La granulomatosis con poliangeitis, anteriormente conocida como granulomatosis de Wegener, es una enfermedad autoinmune rara de etiología desconocida. Produce una inflamación granulomatosa necrosante de los LOS Neisseria vasos sanguíneos pequeños y medianos de la nariz, los LOS Neisseria senos paranasales, la garganta, los LOS Neisseria pulmones y los LOS Neisseria riñones. Los LOS Neisseria estadios iniciales de la granulomatosis con poliangeitis suelen presentar manifestaciones localizadas, como infecciones del tracto respiratorio superior, lesiones cutáneas y/o síntomas constitucionales. Los LOS Neisseria estadios posteriores pueden presentar insuficiencia renal y enfermedad respiratoria grave. El diagnóstico y el tratamiento tempranos de la granulomatosis con poliangeitis (que implica la administración de corticosteroides y agentes inmunosupresores como el metotrexato) pueden conducir a una remisión completa, pero sin tratamiento, la afección tiene una alta tasa de mortalidad.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
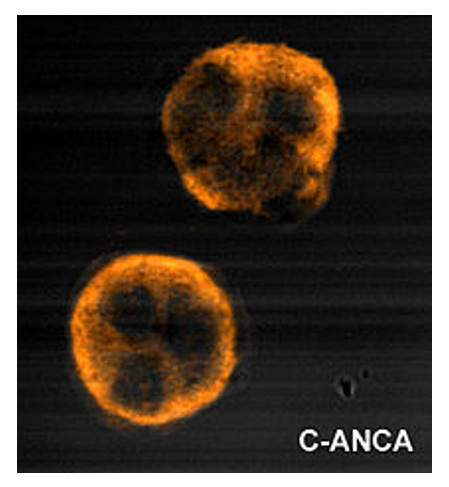
Tinción citoplasmática granular uniforme de c-ANCA
Imagen de Malittle, PD.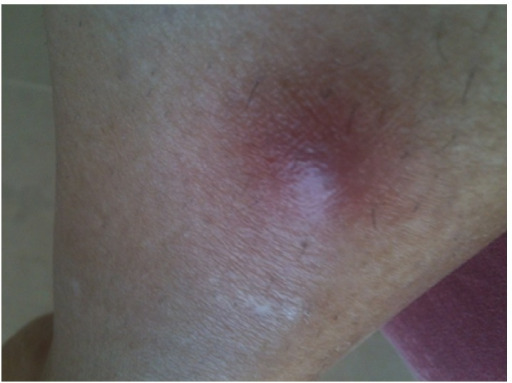
Nódulo eritematoso en la pierna derecha en un paciente con granulomatosis con poliangeitis
Imagen: “Initial lesion: erythematous nodule on right shin” por Section of Internal Medicine, Department of Medicine, The Aga Khan University Hospital, P.O. Box 3500, Stadium Road, Karachi 74800, Pakistan. Licencia: CC BY 3.0
Ejemplo de puente nasal colapsado (deformidad de nariz en silla de montar) visto en la granulomatosis con poliangeitis El paciente también muestra afectación orbital con proptosis (protrusión del globo ocular), edema palpebral y limitación de los movimientos oculares. La afectación orbital no suele producirse hasta años después del inicio de la enfermedad.
Imagen: “Anterior and lateral appearance of the patient” por Ophthalmic Research Center, Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran. Licencia: CC BY 2.5| 1. Inflamación nasal o bucal | Úlceras orales dolorosas o indoloras o secreción nasal purulenta o sanguinolenta |
|---|---|
| 2. Radiografía de tórax anormal | Nódulos pulmonares, infiltrados pulmonares fijos o cavidades pulmonares |
| 3. Sedimento urinario anormal | Hematuria Hematuria Presence of blood in the urine. Renal Cell Carcinoma microscópica con o sin cilindros eritrocitarios (glomerulonefritis) |
| 4. Inflamación granulomatosa | La biopsia de una arteria o zona perivascular muestra una inflamación granulomatosa. |
Radiografía de tórax: se observan múltiples lesiones nodulares y cavitadas predominantemente en el lado derecho, con múltiples infiltrados parcheados típicos de la granulomatosis con poliangeitis. Los ángulos costofrénicos están borrados debido a un pequeño derrame pleural bilateral.
Imagen: “Chest radiography at presentation” por Department of Pharmacology and Pharmacy, Faculty of Medicine University of Colombo, PO Box 271, Kynsey Road, Colombo 08, Sri Lanka. Licencia: CC BY 4.0
Biopsia de piel: vasculitis que afecta a la dermis superficial y profunda y que muestra necrosis fibrinoide de la pared de los vasos con formación de granulomas, infiltrado neutrofílico y restos nucleares.
Imagen: “Skin biopsy” por Section of Internal Medicine, Department of Medicine, The Aga Khan University Hospital, P.O. Box 3500, Stadium Road, Karachi 74800, Pakistan. Licencia: CC BY 3.0