Imaging of the Urinary System
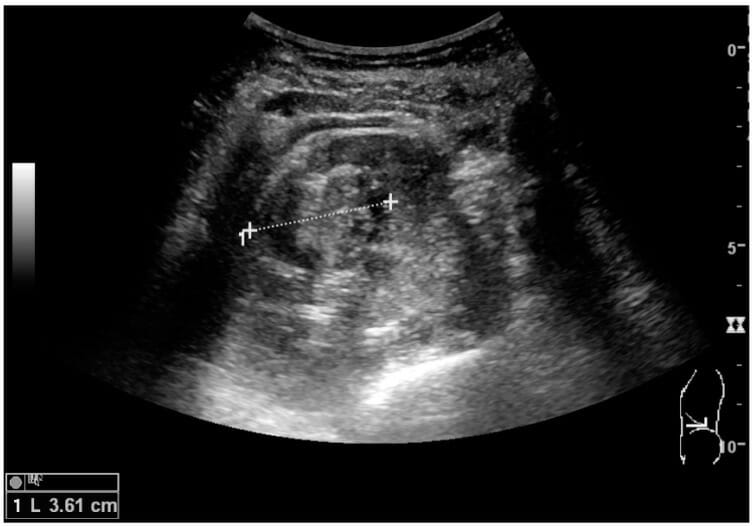
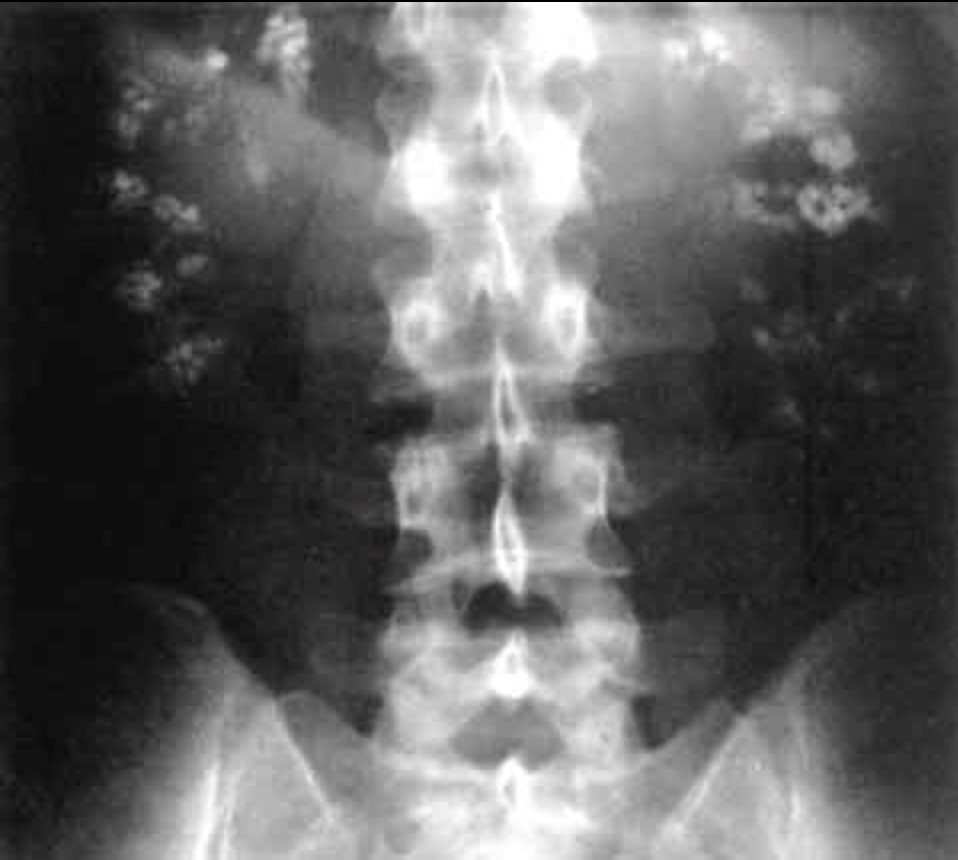
Introduction Imaging methods The common radiologic methods in use to evaluate the urinary tract are: Preparation and orientation Radiography Overview Exam technique Interpretation and evaluation As the obtained image contains multiple organs and structures (and not just the urinary tract), an inside-out approach (central to peripheral) is taken to provide interpretation: Normal findings AP view: […]
Body Fluid Compartments
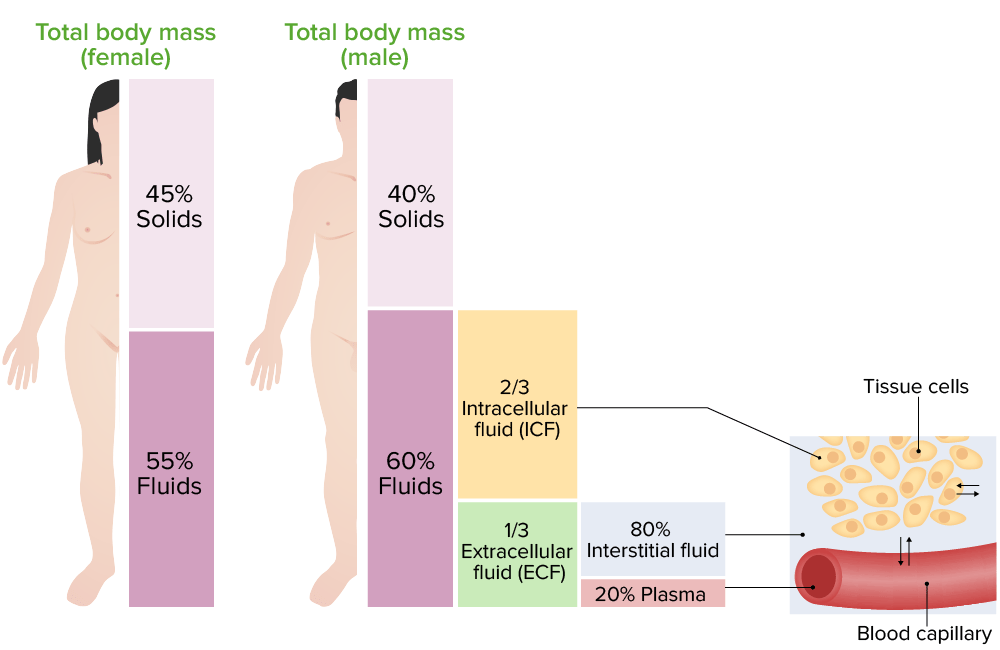
Overview Water in the adult human body makes up approximately 60% of the total body weight. The fluid is distributed in various organs, organ systems, and tissues. The sum of the water in these tissues is known as total body water. Body Fluid Compartments Overview The total body water is distributed primarily between 2 compartments, […]
Nephritic Syndrome
Overview Definition Nephritic syndrome is defined by some or all of the following findings: Glomerular hematuria: active urine sediment Dysmorphic RBCs RBC casts Mild-to-moderate proteinuria (500–3500 mg/day called “subnephrotic”) Hypertension due to: Volume overload/Na retention Suppression of the RAAS Azotemia: Elevated BUN BUN-to-creatinine ratio > 15 Oliguria: < 500 mL of urine/day Etiology Acute glomerulonephritis […]
Nephrotic Syndrome
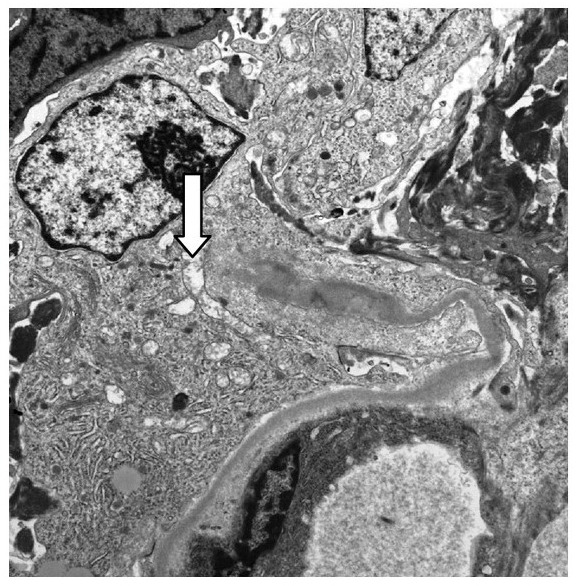
Overview Definition Nephrotic syndrome is characterized by heavy proteinuria (> 3.5 g/day), low serum albumin (< 3 g/dL), and peripheral edema. Epidemiology Primary etiologies (“immune podocytopathies”) Secondary etiologies Pathophysiology The major target of injury in diseases that cause primary nephrotic syndrome is the podocyte. Increased filtration across the glomerular capillary wall results in proteinuria. Nephron […]
Renal Tubular Acidosis
Overview Definition Renal tubular acidosis (RTA) is an imbalance in physiologic pH caused by the kidney’s inability to acidify urine to maintain blood pH at physiologic levels. Classification RTA can be classified based on the clinical characteristics and physiologic defect: Comparison of the types of RTA, including the clinical characteristics, physiologic defects, and potential etiologies: […]
Kidneys: Anatomy
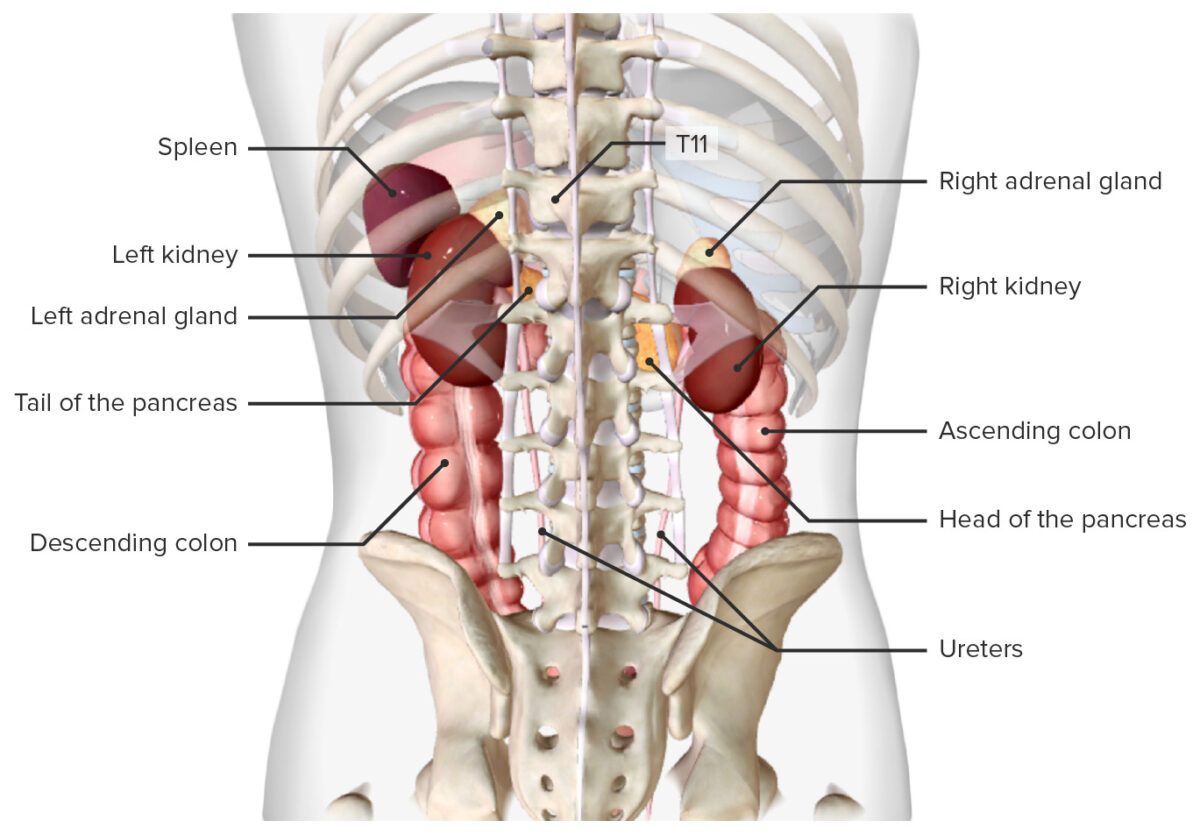
Embryology The kidney develops from embryonic mesoderm in 3 successive forms from the nephrogenic cords as they elongate in a cranial-to-caudal direction. Pronephros Mesonephros Metanephros The permanent kidney is formed from the metanephros. Position of the kidney and changes in vascularization Gross Anatomy Location Anatomical relations Table: Anatomic relations of the kidneys Direction (in relation […]
Membranoproliferative Glomerulonephritis
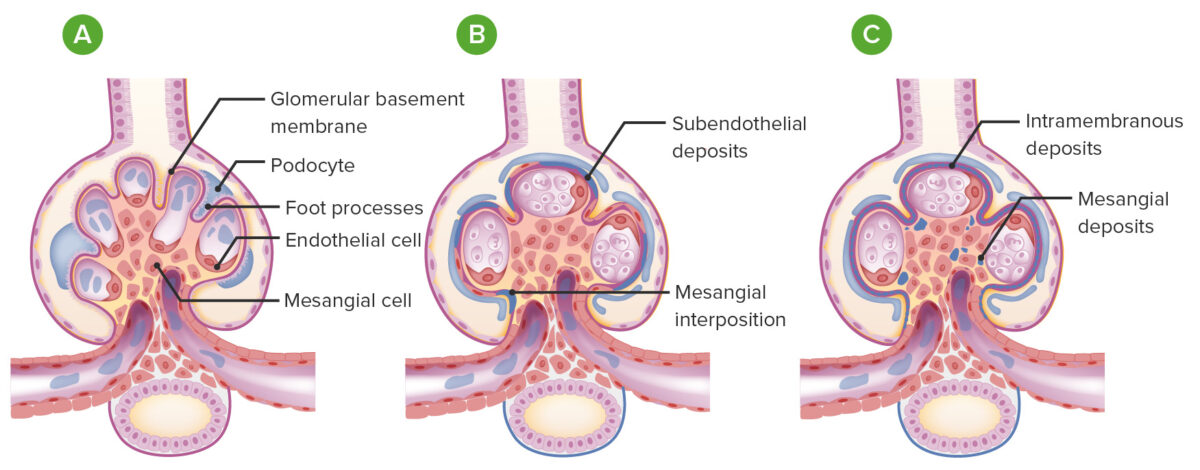
Overview Definition Membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis (MPGN) is a glomerular injury characterized by glomerular basement membrane (GBM) thickening (“membrano-”) and increased endocapillary and mesangial cellularity (“proliferative”). Epidemiology Pathophysiology and Etiology Glomerular injury Classification (electron microscopy) Traditionally, MPGN was classified based on electron microscopy findings (old classification): Classification (immunofluorescence microscopy) and etiology A different classification based on the […]
Hyponatremia
Overview Physiology and classification Epidemiology Etiology The etiology of hyponatremia is determined by knowing the volume status, as well as the serum and urine osmolality. Hypovolemic: Euvolemic: Hypervolemic: Pathophysiology Clinical Presentation Acute (< 48 hours) Chronic (> 48 hours) Diagnosis The 3 most important tests that need to be completed are: Serum or plasma osmolality […]
Rapidly Progressive Glomerulonephritis
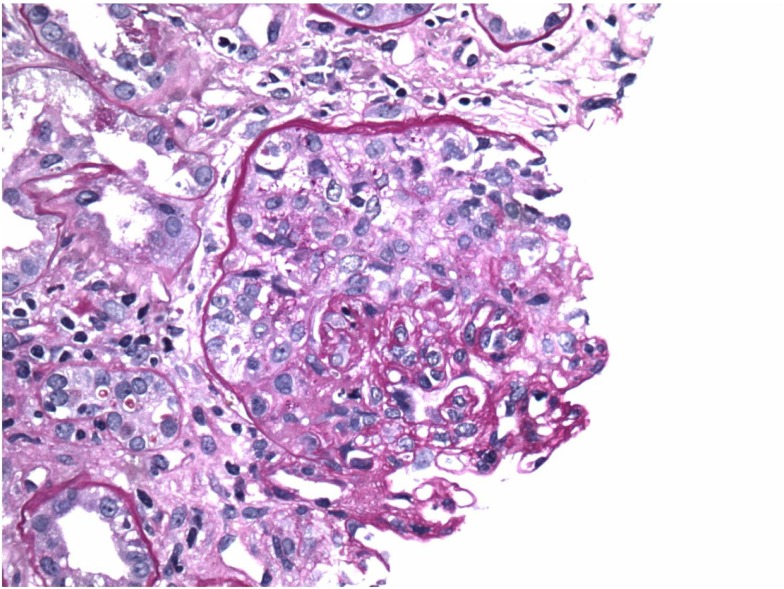
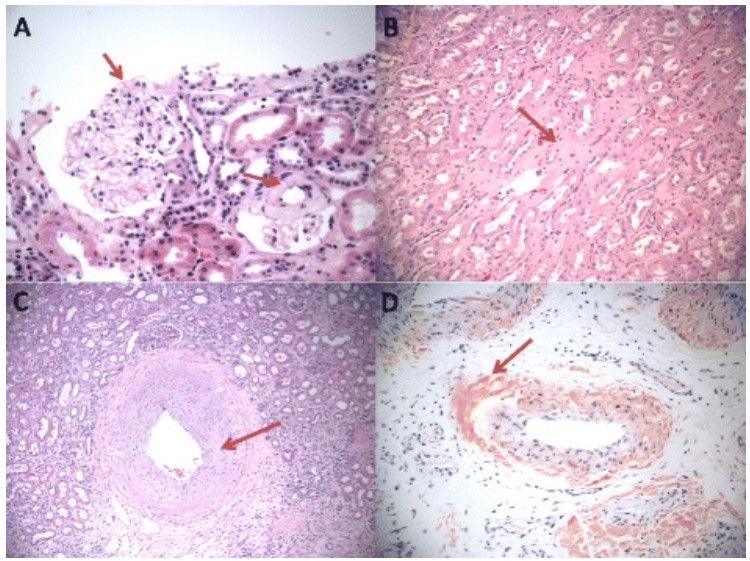
Overview Definition Rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis (RPGN) is a syndrome of severe glomerular disease with progressive loss of kidney function within weeks to months. Classification Most cases are from immunological injury of the glomeruli. The mechanisms and findings are classified as: Epidemiology Etiology Pathophysiology Clinical Presentation Diagnosis Laboratory evaluation Renal biopsy Table: Microscopic findings in common […]
Thin Basement Membrane Nephropathy (TBMN)
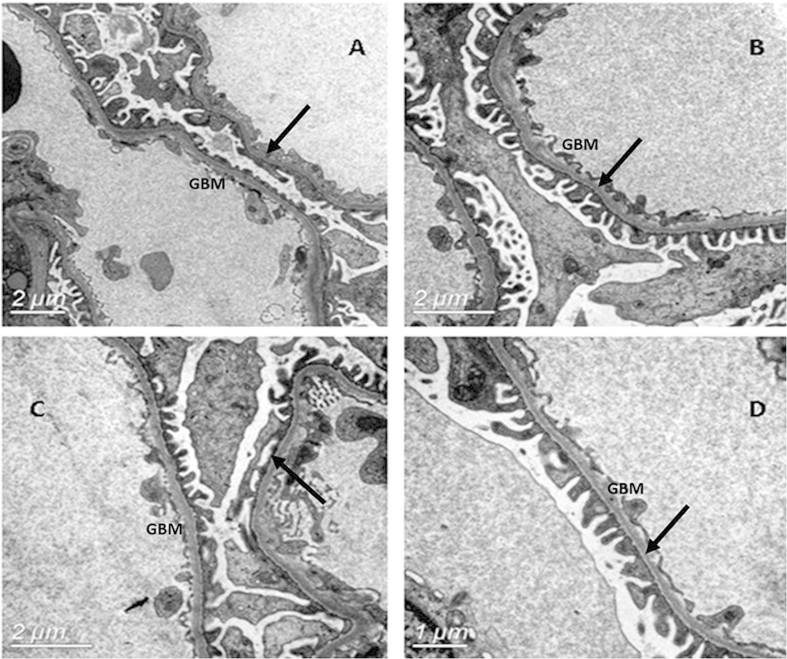
Overview Epidemiology The frequency may be approximately 5%‒9%. However, TBMN is clinically diagnosed in < 1% of the general population. Most common cause of persistent hematuria Etiology Autosomal dominant inheritance In some families, TBMN appears to be caused by mutations in: COLA4A3 → encodes the alpha-3 chains of type IV collagen COLA4A4 → encodes the […]