La faringitis es una inflamación de la parte posterior de la garganta (faringe). La faringitis suele ser causada por una infección de las vías respiratorias superiores, que en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la mayoría de los LOS Neisseria casos es viral. Suele provocar dolor Dolor Inflammation de garganta y fiebre. Otros síntomas pueden ser secreción nasal, tos TOS Thoracic outlet syndrome (TOS) is a broad term used for a spectrum of syndromes related to the general region of the thoracic outlet, which involves the compression or irritation of elements of the brachial plexus, subclavian artery, or subclavian vein. Thoracic Outlet Syndrome, cefalea y disfonía. Determinar el agente causal basándose únicamente en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria síntomas es difícil. Por ello, a menudo se realiza un frotis de garganta para descartar una causa bacteriana. La base del tratamiento es sintomática y de soporte, y las causas bacterianas requieren antibióticos.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
La faringitis se define como una inflamación de la faringe y las estructuras circundantes.
La mayoría de los LOS Neisseria casos se deben a un organismo infeccioso que se adquiere por contacto cercano con un individuo infectado.
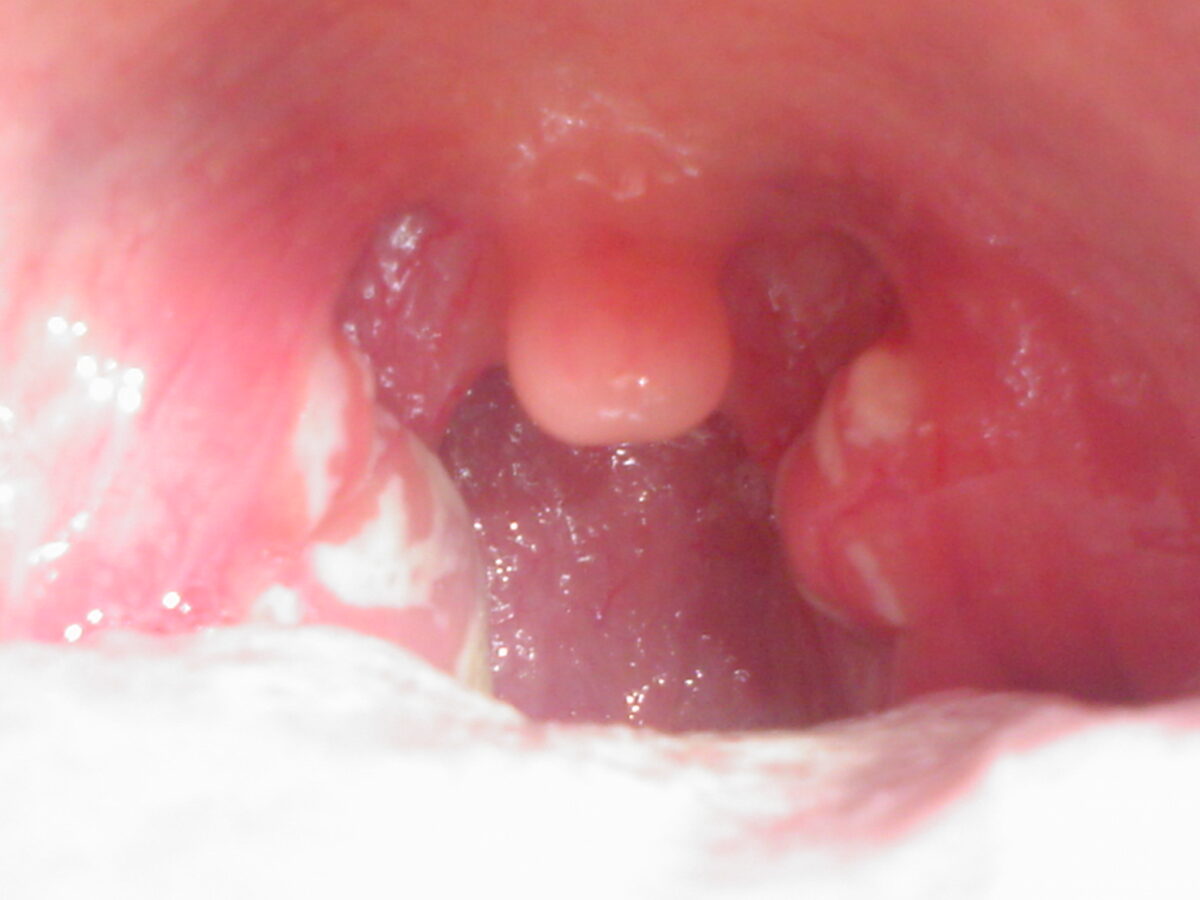
La faringitis provoca la inflamación de los ganglios linfáticos y de las amígdalas con manchas blancas de pus, como se observa aquí. Estas manifestaciones clínicas dan lugar a importantes molestias en la garganta, dolor al tragar y disfonía.
Imagen: “Streptococcal pharyngitis” por RescueFF. Licencia: Dominio Público.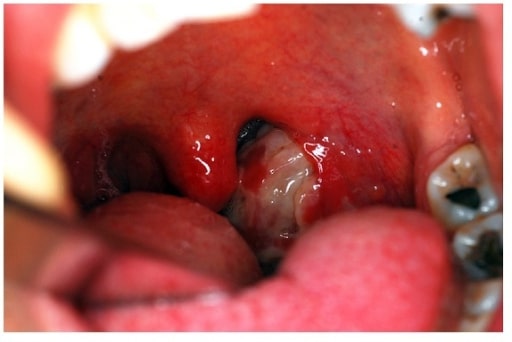
Faringoamigdalitis por Chlamydia trachomatis. Hay hiperemia faríngea y amigdalar generalizada con exudado purulento difuso en la amígdala izquierda, con inflamación de los pilares anteriores y la úvula.
Imagen: “Chlamydia trachomatis tonsillopharyngitis” por Department of Otorhinolaryngology and Head and Neck Surgery, School of Medicine, Istanbul Medipol University, 34718 Istanbul, Turkey. Licencia: CC BY 3.0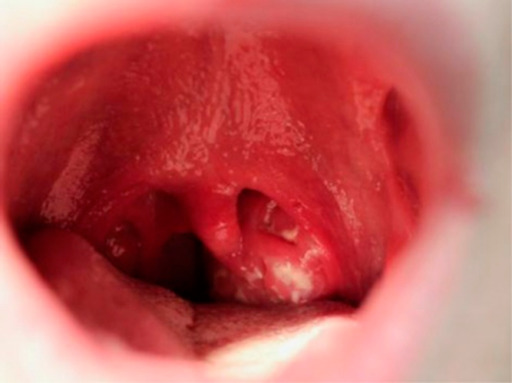
Faringitis que muestra una amigdalitis exudativa y una úvula agrandada en un paciente adolescente 5 días después del inicio de la mononucleosis infecciosa.
Imagen: “Infectious mononucleosis” por University of Minnesota Medical School, Minneapolis, MN, USA. Licencia: CC BY 4.0Puntaje de Centor: estima la probabilidad de que la faringitis sea estreptocócica y sugiere el curso terapéutico para los LOS Neisseria adultos
Diagnóstico de laboratorio:
La identificación de la infección por estreptococos beta-hemolíticos es de suma importancia, ya que se asocia con desarrollo de cardiopatía reumática si no se trata.
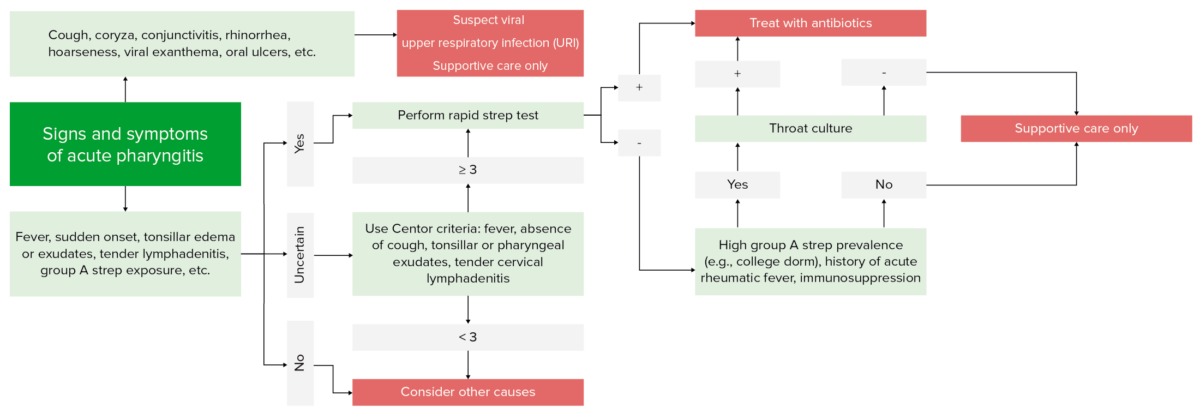
Algoritmo diagnóstico de la faringitis
Imagen por Lecturio.Para recordar los LOS Neisseria criterios de Centor ( en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum inglés):
Las siguientes condiciones son diagnósticos diferenciales de la faringitis: