcoma pleural > dos-tercios del límite superior de la LDH LDH Osteosarcoma sérica normal | |
| Causas comunes |
|
|
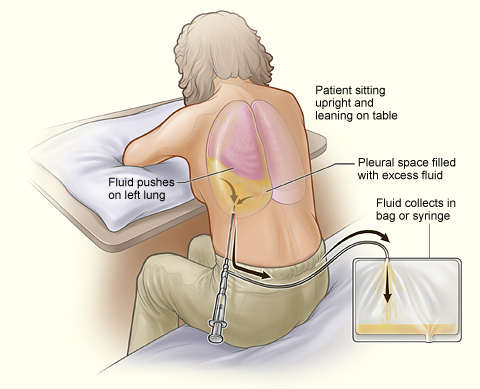
Paciente sometido a una toracocentesis. Obsérvese que la persona se sienta erguida y se apoya en una mesa. El exceso de líquido del espacio pleural se drena en una bolsa.
Imagen:“A person undergoing thoracentesis.” por National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute. Licencia: Dominio Público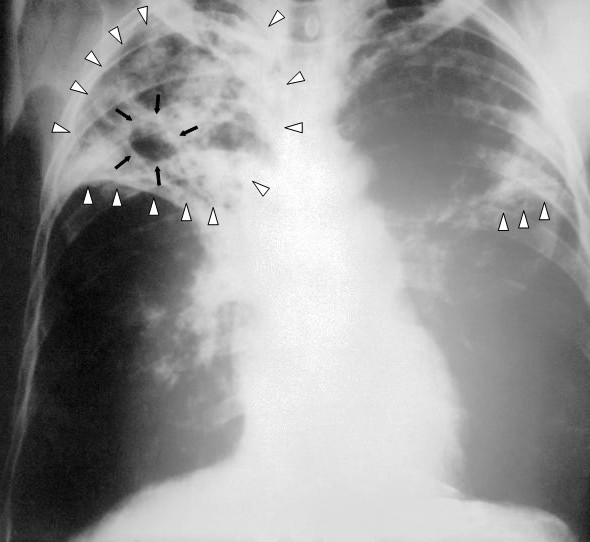
Radiografía de tórax que muestra una tuberculosis pulmonar bilateral avanzada. Nótese la presencia de infiltrados pulmonares bilaterales (triángulos blancos) y la formación una cavidad (flechas negras) en la región apical derecha.
Imagen: “An anteroposterior X-ray of a patient diagnosed with advanced bilateral pulmonary tuberculosis” por Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Public Health Image Library (PHIL). Licencia: Dominio Público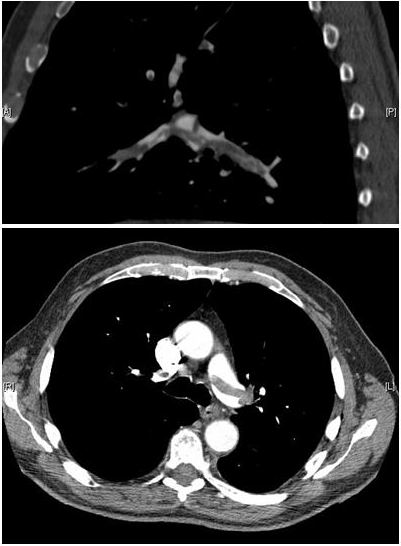
Angiografía pulmonar por TC que muestra un “émbolo en silla de montar” en la bifurcación de la arteria pulmonar principal y una carga de trombos en las arterias lobares de ambos lados. Puede causar sintomatología pleurítica.
Imagen: “CT pulmonary angiography images confirming the presence of a saddle embolus” por Aung Myat y Arif Ahsan. Licencia: CC BY 2.0