Además de las otras tres clases principales de agentes antimicóticos ( azoles Azoles Azoles are a widely used class of antifungal medications inhibiting the production of ergosterol, a critical component in the fungal cell membrane. The 2 primary subclasses of azoles are the imidazoles, older agents typically only used for topical applications, and the triazoles, newer agents with a wide spectrum of uses. Azoles, polienos y equinocandinas), se utilizan otros agentes antimicóticos clínicamente importantes, que incluyen flucitosina, griseofulvina y terbinafina. Cada medicamento tiene un mecanismo de acción distinto y características e indicaciones únicas. La flucitosina es un análogo de pirimidina que interrumpe la síntesis de ADN y ARN fúngico. La flucitosina siempre se usa en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum combinación con otros agentes antimicóticos y se usa principalmente para tratar la meningitis Meningitis Meningitis is inflammation of the meninges, the protective membranes of the brain, and spinal cord. The causes of meningitis are varied, with the most common being bacterial or viral infection. The classic presentation of meningitis is a triad of fever, altered mental status, and nuchal rigidity. Meningitis criptocócica. Tanto la griseofulvina como la terbinafina actúan dentro del estrato córneo de la piel y se emplean para tratar las infecciones por dermatofitos de la piel, el cabello y las uñas.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Además de las 3 clases principales de agentes antimicóticos ( azoles Azoles Azoles are a widely used class of antifungal medications inhibiting the production of ergosterol, a critical component in the fungal cell membrane. The 2 primary subclasses of azoles are the imidazoles, older agents typically only used for topical applications, and the triazoles, newer agents with a wide spectrum of uses. Azoles, polienos y equinocandinas), existen varios otros agentes antimicóticos clínicamente importantes. Estos medicamentos incluyen:
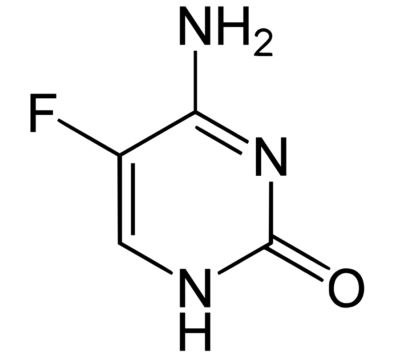
Estructura química de la flucitosina.
Imagen : “Structural diagram of 5-fluorocytosine” por Fvasconcellos. Licencia: Dominio Público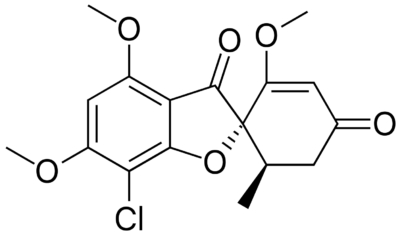
Estructura química de griseofulvina
Imagen : “Griseofulvin” por Fvasconcellos. Licencia: Dominio Público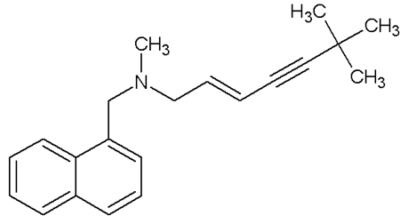
Estructura química de la terbinafina
Imagen : “Terbinafine” por Rodrica8. Licencia: Dominio PúblicoLa flucitosina es un análogo de la pirimidina que interrumpe la síntesis de ADN y ARN.
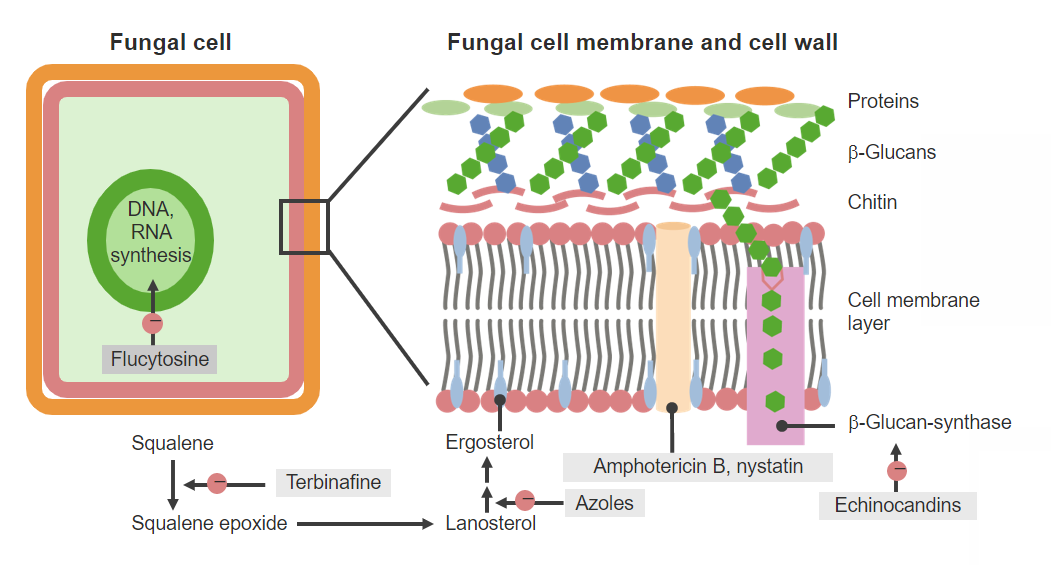
Agentes antifúngicos y mecanismos de acción.
Imagen por Lecturio. Licencia: CC BY-NC-SA 4.0Los LOS Neisseria mecanismos exactos de la griseofulvina no se comprenden completamente, pero se han sugerido dos mecanismos generales de acción:
La terbinafina ejerce sus efectos provocando el deterioro de la membrana celular fúngica al AL Amyloidosis inhibir la producción de epóxido de escualeno, un precursor del ergosterol Ergosterol A steroid occurring in fungi. Irradiation with ultraviolet rays results in formation of ergocalciferol (vitamin d2). Azoles.
| Medicamentos | Flucitosina | Griseofulvina | Terbinafina |
|---|---|---|---|
| Absorción |
|
|
|
| Distribución |
|
|
|
| Metabolismo |
|
|
|
| Excreción |
|
|
|
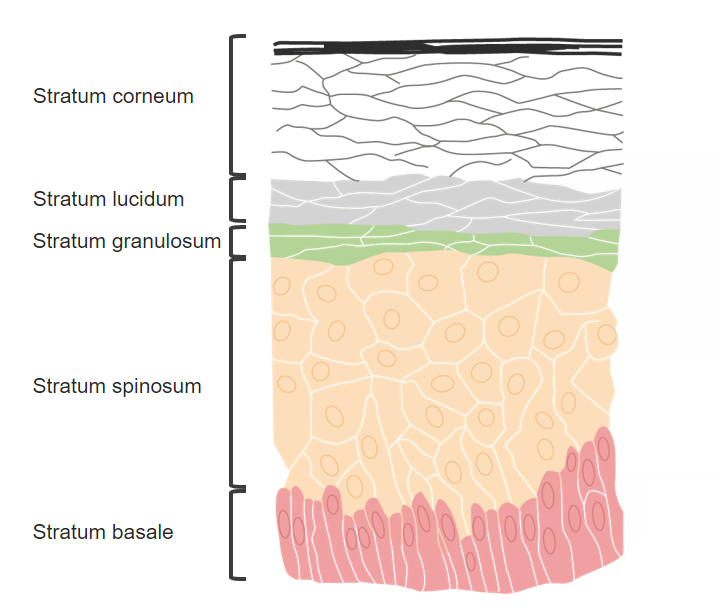
Capas de la piel:
La griseofulvina y la terbinafina se distribuyen en el estrato córneo.
La flucitosina tiene un espectro de actividad estrecho. Debido a su sinergia demostrada con otros agentes antifúngicos y al AL Amyloidosis alto riesgo de resistencia secundaria cuando se usa como monoterapia, la flucitosina no se usa como agente único.
La flucitosina a menudo se administra con el agente altamente nefrotóxico anfotericina B. La insuficiencia renal inducida por anfotericina B puede conducir a la acumulación de 5-fluoracilo (que se elimina por vía renal) y toxicidad directa de 5-fluoracilo, que incluye:
La griseofulvina se usa principalmente para tratar las infecciones por dermatofitos del cabello, piel o uñas. Sin embargo, la griseofulvina está siendo reemplazada por agentes más nuevos como la terbinafina o el itraconazol para muchas de sus indicaciones.
En EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum general, la griseofulvina tiene un nivel de toxicidad relativamente bajo. Los LOS Neisseria efectos secundarios pueden incluir:
Los LOS Neisseria efectos secundarios suelen ser leves y autolimitados.
| Clase de droga (ejemplos) | Mecanismo de acción | Relevancia clínica |
|---|---|---|
| Azoles Azoles Azoles are a widely used class of antifungal medications inhibiting the production of ergosterol, a critical component in the fungal cell membrane. The 2 primary subclasses of azoles are the imidazoles, older agents typically only used for topical applications, and the triazoles, newer agents with a wide spectrum of uses. Azoles (fluconazol, voriconazol) |
|
|
| Polienos (anfotericina B, nistatina) |
|
Anfotericina B:
Nistatina:
|
| Equinocandinas (caspofungina, micafungina, anidulafungina) |
|
|
| Griseofulvina |
|
|
| Terbinafina |
|
|
| Flucitosina |
|
|