Bartonella Bartonella Bartonella is a genus of gram-negative bacteria in the family Bartonellaceae. As a facultative intracellular parasite, Bartonella can infect healthy people as well as act as an opportunistic pathogen. Bartonella species are transmitted by vectors such as ticks, fleas, sandflies, and mosquitoes. B. henselae is the most common of the 3 species known to cause human disease. Bartonella es un género de bacterias gram-negativas de la familia Bartonellaceae Bartonellaceae A family of small gram-negative bacteria whose organisms are parasites of erythrocytes in man and other vertebrates and the etiologic agents of several diseases. Bartonella. Como parásito intracelular facultativo, Bartonella Bartonella Bartonella is a genus of gram-negative bacteria in the family Bartonellaceae. As a facultative intracellular parasite, Bartonella can infect healthy people as well as act as an opportunistic pathogen. Bartonella species are transmitted by vectors such as ticks, fleas, sandflies, and mosquitoes. B. henselae is the most common of the 3 species known to cause human disease. Bartonella puede infectar a personas sanas a la vez que actúa como un patógeno oportunista. Las especies de Bartonella Bartonella Bartonella is a genus of gram-negative bacteria in the family Bartonellaceae. As a facultative intracellular parasite, Bartonella can infect healthy people as well as act as an opportunistic pathogen. Bartonella species are transmitted by vectors such as ticks, fleas, sandflies, and mosquitoes. B. henselae is the most common of the 3 species known to cause human disease. Bartonella son transmitidas por vectores como garrapatas, pulgas, flebótomos y mosquitos. B. henselae es la más común de las 3 especies que causan enfermedades en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum humanos; es una zoonosis que causa la enfermedad por arañazo de gato y la angiomatosis bacilar. Las otras 2 especies son específicas de los LOS Neisseria humanos: B. bacilliformis causa fiebre de las trincheras y angiomatosis bacilar, y B. quintana causa fiebre de la Oroya, verruga peruana Verruga peruana Bartonella y enfermedad de Carrión.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
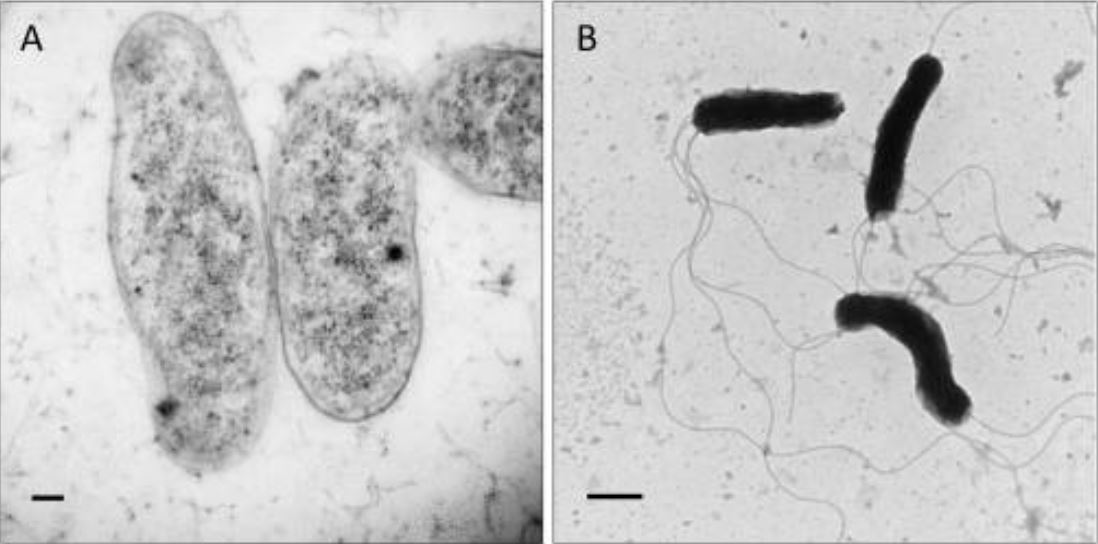
Micrografías electrónicas de transmisión que muestran la morfología de Bartonella bacilliformis:
Las barras de escala representan 100 nm en el panel A y 500 nm en el panel B.
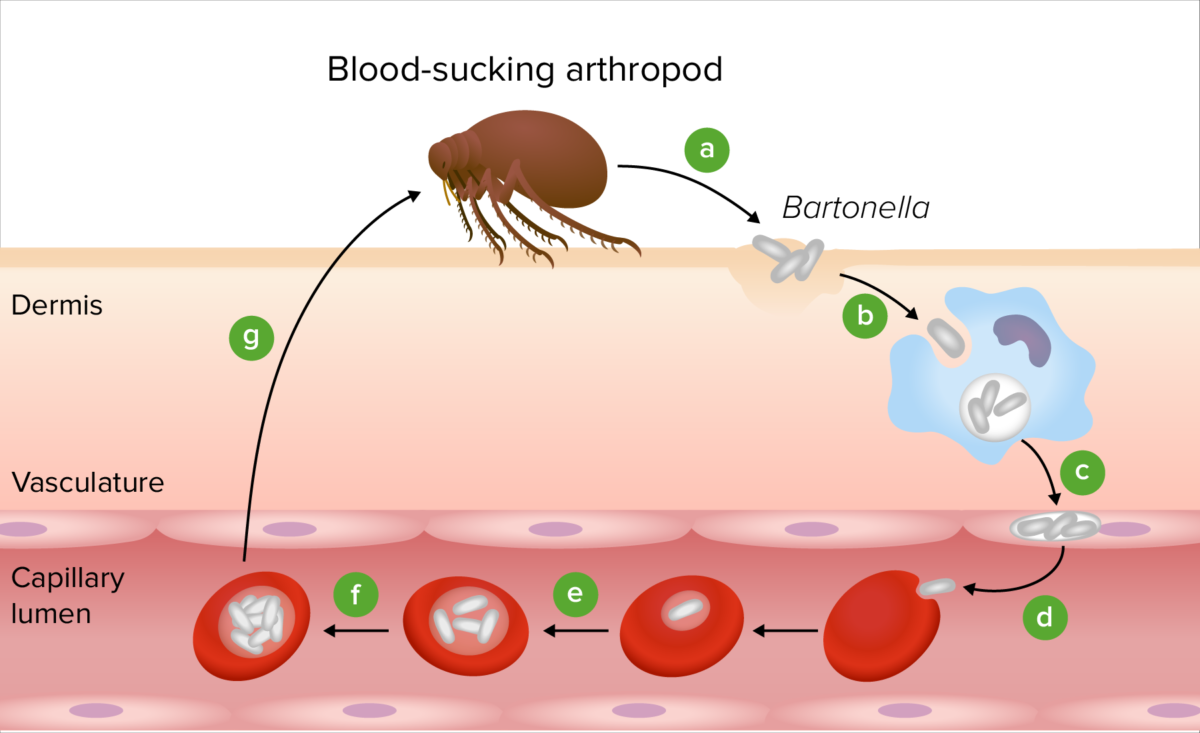
Patogénesis de Bartonella:
Después de la transmisión por un vector artrópodo (a), la bacteria Bartonella coloniza la piel (b). Luego, las bacterias son transportadas al endotelio vascular (c) e ingresan en el torrente sanguíneo para invadir los eritrocitos (d). Después de la replicación dentro de los eritrocitos (e), las bacterias persisten en el nicho intraeritrocitario (f), haciéndolos competentes para la transmisión por otro artrópodo que se alimenta de sangre (g).
La bartonelosis en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum humanos es causada por 3 especies principales de bacterias Bartonella Bartonella Bartonella is a genus of gram-negative bacteria in the family Bartonellaceae. As a facultative intracellular parasite, Bartonella can infect healthy people as well as act as an opportunistic pathogen. Bartonella species are transmitted by vectors such as ticks, fleas, sandflies, and mosquitoes. B. henselae is the most common of the 3 species known to cause human disease. Bartonella y produce una amplia gama de síntomas y enfermedades según la especie y el estado inmunitario del individuo infectado.
| Especies | Enfermedad |
|---|---|
| B. bacilliformis |
Enfermedad de Carrión, también conocida como:
|
| B. quintana |
|
| B. henselae |
|
Transmisión:
Presentación clínica:
Transmisión:
Presentación clínica:
Transmisión:
Presentación clínica:
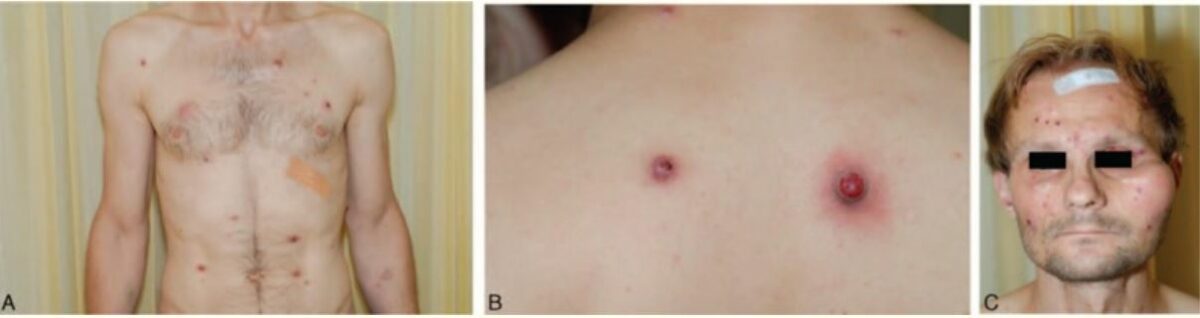
Presentación clínica de un paciente con angiomatosis bacilar:
A: Múltiples pápulas eritematosas en el tórax y el abdomen
B: 2 nódulos en la espalda
C: Pápulas en la cara con lesión de masa subcutánea sobre el arco cigomático izquierdo
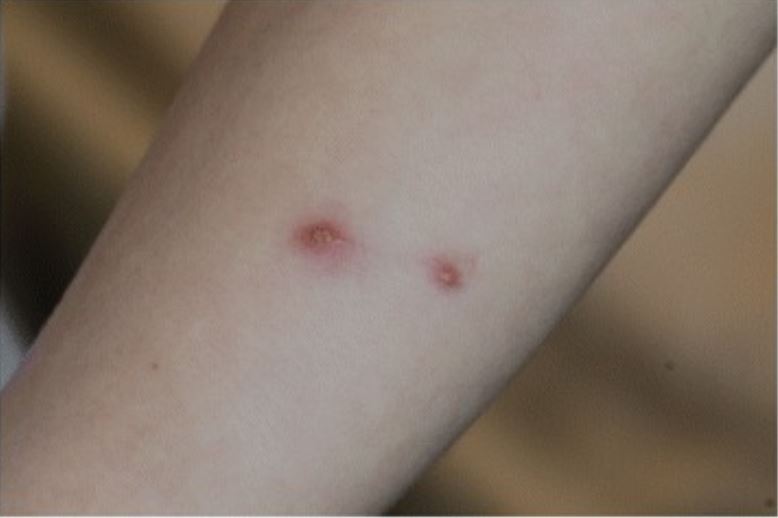
Enfermedad por arañazo de gato:
Las lesiones cutáneas activas, normalmente indoloras, se observan unos días a 2 semanas después de la inoculación en ⅓ a ⅔ de los pacientes. La linfadenopatía regional dolorosa generalmente se desarrolla de 1–3 semanas después de la inoculación.
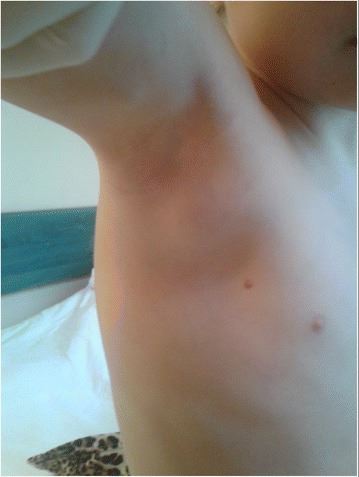
Adenopatías axilares periféricas en un niño de 5 años con enfermedad por arañazo de gato
Imagen: “The significance of Bartonella henselae bacterias for oncological diagnosis in children” por Mazur-Melewska K, Jończyk-Potoczna K, Mania A, Kemnitz P, Szydłowski J, Służewski W, Figlerowicz M. Licencia: CC BY 4.0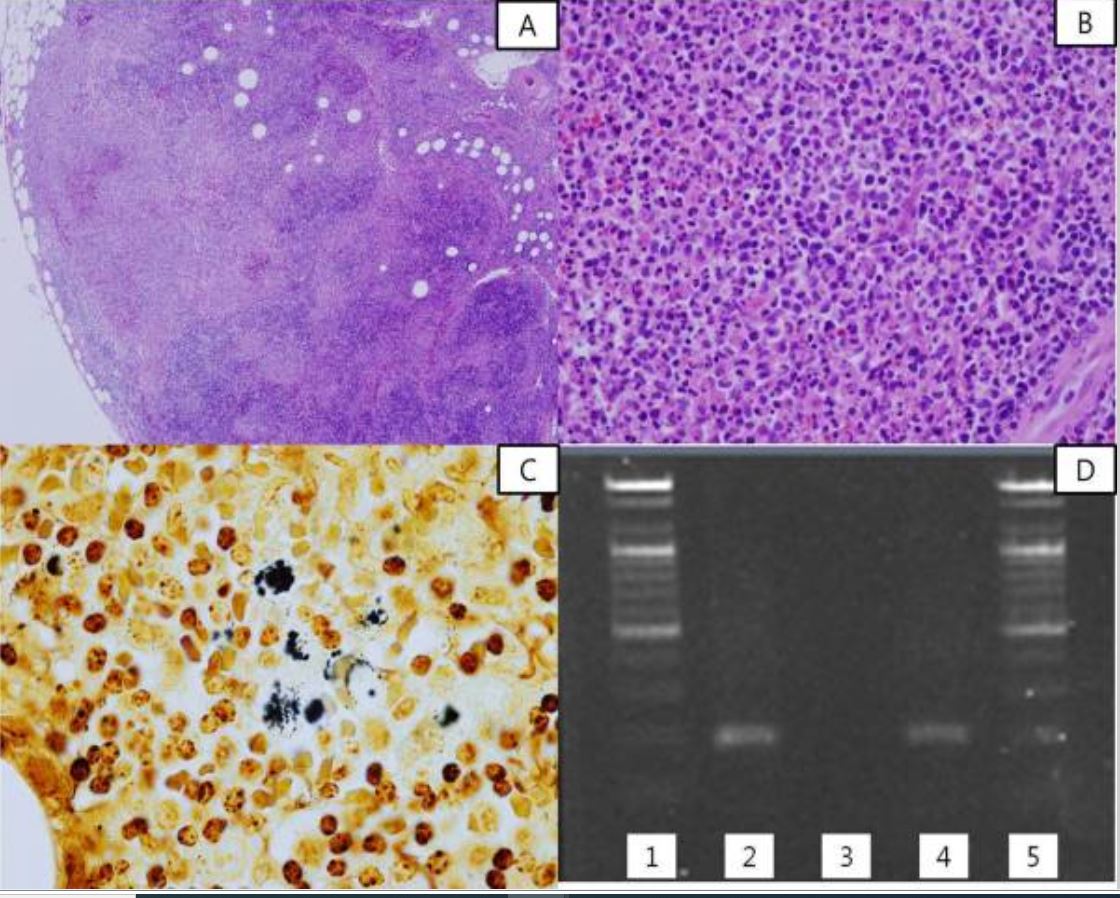
Histopatología, tinción de plata y reacción en cadena de la polimerasa (PCR, por sus siglas en inglés) de la enfermedad por arañazo de gato:
A: El ganglio linfático afectado muestra hiperplasia folicular reactiva y múltiples microabscesos geográficos.
B: Se observan numerosos neutrófilos en los focos necróticos del ganglio linfático.
C: Se encuentran algunos grupos de bacterias en el ganglio linfático (tinción con plata negra).
D: Resultados de la PCR semianidada para Bartonella henselae. Los carriles 1 y 5 muestran el marcador de la escalera de ADN; el carril 2 muestra un control positivo, el carril 3 un control negativo y el tejido del ganglio linfático del carril 4 del paciente.
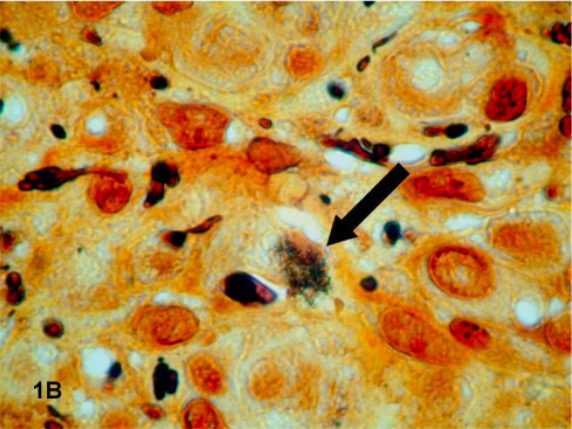
Muestra de histopatología de un paciente con angiomatosis bacilar:
Un grupo de Bartonella quintana con tinción oscura (indicado por una flecha) se revela con la tinción de Warthin-Starry de una muestra de tejido.
La mayoría de los LOS Neisseria casos de bartonelosis pueden ser diagnosticados mediante la detección de síntomas y hallazgos físicos característicos y una toma completa de los LOS Neisseria antecedentes médicos. Se utilizan pruebas de laboratorio especializadas para confirmar el diagnóstico.
Aparte de los LOS Neisseria cuidados de soporte, el tratamiento depende de la especie específica de Bartonella Bartonella Bartonella is a genus of gram-negative bacteria in the family Bartonellaceae. As a facultative intracellular parasite, Bartonella can infect healthy people as well as act as an opportunistic pathogen. Bartonella species are transmitted by vectors such as ticks, fleas, sandflies, and mosquitoes. B. henselae is the most common of the 3 species known to cause human disease. Bartonella adquirida y la gravedad de cada caso.