La ictericia es la coloración amarillenta anormal de la piel y/o la esclerótica causada por la acumulación de bilirrubina. La hiperbilirrubinemia es causada por un aumento en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la producción de bilirrubina o por una disminución en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la captación, conjugación o excreción hepática de bilirrubina. Las etiologías suelen afectar al AL Amyloidosis hígado y pueden ser prehepáticas, intrahepáticas o posthepáticas. Otros síntomas de hiperbilirrubinemia incluyen prurito, heces pálidas y orina oscura. El diagnóstico se realiza con base en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum pruebas de función hepática e imagenología. El tratamiento se enfoca en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el tratamiento de la condición subyacente.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
La ictericia es causada por una elevación de la bilirrubina sérica (hiperbilirrubinemia), que puede ser causada por:
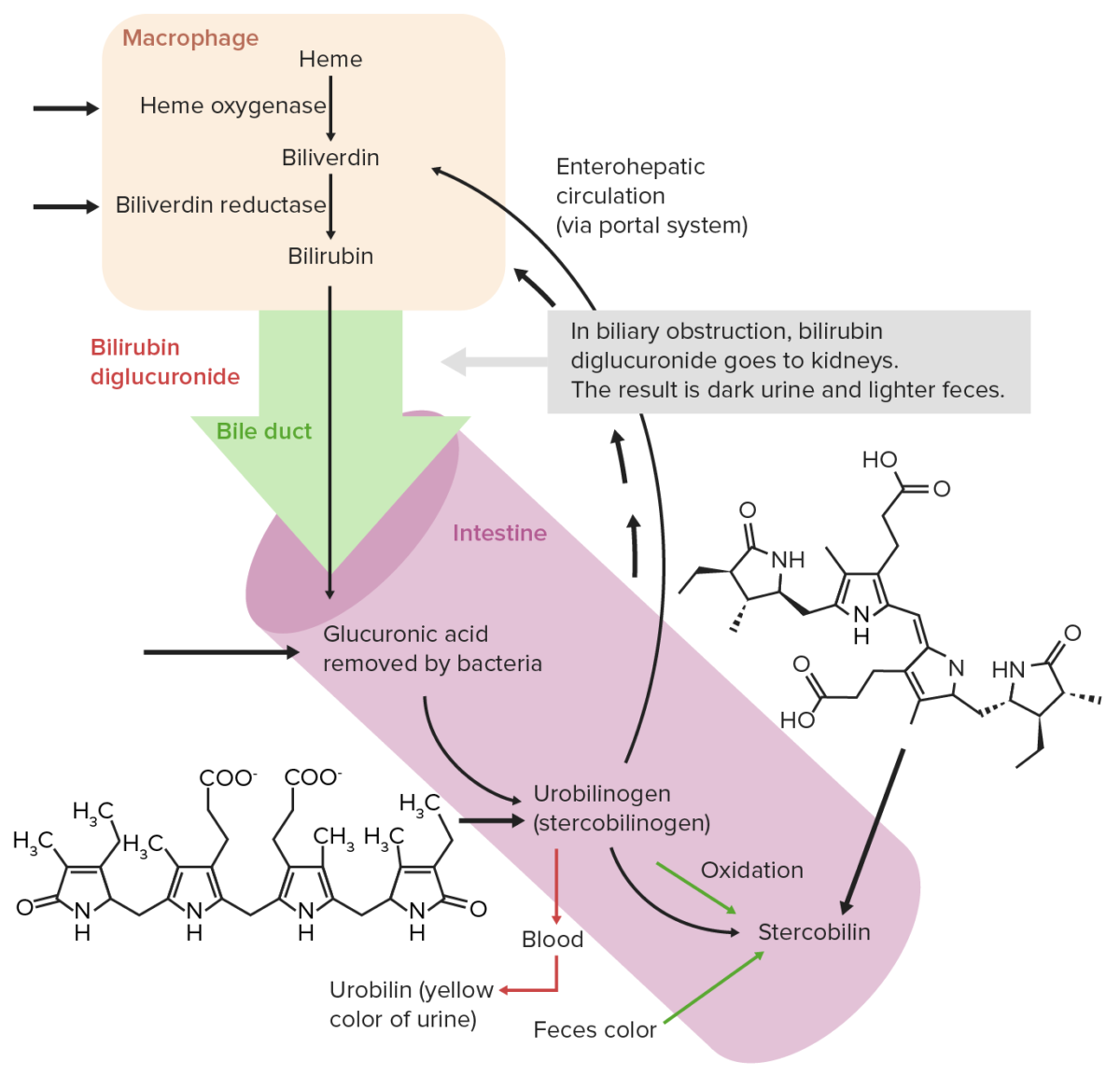
Circulación extrahepática normal de bilirrubina
Imagen por Lecturio. Licencia: CC BY-NC-SA 4.0Las causas comunes de la hiperbilirrubinemia se pueden recordar con la mnemotecnia “HOT Liver Liver The liver is the largest gland in the human body. The liver is found in the superior right quadrant of the abdomen and weighs approximately 1.5 kilograms. Its main functions are detoxification, metabolism, nutrient storage (e.g., iron and vitamins), synthesis of coagulation factors, formation of bile, filtration, and storage of blood. Liver: Anatomy” ( en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum inglés):
Las etiologías de la ictericia se pueden dividir en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum las que causan una hiperbilirrubinemia indirecta, directa o mixta (consulte la tabla a continuación).
| Hiperbilirrubinemia indirecta (no conjugada) | Trastornos hemolíticos | Heredados:
|
|---|---|---|
| Eritropoyesis ineficaz | Heredada:
|
|
| Aumento de la producción de bilirrubina | Secundario a:
|
|
| Disminución de la conjugación de bilirrubina |
|
|
| Medicamentos |
|
|
| Hiperbilirrubinemia directa (conjugada) | Obstrucción del tracto biliar | Secundaria a:
|
| Enfermedad del tracto biliar |
|
|
| Disminución de la excreción/recaptación de bilirrubina: |
|
|
| Hiperbilirrubinemia mixta (tanto indirecta como directa) | Condiciones crónicas |
|
Las etiologías de la ictericia también se pueden dividir según el sistema de órganos (condiciones hepáticas y colestásicas).
Intrahepáticas
Extrahepáticas
Estos síntomas pueden estar asociados con:
En EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la imagen a continuación se describen más estudios.
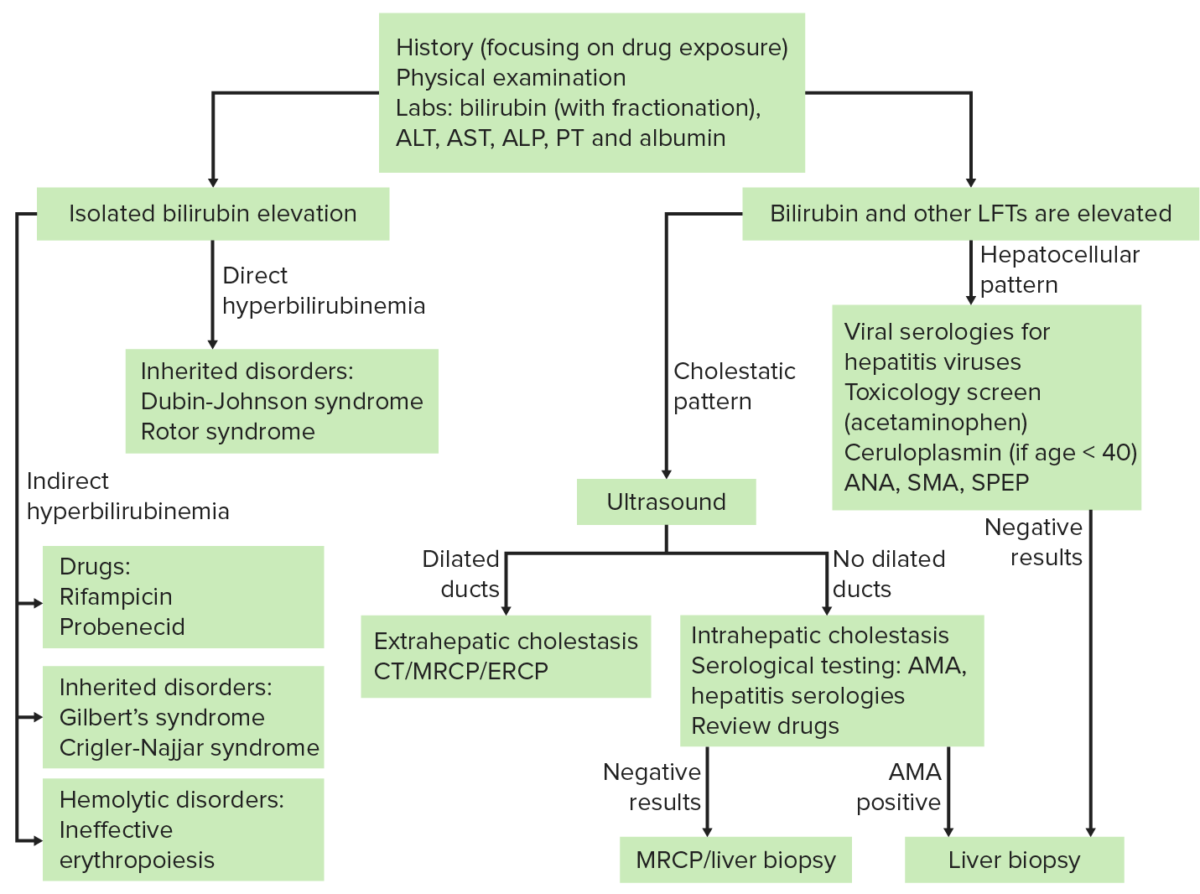
Abreviaturas clave:
ANA: anticuerpo antinuclear
SMA: anticuerpo de músculo liso
SPEP: electroforesis de proteínas séricas
AMA: anticuerpo antimitocondrial
CPRM: colangiopancreatografía por resonancia magnética
| Prehepática | Intrahepática | Posthepática | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Color de las heces | Oscura | Pálida, color arcilla | Pálida, color arcilla | |
| Análisis sanguíneo | Bilirrubina indirecta | ↑↑ | ↑ | Normal |
| Bilirrubina directa | Normal | ↑ | ↑↑ | |
| Anemia Anemia Anemia is a condition in which individuals have low Hb levels, which can arise from various causes. Anemia is accompanied by a reduced number of RBCs and may manifest with fatigue, shortness of breath, pallor, and weakness. Subtypes are classified by the size of RBCs, chronicity, and etiology. Anemia: Overview and Types | Presente | Ausente | Ausente | |
| Fosfatasa alcalina | Normal | ↑ | ↑↑ | |
| Transaminasas | Normal | ↑↑ | ↑ | |
| Análisis de orina | Color | Normal u oscura | Oscura | Oscura o muy oscura |
| Urobilinógeno | ↑↑ | Normal o ↑ | Bajo o ausente | |
| Sal biliar | Ausente | Ausente | Presente | |
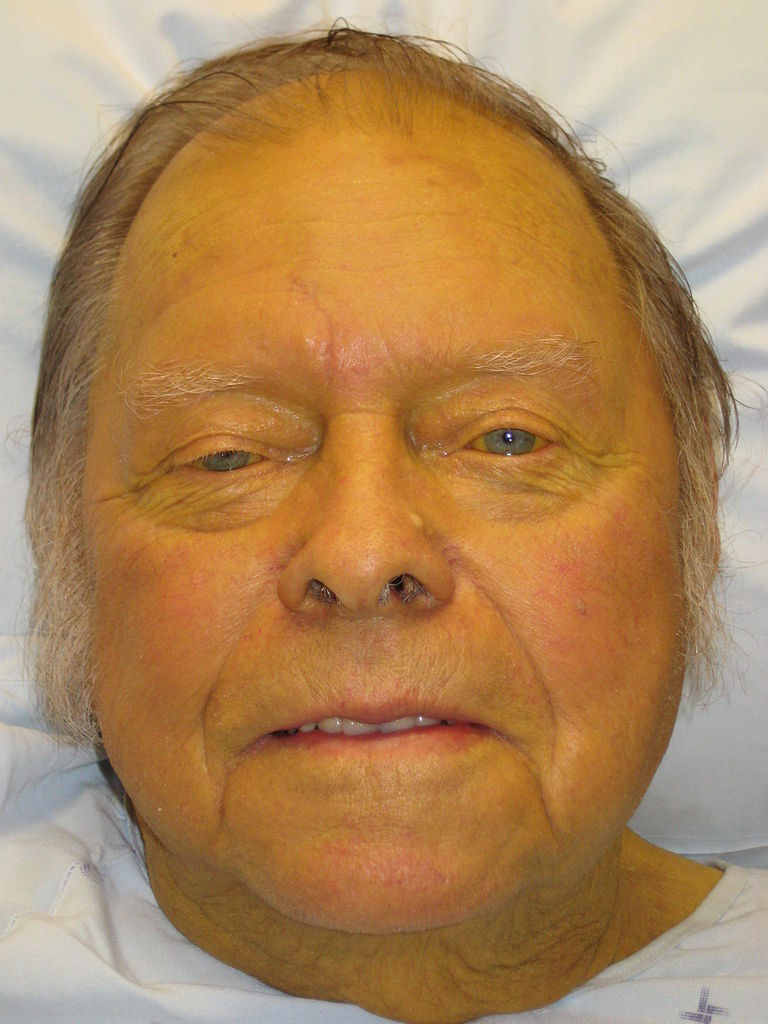
Ictericia: coloración amarilla de la piel debido a la deposición de bilirrubina
Imagen: “Jaundice08” por James Heilman, MD. Licencia: CC BY 3.0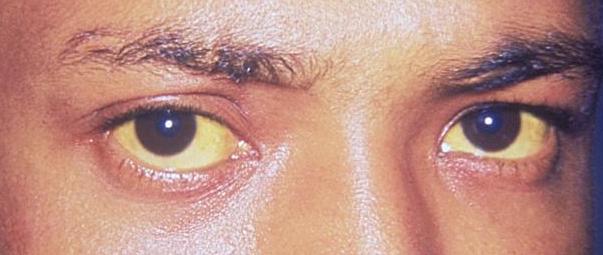
Ictericia escleral: El primer signo clínico de depósito de bilirrubina en el cuerpo.
Imagen: “Jaundice eye new” por CDC/Dr. Thomas F. Sellers/Emory University. Licencia: Dominio PúblicoEl tratamiento se basa en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el tratamiento de la condición subyacente.
Pseudoictericia ( carotenosis Carotenosis Jaundice): decoloración amarilla o anaranjada de la piel causada por la deposición de caroteno. Se puede distinguir de la ictericia verdadera porque no causa decoloración de las membranas conjuntivales de la esclerótica y los LOS Neisseria niveles de bilirrubina se mantienen normales. Suele ser secundaria a la ingesta excesiva de sustancias ricas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum carotenoides (e.g., suplementos multivitamínicos, naranjas, zanahorias, manzanas, brócoli, papayas, col rizada).