Calcimimetics

Pharmacodynamics Medications in the class Mechanism of action Physiologic effects Calcimimetics prevent the progression of bone disease and adverse effects associated with hyperparathyroidism. Pharmacokinetics Absorption Distribution and metabolism Excretion Indications Adverse Effects and Contraindications Adverse effects Important adverse effects for the calcimimetic class include: Contraindications Drug interactions Monitoring Calcium levels should be monitored. Comparison of […]
Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System Inhibitors
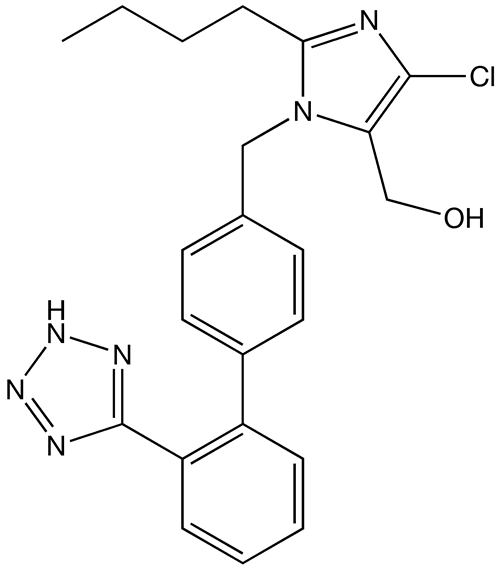
Overview Definition Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system inhibitors constitute an important class of medications for the treatment of cardiovascular diseases, and are 1st-line agents for the treatment of hypertension. Review of the RAAS Drugs in the RAAS inhibitor class Drugs in the RAAS inhibitor class include: Overview of antihypertensive agents Table: Drugs used to treat hypertension Location of […]
Tetracyclines
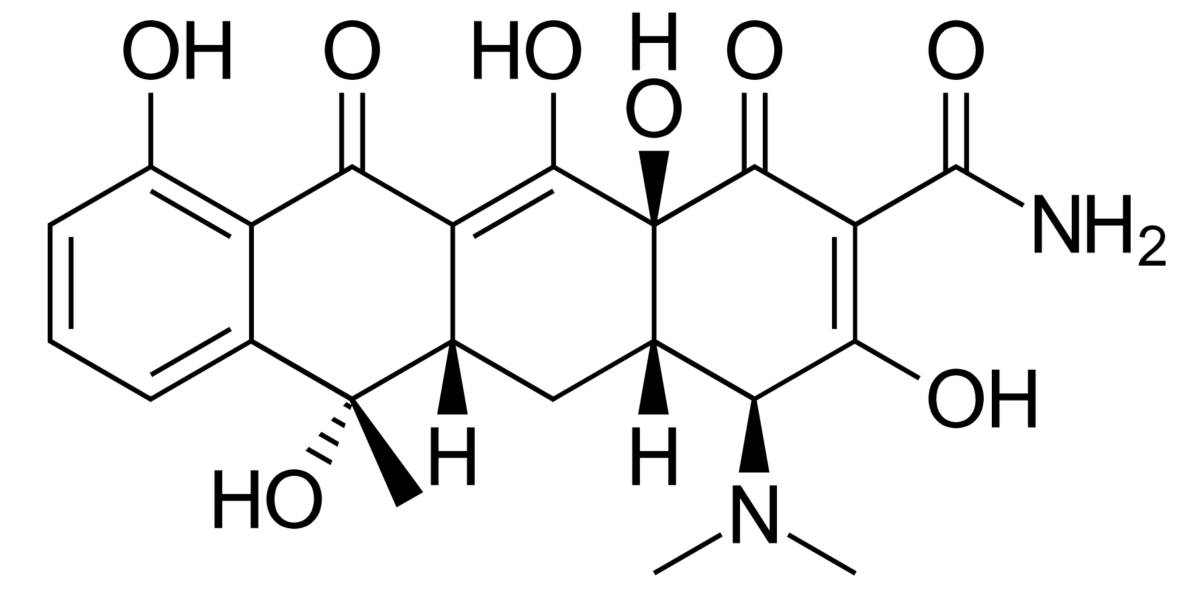
Chemistry and Pharmacodynamics Chemical structure Mechanism of action Pharmacokinetics Indications Table: Tetracyclines and their indications Drug Indications Pearls Tetracycline (oral tablet) Actinomycosis: when penicillin contraindicated Gram-negative infections: Klebsiella Escherichia coli Acinetobacter Bacteroides Enterobacter Shigella Acne: Cutibacterium (Propionibacterium) acnes Respiratory infections: Haemophilus influenzae Streptococcus pneumoniae S. pyogenes Klebsiella Mycoplasma pneumoniae Skin and soft tissue infections (SSTIs) […]
Benzodiazepines
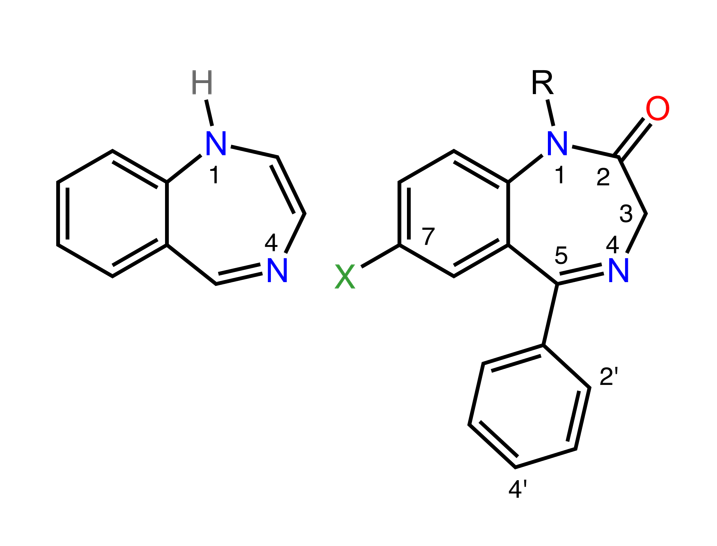
Chemistry and Pharmacodynamics Chemical structure Mechanism of action Physiologic effects GABA: GABA receptors: Benzodiazepine therapeutic effects: Pharmacokinetics Absorption Lipophilic benzodiazepines have a more rapid absorption. Distribution Metabolism Excretion Elimination occurs through the kidney (glucuronides are excreted in the urine). Pharmacokinetics comparison table The table below highlights important benzodiazepine medications and addresses the properties of each. […]
Antiprogestins and Selective Progesterone Modulators
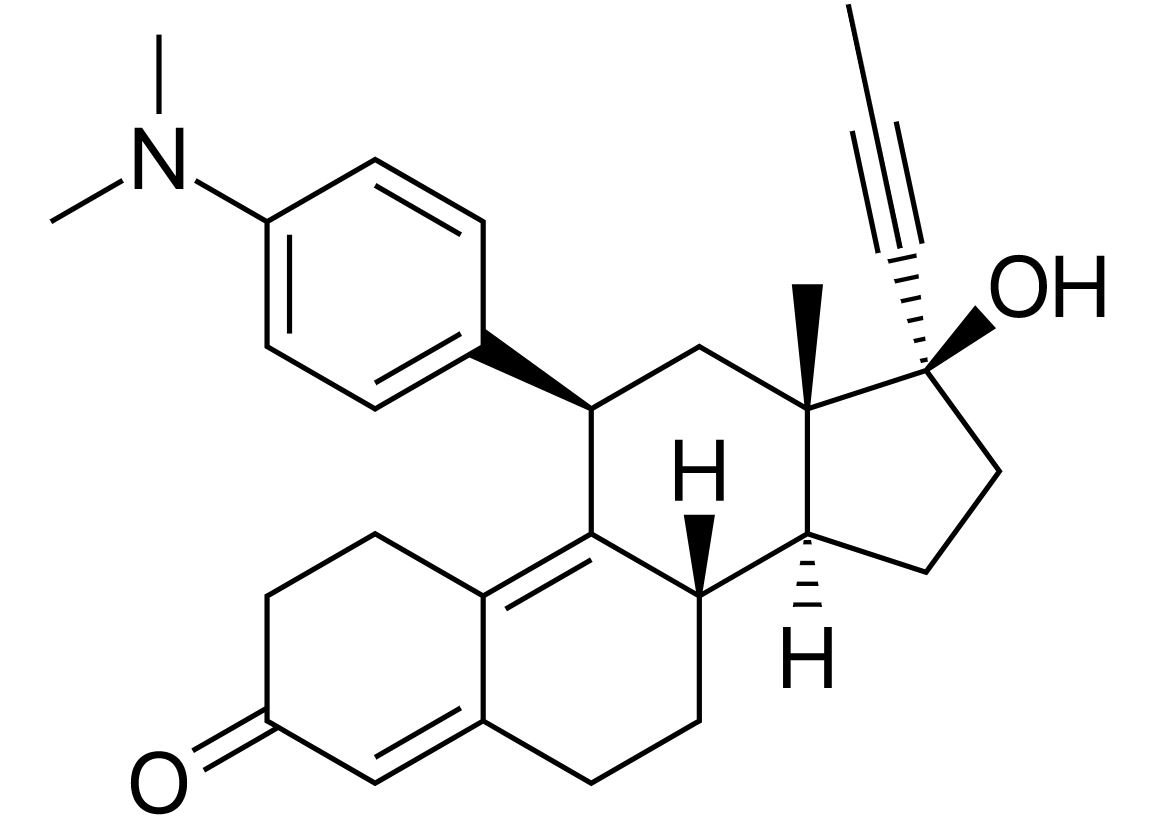
Overview Definition Classification General indications Common side effects Physiology of progesterone Antiprogestins: Mifepristone Chemical structure Mifepristone is a synthetic steroid hormone. Mechanism of action Pharmacological effects Antiprogestin actions: Antiglucocorticoid effect: Pharmacokinetics The following information is for the representative antiprogestin, mifepristone: Indications Side effects Contraindications Cautions Selective Progesterone Receptor Modulators: Ulipristal Chemical structure Mechanism of action […]
Triptans and Ergot Alkaloids
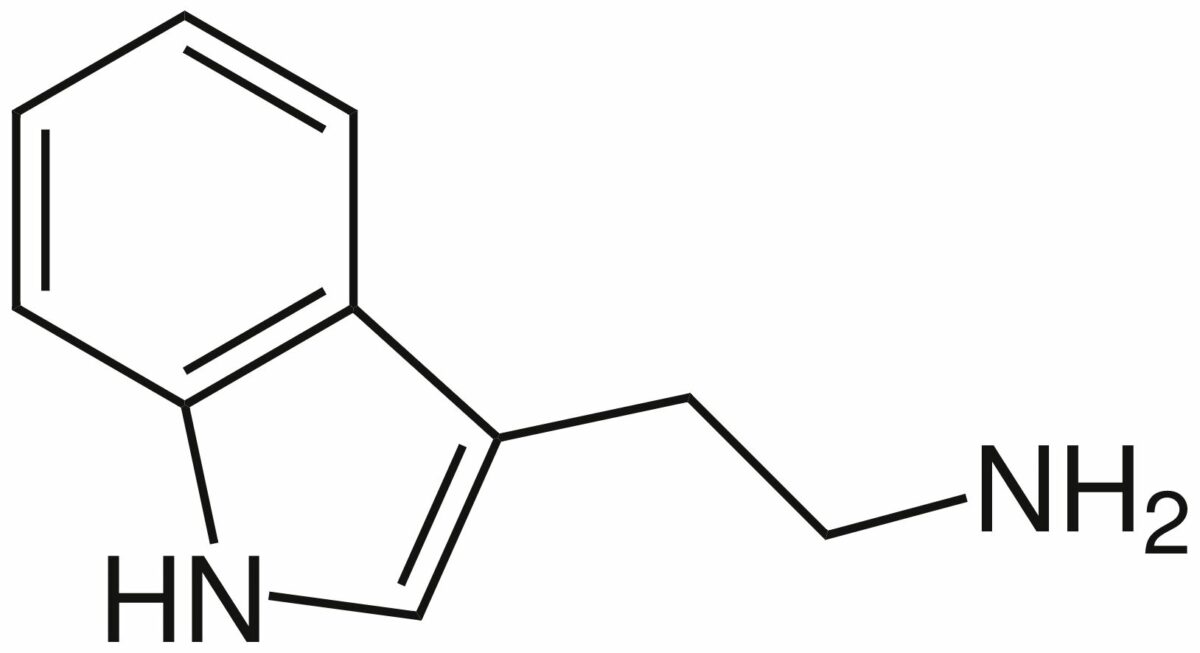
Overview Pathophysiology of migraine The role of triptans and ergot alkaloids Triptans Chemistry Triptans and serotonin share a similar core molecule (tryptamine). Pharmacodynamics Pharmacokinetics Pharmacokinetic variability exists among the triptan medications. Absorption: Distribution: Metabolism: Excretion: Table: Comparison of the pharmacokinetics of triptan medications Medication Onset of action and formulation Elimination half-life Metabolism and excretion Sumatriptan […]
Nitrates
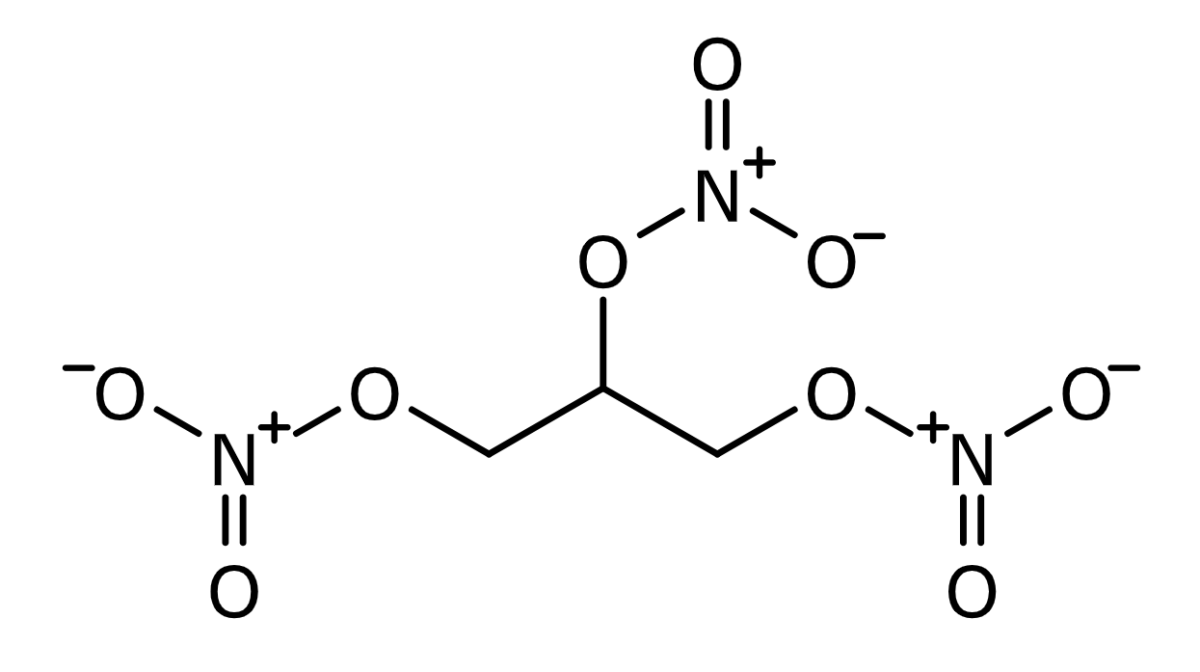
Chemistry and Pharmacodynamics Chemistry Mechanism of action Exogenously administered nitrates are converted to NO after entering the cell: Physiologic effects Pharmacokinetics Absorption Distribution Metabolism Excretion Indications Table: Comparison of nitrates Medications Common formulations Indications Clinical pearls Nitroglycerin Sublingual Oral Transdermal IV Angina Acute MI (unless a right ventricular or inferior infarct) Heart failure Variant angina […]
Potassium-sparing Diuretics
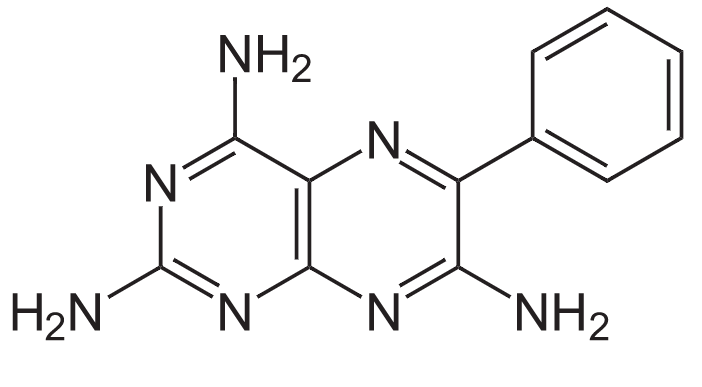
Overview Definition Potassium-sparing diuretics are medications that act in the principal cells in the collecting ducts (CDs) to induce diuresis that does not result in excretion of potassium. Overview of antihypertensive agents Table: Drugs used to treat hypertension Location of action Class Subclasses Renal drugs Drugs affecting the RAAS ACEis ARBs Direct renin inhibitors Diuretics […]
Loop Diuretics
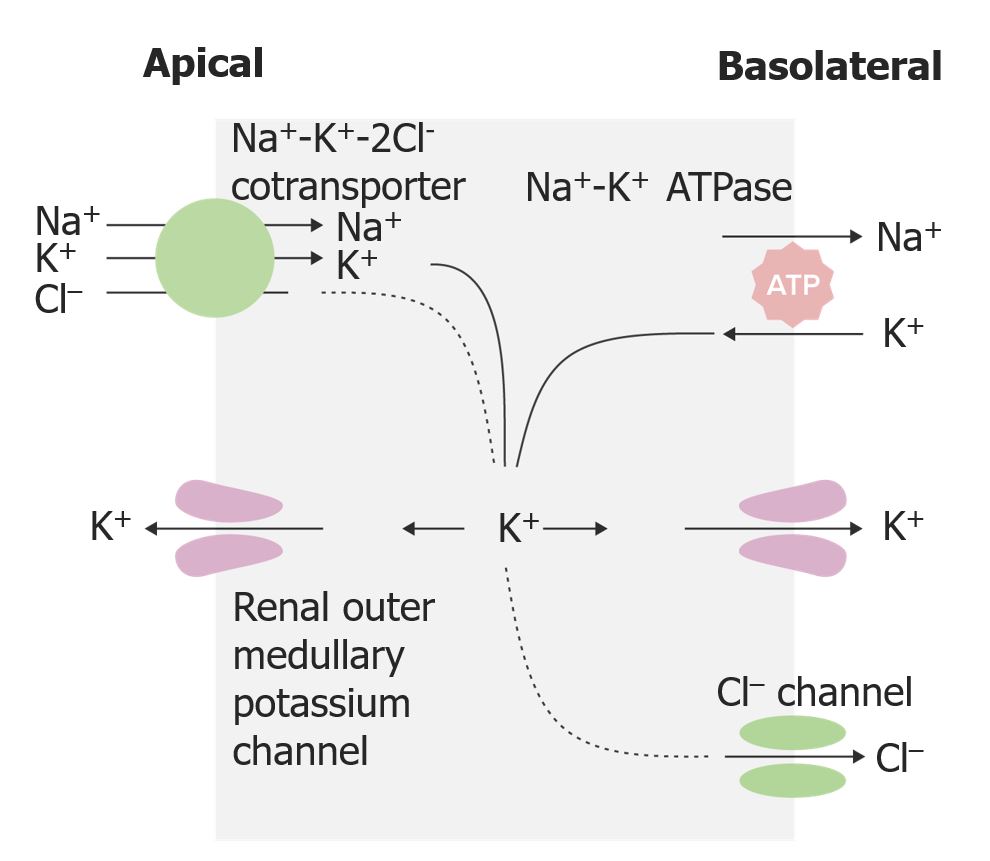
Overview Definition Loop diuretics are a group of medications primarily used to treat edema (and sometimes hypertension) by inhibiting sodium reabsorption through the NKCC2 cotransporter (as known as the Na+-K+-Cl– cotransporter) in the thick ascending limb of the loop of Henle (TAL), which lead to significant diuresis. Overview of antihypertensive agents Table: Drugs used to […]
Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs (DMARDs)
Overview of Antirheumatic Drugs Definition Antirheumatic drugs are used to treat rheumatoid arthritis by slowing the progression of the disease. General indications Antirheumatic drugs are given for: Classification Leflunomide Table: Leflunomide Mechanism of action Inhibits dihydroorotate dehydrogenase Interrupts de novo synthesis of pyrimidines Inhibits proliferation of immune cells Physiologic effects Antiinflammatory effect Antiproliferative effect Metabolism […]