El cáncer colorrectal es la segunda causa de muerte relacionada con el cáncer en Estados Unidos. El cáncer colorrectal es una enfermedad heterogénea que surge de anomalías genéticas y epigenéticas, con influencia de factores ambientales. Casi todos los casos de cáncer colorrectal son adenocarcinomas, y la mayoría de las lesiones provienen de la transformación maligna de un pólipo adenomatoso. Dado que la mayoría de los casos de cáncer colorrectal son asintomáticos, generalmente se recomienda la colonoscopia de tamizaje o análisis de heces en pacientes ≥ 45 años de edad. Junto con el tamizaje, el diagnóstico se realiza mediante colonoscopia, que permite la visualización y la toma de muestras de tejido. El tratamiento es principalmente quirúrgico, y la quimioterapia se reserva para la enfermedad avanzada.
Last updated: Jan 21, 2026
Tipos de pólipos:
Pólipos de alto riesgo:
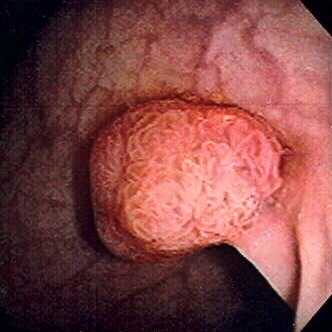
Pólipo de colon sigmoide revelado por colonoscopia: El pólipo es pedunculado (con un tallo corto).
Imagen: “Colon polyp” por Dr. F.C. Turner. Licencia: CC BY 2.5La mayoría de los LOS Neisseria pólipos son benignos. La transformación maligna se ve VE Ventilation: Mechanics of Breathing afectada por una serie de mutaciones y factores ambientales.
Mutaciones:
Gen poliposis adenomatosa coli:
La mutación del gen poliposis adenomatosa coli es inicial
La progresión del cáncer colorrectal requiere múltiples golpes genéticos.
Acumulación de mutaciones y eventos moleculares:
La acumulación de mutaciones y eventos moleculares (e.g., alteración genética, metilación del ADN, sobreexpresión) contribuye a la carcinogénesis.
Sobreexpresión de la ciclooxigenasa (COX)-2:
Secuencia adenoma-carcinoma:
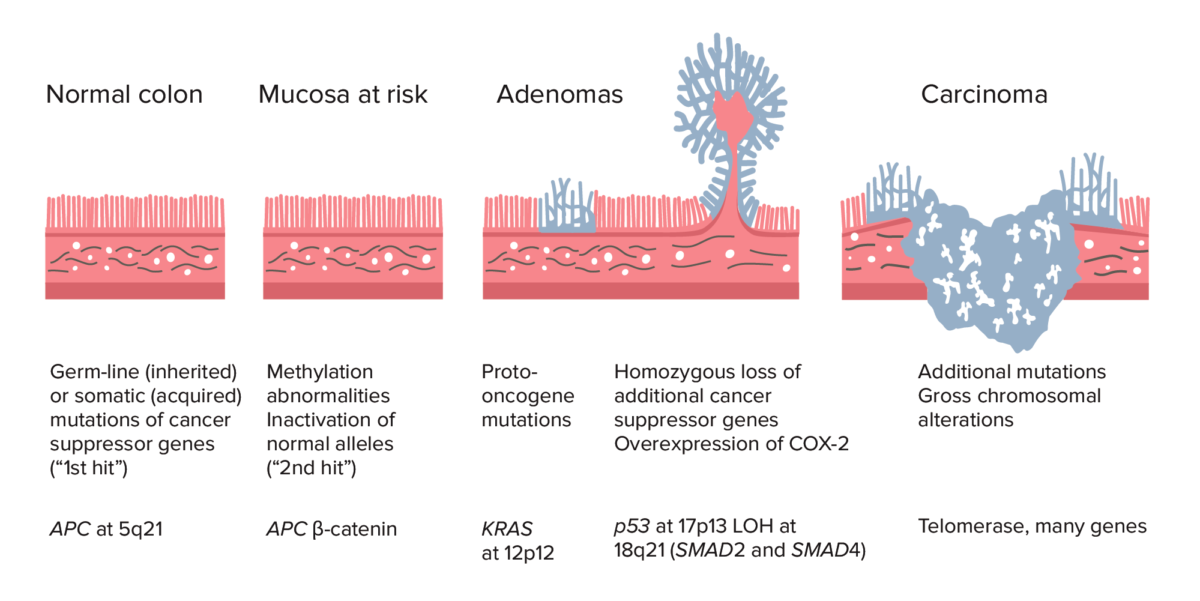
Adenoma–carcinoma sequence from normal colon to carcinoma:
Colorectal cancer (CRC) formation begins with APC gene mutation (inherited or acquired) and methylation abnormalities. Other changes can include KRAS gene mutation. Late in the process, p53 deletion, loss of heterozygosity (LOH) at 18q21 (involving SMAD2 and SMAD4), with overexpression of COX-2 can contribute to further growth and progression to cancer. The accumulation of mutations, rather than the timing of occurrence, is most crucial in carcinogenesis.
Vía de los LOS Neisseria pólipos serrados:
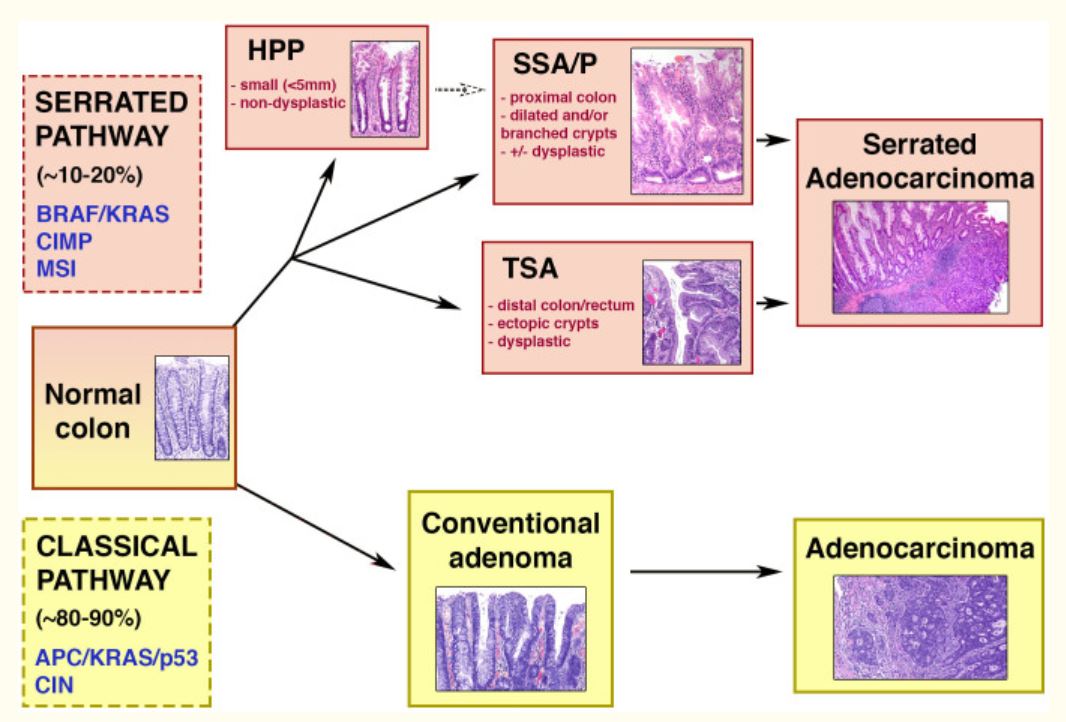
Diagrama esquemático de las vías clásicas (adenoma-carcinoma) y serrada.
Mitad superior: vía serrada de la carcinogénesis colorrectal, que se da en 10%–20% de los cánceres colorrectales. La vía está asociada a las siguientes características genéticas: mutaciones BRAF/KRAS, MSI (inestabilidad microsatelital) y CIMP (fenotipo metilador de islas CpG). Las lesiones serradas pueden ser pólipos hiperplásicos (HPP), adenomas/pólipos serrados sésiles (SSA/Ps) y adenomas serrados tradicionales (TSA). Estos dos últimos están asociados a la displasia y a la progresión hacia el carcinoma.
Mitad inferior: adenoma-carcinoma o vía clásica, que se da en la mayoría de los cánceres colorrectales. Entre las características genéticas se encuentran las mutaciones en los genes APC/KRAS/p53 y la inestabilidad cromosómica (CIN). A través de esta secuencia, el adenoma se convierte en adenocarcinoma.
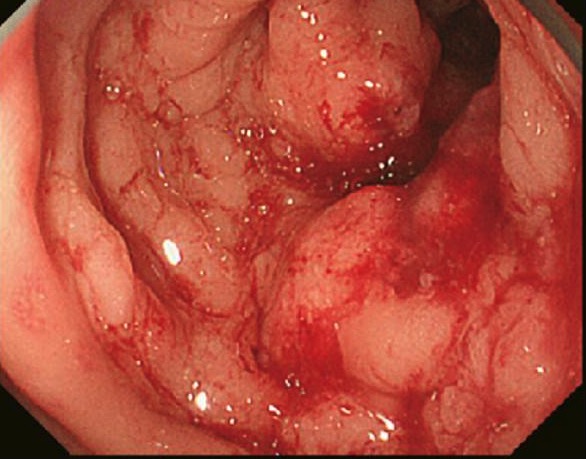
Cáncer de colon detectado en la colonoscopia y confirmado mediante biopsia
Imagen: “Primary tumor” por Second Department of Surgery, Wakayama Medical University, School of Medicine, 811-1 Kimiidera, Wakayama 641-8510, Japan. Licencia: CC BY 2.0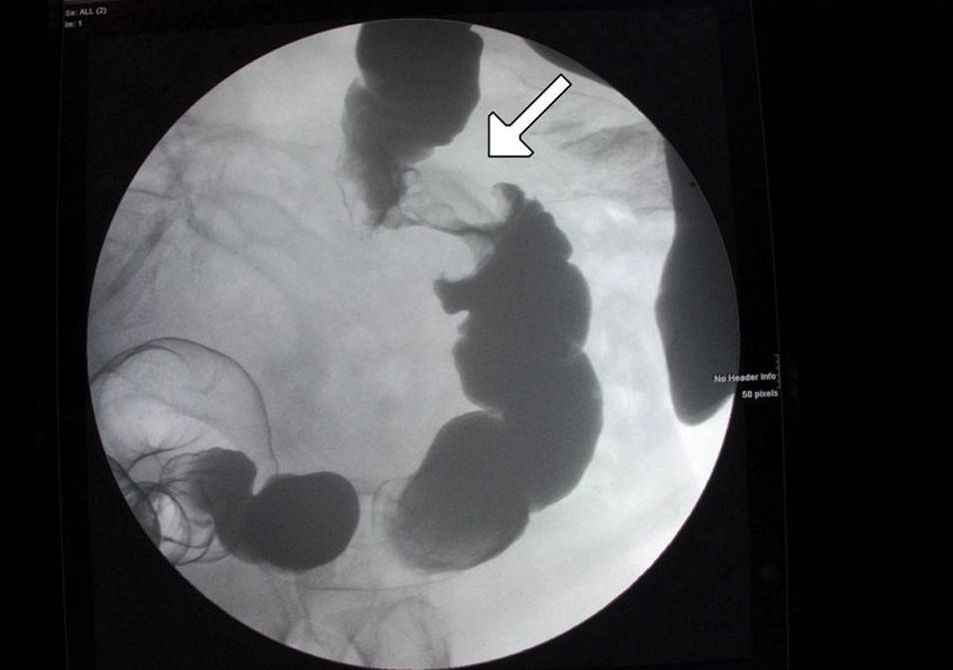
Una lesión en “coronta de manzana” en el colon mostrada en un enema de contraste: Esto se relaciona con cáncer.
Imagen: “Figure 6” por Alzaraa et al. Licencia: CC BY 3.0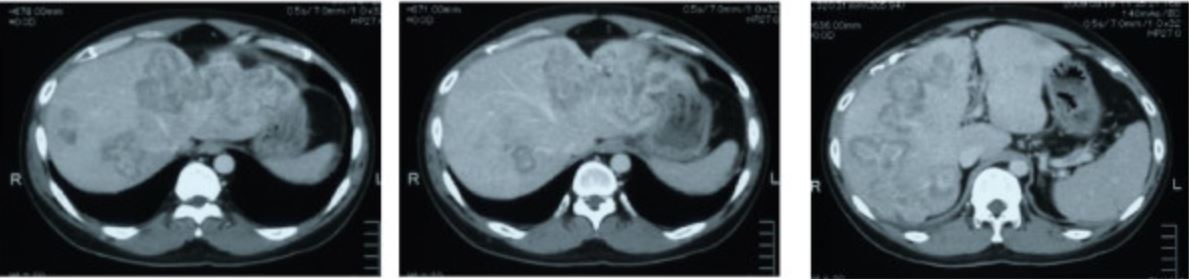
Metástasis en TC por cáncer de colon sigmoide
Imagen: “CT scan showing liver metastasis from sigmoid colon cancer” por Department of Surgery, The Jikei University Kashiwa Hospital, Kashiwashita, Kashiwa City, Japan. Licencia: CC BY 2.0Después de establecer el diagnóstico de cáncer colorrectal, es necesario estadificar la enfermedad para un tratamiento adecuado.
Sistema de estadificación TNM ( tumor Tumor Inflammation, nódulos (ganglios), metástasis):
| Estadio | Tumor Tumor Inflammation (T) | Nódulos (ganglios) linfáticos regionales (N) | Metástasis a distancia (M) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Estadio 0 |
|
|
|
| Estadio I |
|
|
|
| Estadio II |
|
|
|
| Estadio III |
|
|
|
| Estadio IV |
|
|
|
El estadio del cancer colorrectal y la biología molecular ( en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el caso de la terapia dirigida) dictan el papel de los LOS Neisseria tratamientos quirúrgicos y farmacológicos.
Antígeno carcinoembrionario:
Colonoscopia:
Imagenología:
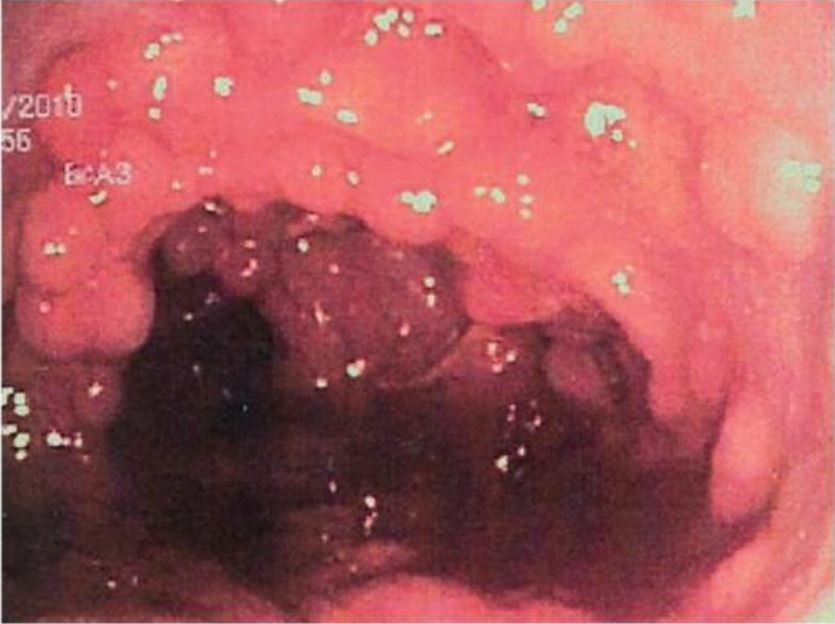
Mucosa colónica tapizada de pólipos adenomatosos en la poliposis adenomatosa familiar
Imagen: “Colonic mucosa carpeted by adenomatous polyps in familial adenomatous polyposis FAP” por Shussman N., Wexner SD. Licencia: CC BY 3.0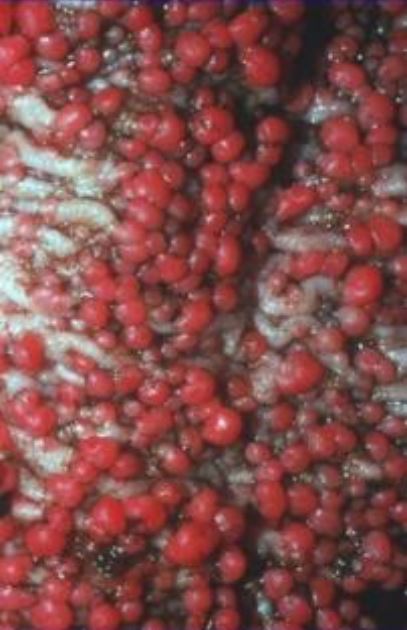
Vista endoscópica de adenomas en la polipomatosis adenomatosa familiar establecidos y múltiples
Imagen: “Endoscopic view of established, multiple FAP adenomas” por Bercovich D., Rozen P. Licencia: CC BY 2.0