Pulmonary Function Tests
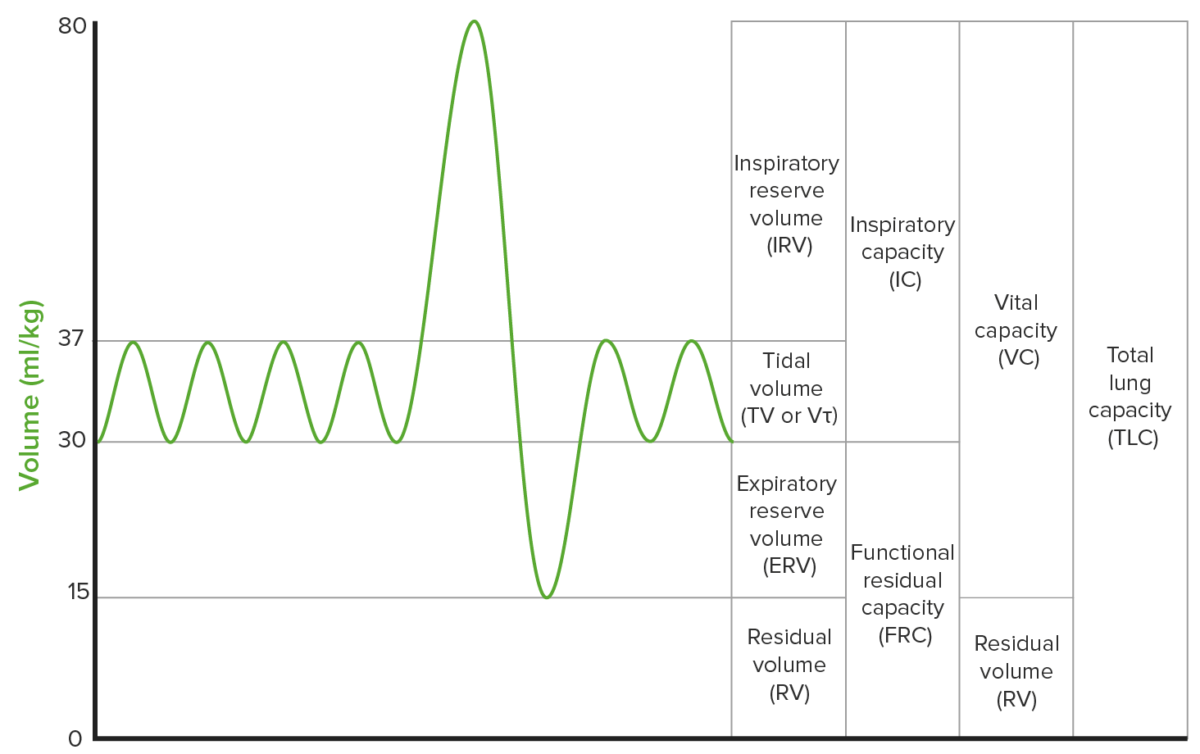
Overview Definition Examples Indications Contraindications Lung Volumes Lung volumes are measured by: Lung volumes: Lung capacities: Spirometry Spirometry records the volume of air moving in and out of an individual’s lungs. Diffusing Capacity of the Lung for Carbon Monoxide (DLCO) Table: Parameters of obstructive and restrictive lung disease Parameter Obstructive lung disease Restrictive lung disease […]
Coronavirus
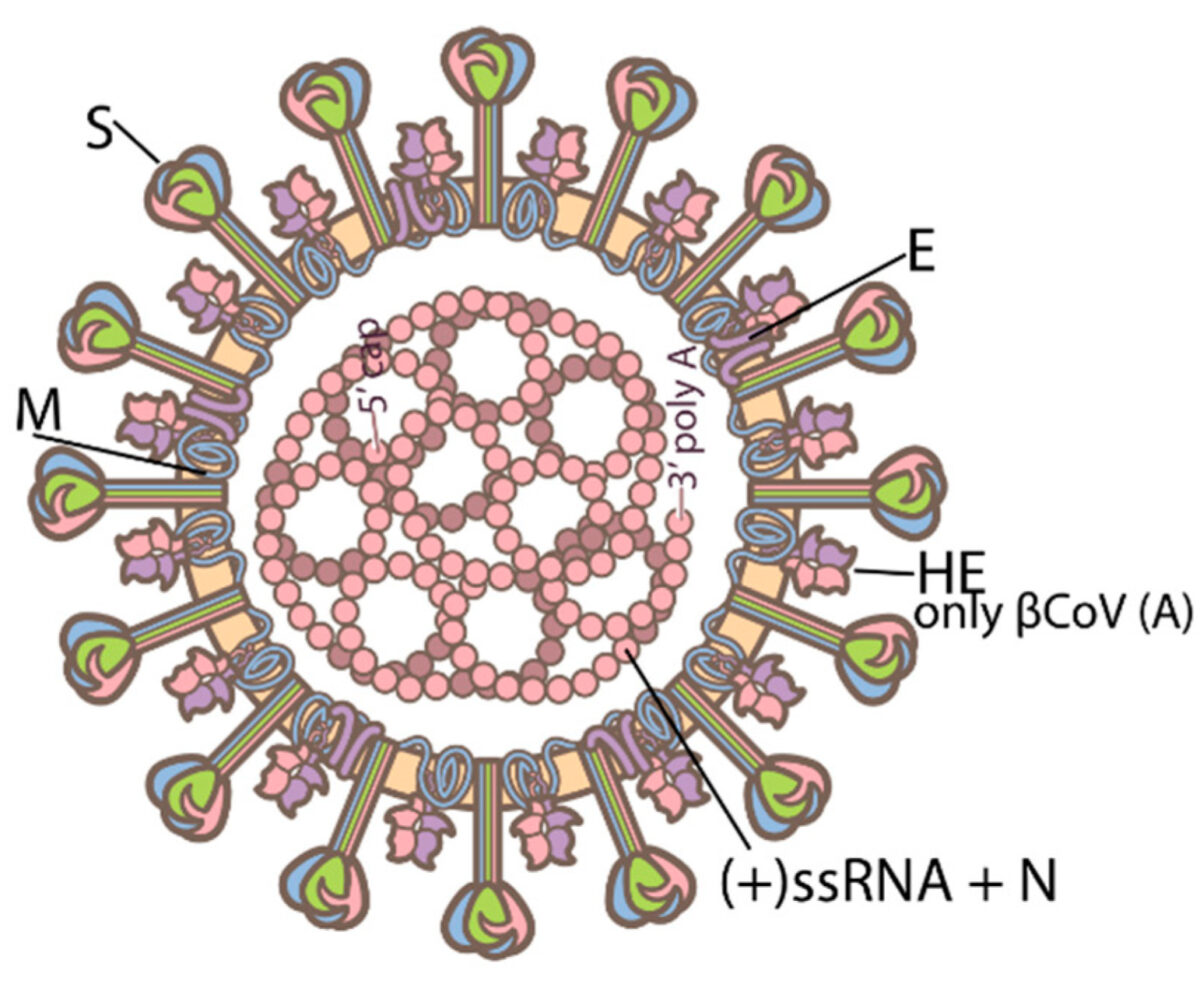
Classification General Characteristics Structure Clinically relevant species Pathogenesis Transmission Virulence factors Most coronaviruses have 4 structural proteins: S, E, M, and N. Replication cycle Diseases Caused by Coronaviruses Table: Epidemiology of respiratory coronavirus diseases MERS-CoV SARS-CoV SARS-CoV-2 Date of first identified case June 2012 November 2002 December 2019 Location of first identified case Jeddah, Saudi […]
Pneumocystis jirovecii/Pneumocystis Pneumonia (PCP)
General Characteristics Basic features of Pneumocystis Pneumocystis is a yeast-like fungus. Clinically relevant species P. jirovecii (formerly known as P. carinii) causes pneumocystis pneumonia (PCP). Epidemiology and Pathogenesis Epidemiology Reservoir The reservoir for P. jirovecii is unknown, but immunocompetent humans may play a role. Transmission P. jirovecii spreads through airborne transmission. Host risk factors Pneumocystis […]
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)
Overview Definition Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a lung disease characterized by airflow limitation resulting from airway disease and/or parenchymal destruction. Types The subtypes may have differing presentations and response to therapy. Patients may have any combination of both. Epidemiology Etiology Risk factors Pathophysiology Chronic bronchitis Inhaled agents cause chronic inflammation in the airways, […]
Imaging of the Lungs and Pleura
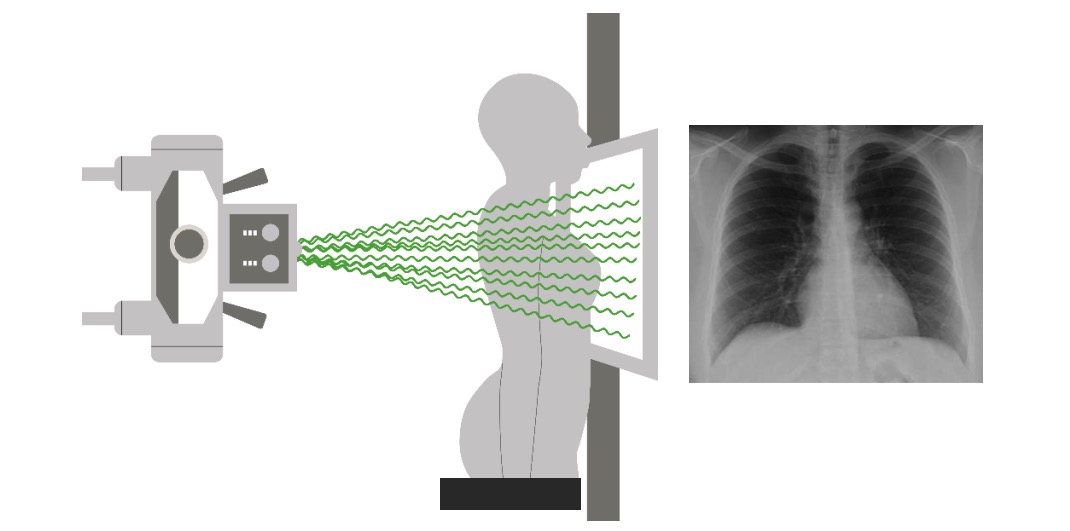
Introduction Before interpreting any image, the physician should take certain preparatory steps. The same systematic approach should be followed every time. Chest X-ray Indication Medical indications: Nonmedical indications: Advantages: Disadvantages: Exam technique Positioning: Positioning for specific views: Penetration: Penetration is the degree to which radiation has passed through body, resulting in a darker or lighter […]
Lungs: Anatomy
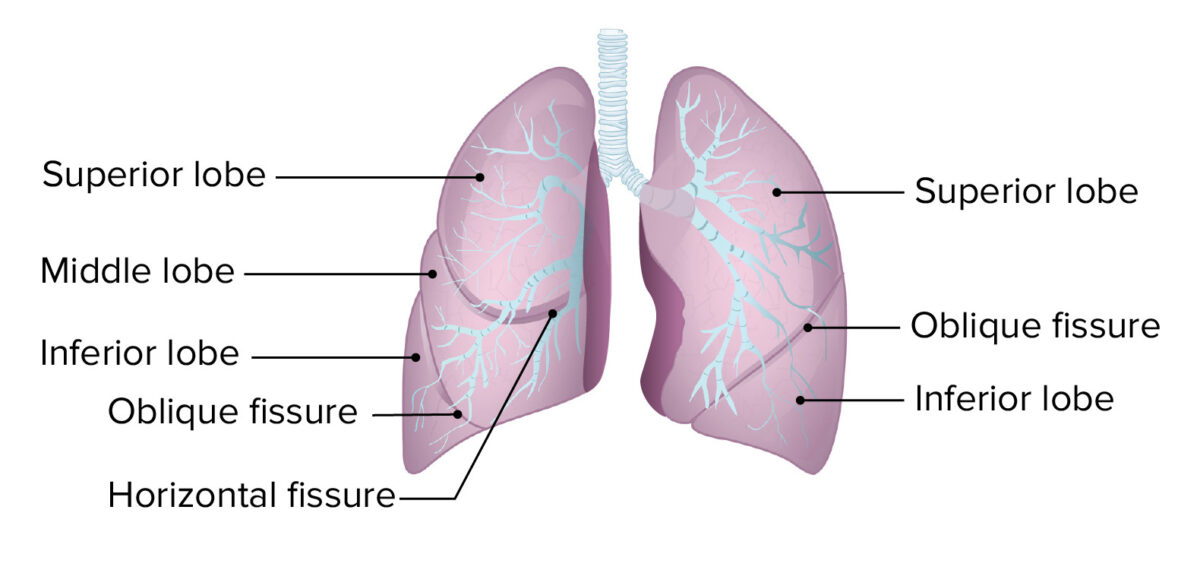
Development Development of the tracheobronchial tree and lungs occurs in 5 stages. The tracheobronchial tree originates from the foregut of the embryonic gut tube, beginning at week 4 of gestation and ending in childhood. Table: Development of the tracheobronchial tree and lungs, and clinical relevance Stage Description Clinical relevance Embryonic period Occurs during weeks 4–7 […]
Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS)
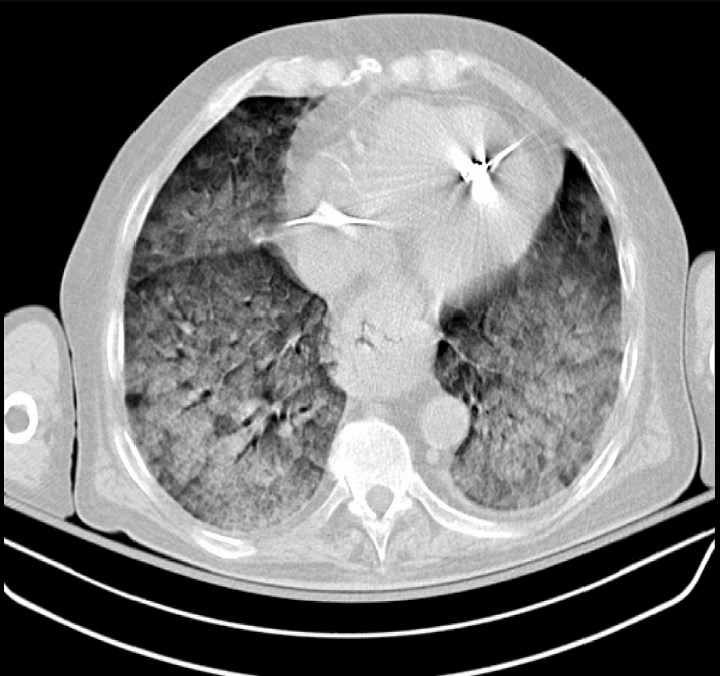
Overview Definition Acute respiratory distress syndrome is a clinical syndrome (not a pathological diagnosis) characterized by a sudden onset of hypoxemia and bilateral pulmonary edema without cardiac failure. The underlying mechanism of ARDS is diffuse alveolar damage (DAD): Acute respiratory distress syndrome is clinically diagnosed using the Berlin diagnostic criteria. Epidemiology Etiology Acute respiratory distress […]
Pulmonary Fibrosis
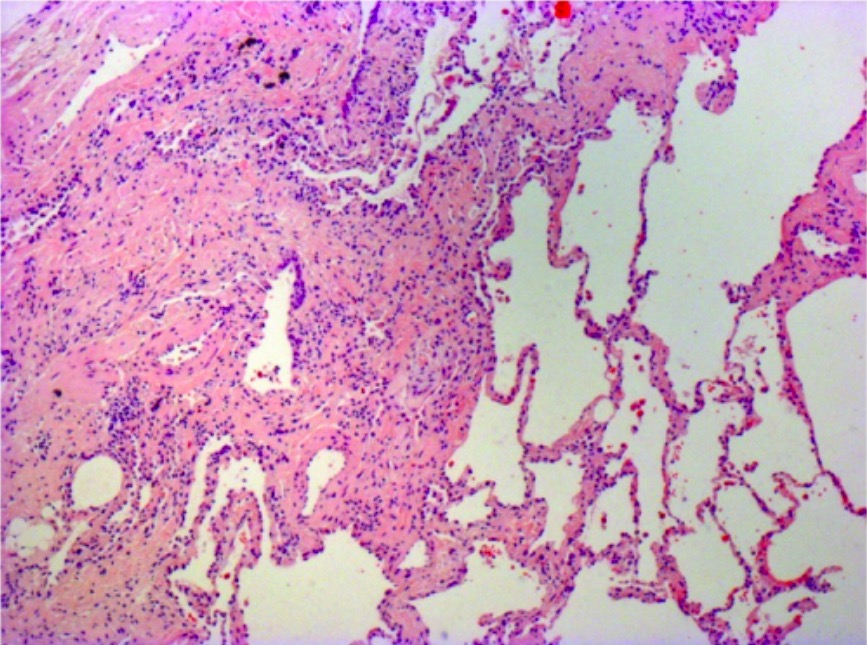
Definition and Epidemiology Definition Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is the most common type of interstitial lung disease (ILD) and is characterized by chronic, progressive, irreversible fibrosis of the lung parenchyma. Epidemiology IPF has been difficult to study because of its rarity and evolution in diagnostic practices. Etiology and Pathophysiology Etiology The cause of IPF remains […]
Pulmonary Hypertension
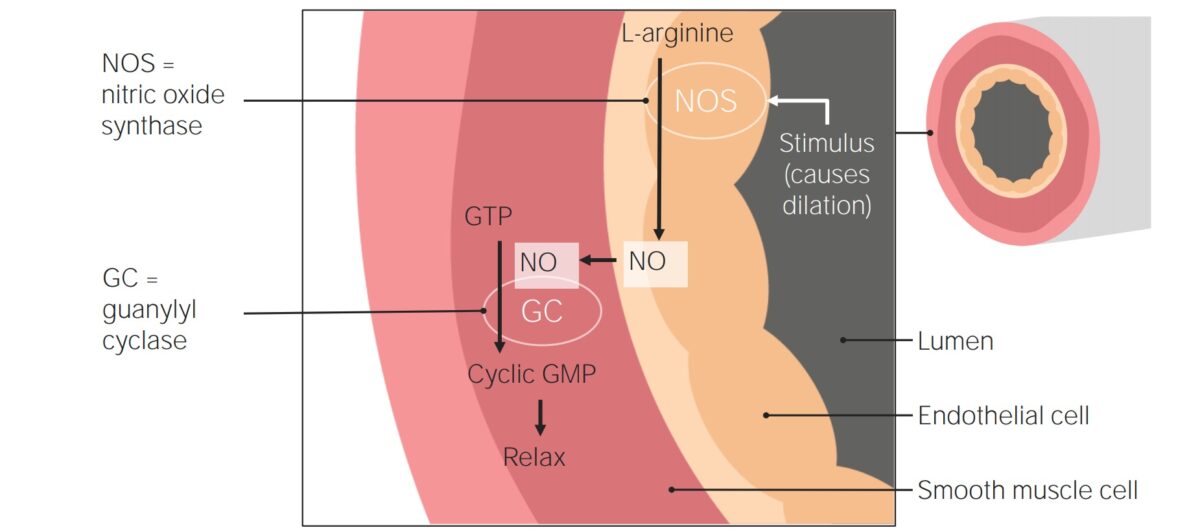
Overview Definition Pulmonary hypertension (PH) is defined as elevated pulmonary arterial pressure. Epidemiology Secondary PH is much more common than the primary variant. The epidemiology of secondary PH is similar to the underlying condition. Primary PH/PAH: Anatomy review Blood flow through the cardiac and pulmonary circulation takes the following path: Classification and Etiology The WHO […]
Respiratory Alkalosis
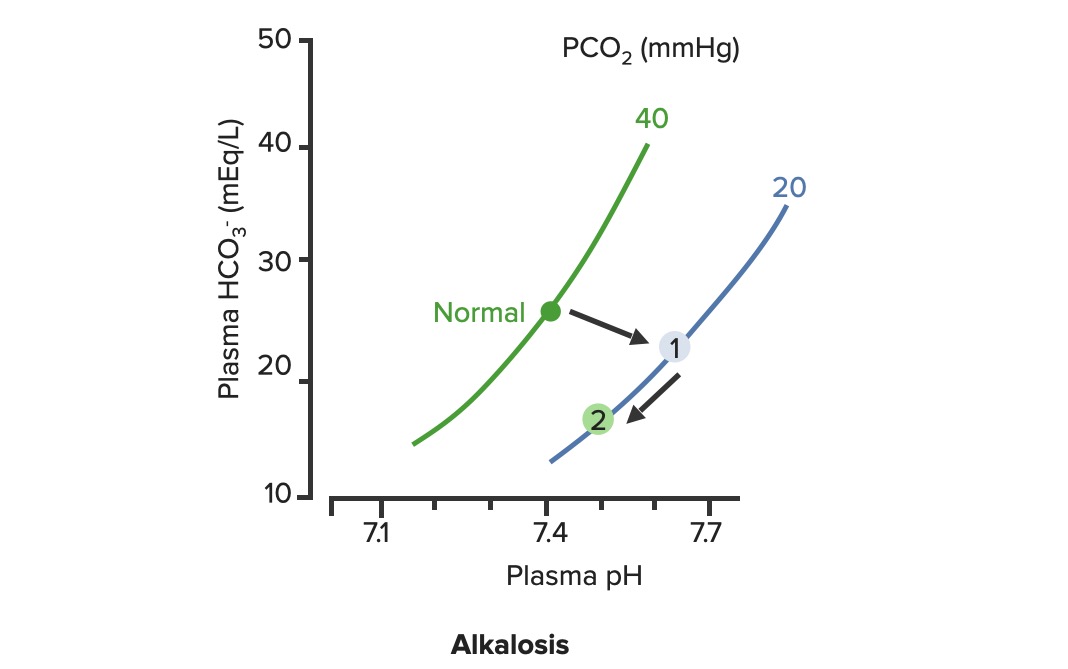
Overview Definition Respiratory alkalosis refers to the process that results in a decreased level of carbon dioxide (CO2) within the blood. Epidemiology Etiology Table: Etiologies of respiratory alkalosis Etiology Examples Physiologic (not pathologic) Pregnancy High altitude Hypoxia-induced Pulmonary embolism Pulmonary edema COPD or asthma exacerbations Medications Aspirin overdose Nicotine overdose Progesterone Intracranial processes Stroke Encephalitis […]