La enfermedad granulomatosa crónica, como su nombre lo indica, es un trastorno crónico que se caracteriza por la formación de granulomas Granulomas A relatively small nodular inflammatory lesion containing grouped mononuclear phagocytes, caused by infectious and noninfectious agents. Sarcoidosis. Este trastorno es consecuencia de células fagocíticas defectuosas que no pueden producir superóxido bactericida debido a un defecto en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la nicotinamida adenina dinucleótido fosfato ( NADPH NADPH Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate. A coenzyme composed of ribosylnicotinamide 5'-phosphate (nmn) coupled by pyrophosphate linkage to the 5'-phosphate adenosine 2. Pentose Phosphate Pathway), la oxidasa responsable del estallido respiratorio en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria leucocitos fagocíticos. El diagnóstico se realiza analizando la función de los LOS Neisseria neutrófilos para la producción de superóxido. Los LOS Neisseria pacientes con enfermedad granulomatosa crónica tienen un mayor riesgo de infecciones potencialmente mortales por hongos y bacterias catalasa positivas. También son posibles las complicaciones inflamatorias como la colitis Colitis Inflammation of the colon section of the large intestine, usually with symptoms such as diarrhea (often with blood and mucus), abdominal pain, and fever. Pseudomembranous Colitis por enfermedad granulomatosa crónica. La introducción de la profilaxis antimicrobiana y el uso de antifúngicos azólicos ha HA Hemolytic anemia (HA) is the term given to a large group of anemias that are caused by the premature destruction/hemolysis of circulating red blood cells (RBCs). Hemolysis can occur within (intravascular hemolysis) or outside the blood vessels (extravascular hemolysis). Hemolytic Anemia aumentado la expectativa de vida general de estos pacientes.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
La enfermedad granulomatosa crónica es causada por mutaciones en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria genes Genes A category of nucleic acid sequences that function as units of heredity and which code for the basic instructions for the development, reproduction, and maintenance of organisms. DNA Types and Structure que codifican las proteínas que forman la nicotinamida adenina dinucleótido fosfato ( NADPH NADPH Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate. A coenzyme composed of ribosylnicotinamide 5′-phosphate (nmn) coupled by pyrophosphate linkage to the 5′-phosphate adenosine 2. Pentose Phosphate Pathway) oxidasa:
La enzima NADPH-oxidasa está alterada en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la célula fagocítica → ↓ producción de anión superóxido O2–, lo que afecta a otros oxidantes. Esta enzima es responsable de la incapacidad para combatir infecciones.
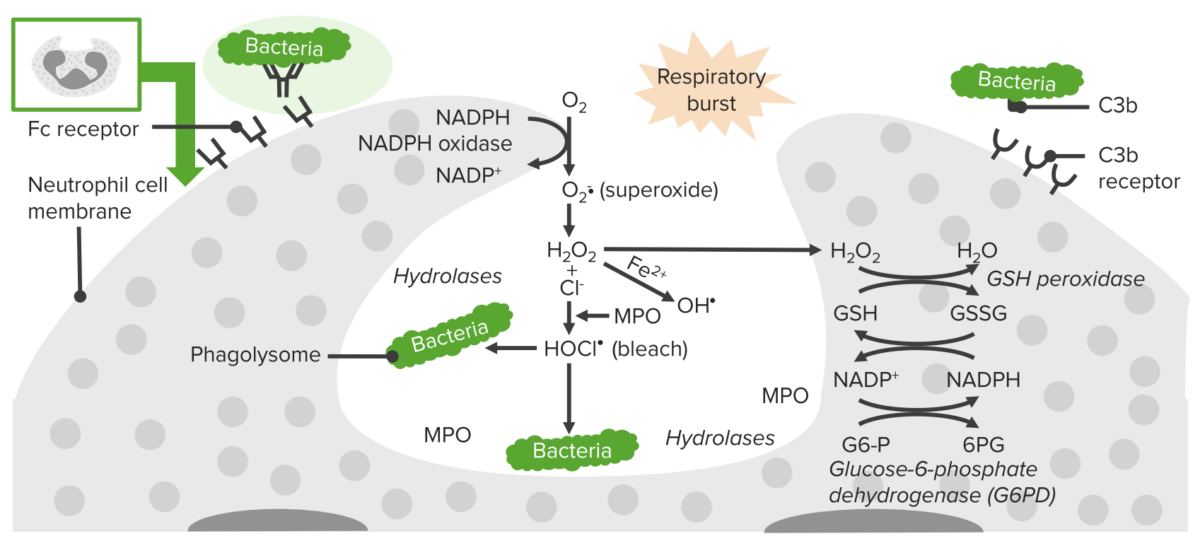
Proceso de fagocitosis en neutrófilos:
Una deficiencia de NADPH oxidasa da como resultado una incapacidad para producir superóxido, lo que disminuye la capacidad de la célula para destruir microorganismos catalasa positivos.
La mayoría de los LOS Neisseria pacientes con enfermedad granulomatosa crónica tienen < 5 años de edad y la gravedad es variable Variable Variables represent information about something that can change. The design of the measurement scales, or of the methods for obtaining information, will determine the data gathered and the characteristics of that data. As a result, a variable can be qualitative or quantitative, and may be further classified into subgroups. Types of Variables (según el defecto genético). La presentación clínica puede incluir:
Los LOS Neisseria pacientes pueden experimentar infecciones repetidas causadas por patógenos bacterianos y fúngicos.
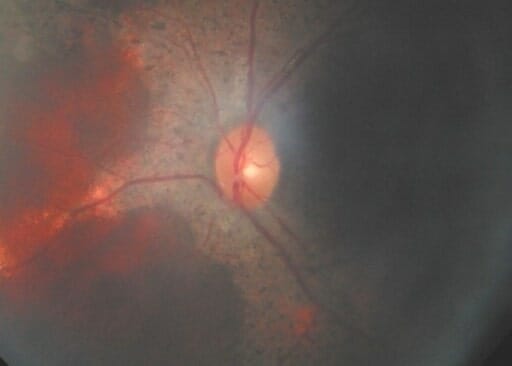
El examen de fondo del ojo de un individuo con enfermedad granulomatosa crónica que muestra una masa retiniana
Imagen: “F3: Brother’s fundus” por Mansour A. M. et al. Licencia: CC BY 2.0Las pruebas de función de neutrófilos deben realizarse:
Pruebas de genética molecular y genotipado:
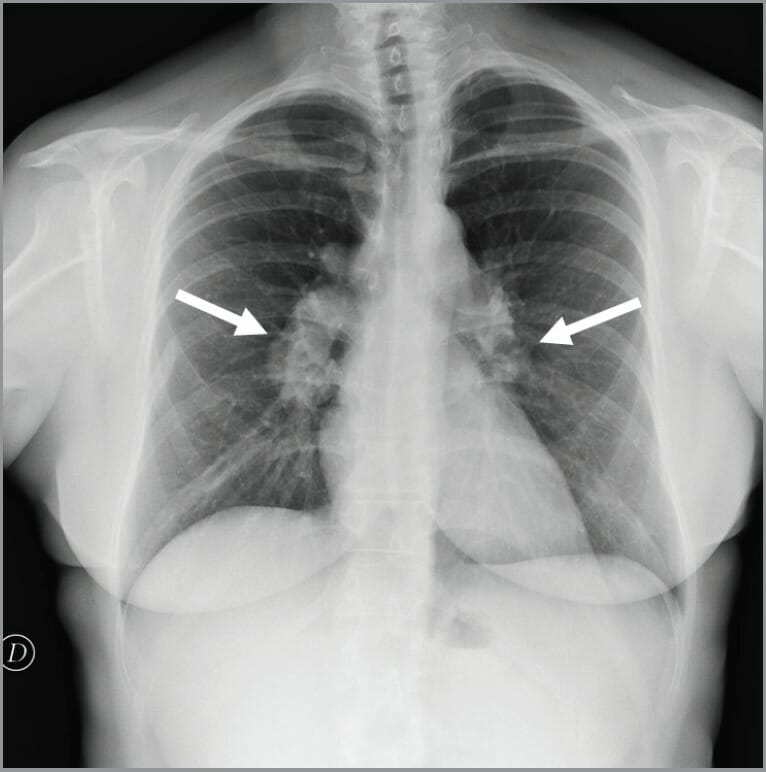
Radiografía de tórax que muestra linfadenopatía hiliar bilateral en un individuo con enfermedad granulomatosa crónica
Imagen: “Chest x-ray showed bilateral hilar lymphadenopathies (arrows) suggestive for chronic granulomatous disease” por Conte G. et al. Licencia: CC BY 3.0