Cancer Immunotherapy
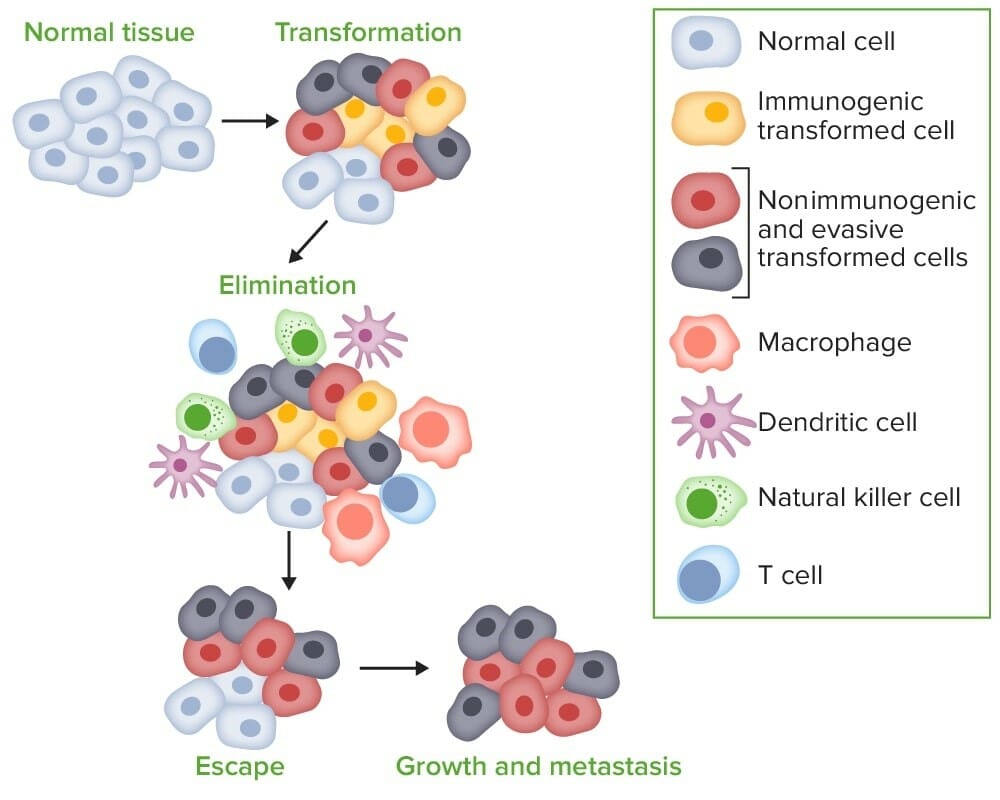
Tumor Immunology Immune system The immune system provides defense (immunity) against invading pathogens ranging from viruses to parasites, and components are interconnected by blood and the lymphatic circulation. The 2 lines of defense (that overlap): Tumor recognition Over 20,000 DNA-damaging events occur each day, which undergo repair via specific pathways, thus causing no lasting effect. […]
Non-Hodgkin Lymphomas
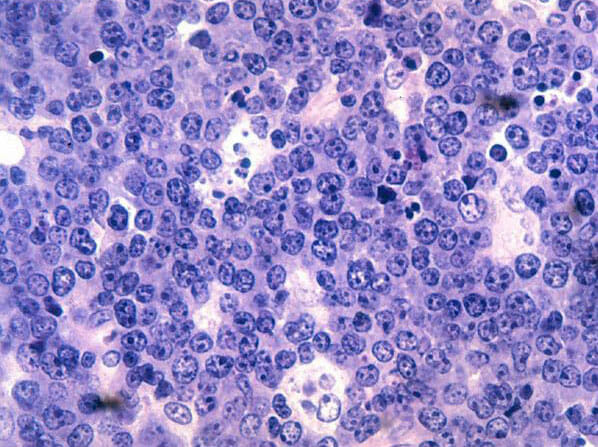
Overview Definition Non-Hodgkin lymphomas (NHLs) are a diverse group of hematologic malignancies that are clonal proliferative disorders of mature or progenitor B cells, T cells, or natural killer (NK) cells. Epidemiology Incidence in the United States: > 70,000 cases annually (6th most common cancer in the United States) Accounts for 4% of all cancers: The […]
Urologic Cancer
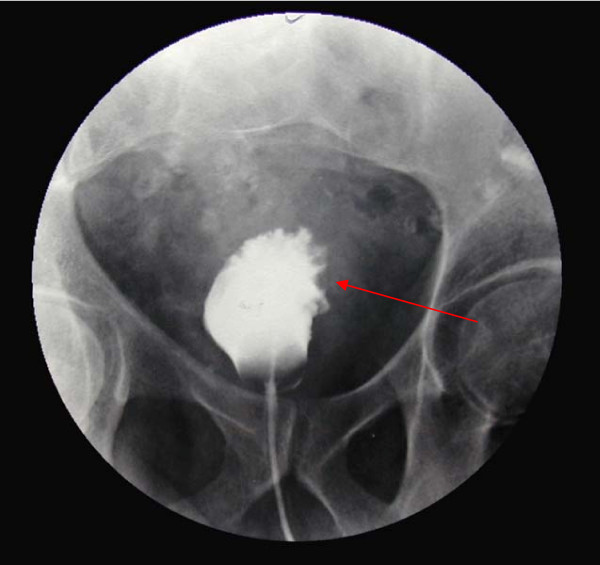
Overview Definition Growth of abnormal cells from the lining of organs of the male and female urinary tracts and the male reproductive organs. Epidemiology Risk factors Types Bladder Cancer Histologic types Clinical presentation Diagnosis Stages of bladder cancer Bladder cancer pathologic stages are based on the TNM staging system. Table: Primary tumor Tumor (T) category […]
Targeted and Other Nontraditional Antineoplastic Therapy
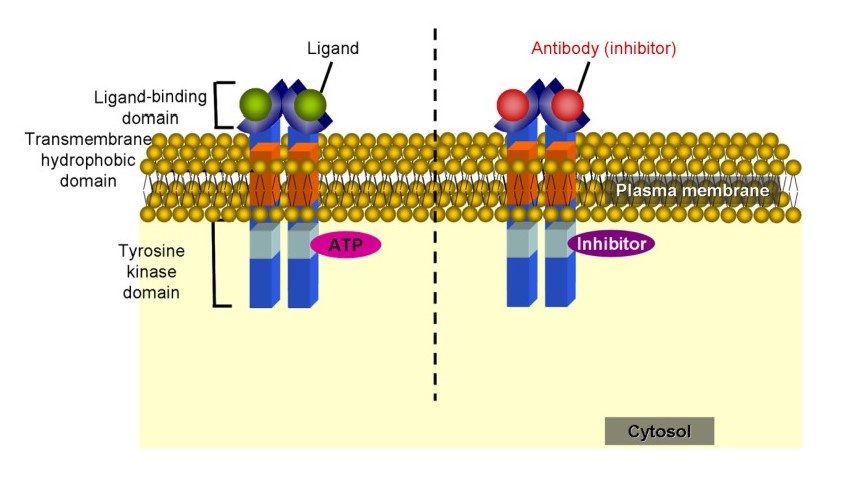
Overview Cancer therapy development Targeted cancer therapy Protein Kinase Inhibitors Protein kinases BCR-ABL kinase inhibitors Table: BCR-ABL kinase inhibitors Imatinib Dasatinib Nilotinib Pharmacodynamics Inhibit BCR-ABL tyrosine kinase (causing apoptosis of BCR-ABL positive cell lines) Inhibit c-KIT, PDGFR Imatinib: also inhibits stem-cell factor Pharmacokinetics Oral Hepatic metabolism Excretion: mostly in feces Indications CML Imatinib, dasatinib: ALL […]
Paraneoplastic Syndromes
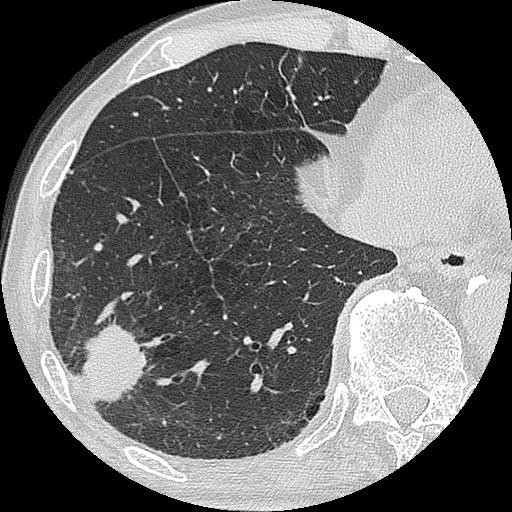
Overview Definition Paraneoplastic syndromes are clinical syndromes that arise from an immune response to a neoplasm, producing substances that are not a direct effect of the tumor, such as metastasis, mass effect, or invasion of the tumor. Epidemiology Etiology There are 2 primary mechanisms: Classification Table: Paraneoplastic endocrinopathies Clinical syndrome Associated neoplasia Pathogenesis Cushing syndrome […]
Ovarian Cancer
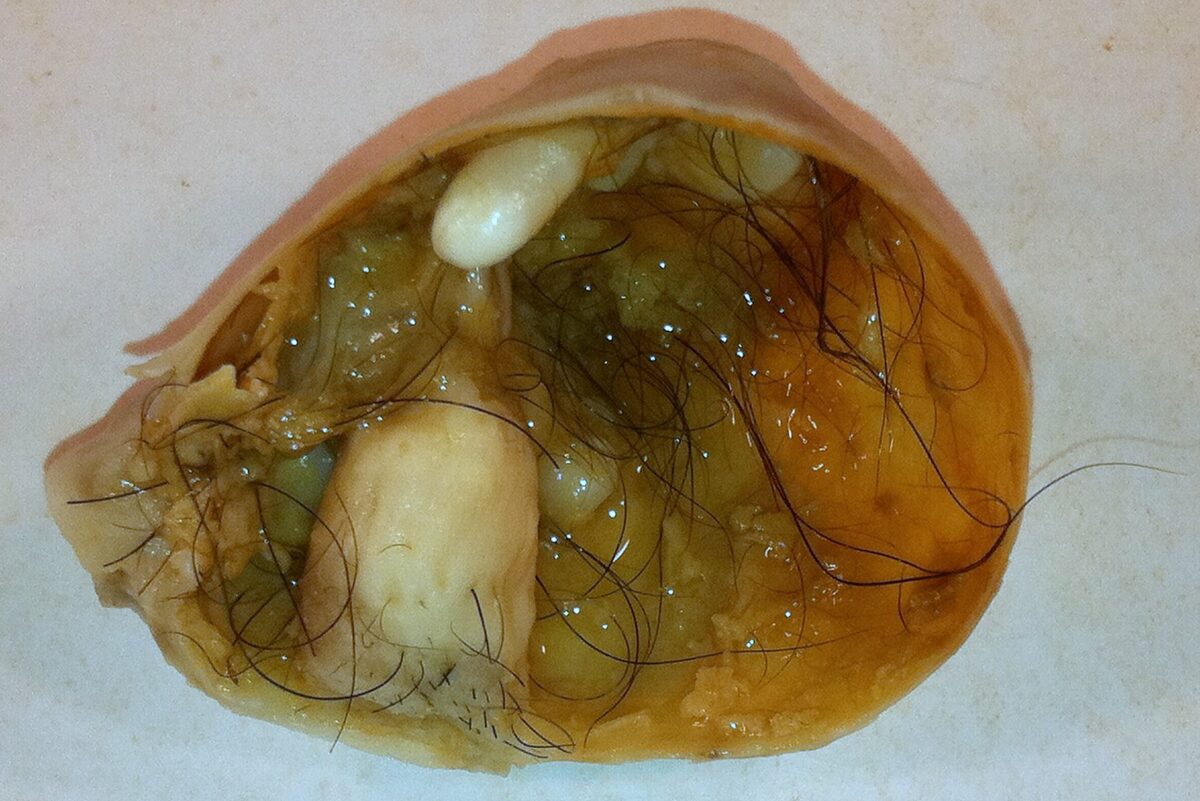
Overview Definition Ovarian cancer is a malignant tumor arising from the ovarian tissues. Epidemiology Risk factors Protective factors Several common factors significantly reduce the risk of ovarian cancer, including: Classification Overview of ovarian tumor classification Table: Summary of ovarian cancer classification Proportion of primary malignant ovarian tumors Commonly affected age group Major types Epithelial tumors […]
Endometrial Hyperplasia and Endometrial Cancer
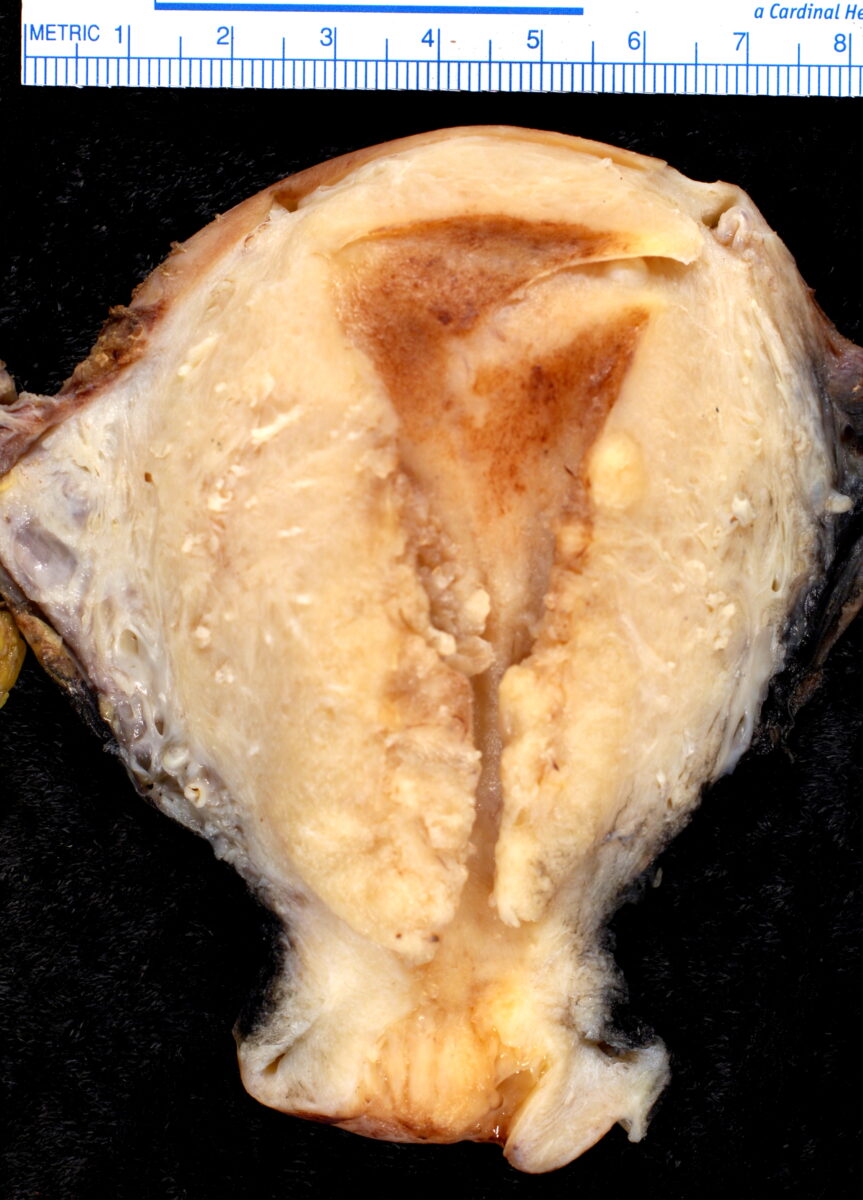
Overview Definition Endometrial hyperplasia (EH) is a state of excessive proliferation of endometrial cells, resulting in an increased gland-to-stroma ratio. Endometrial carcinoma (EC) refers to excessive proliferation of endometrial cells that are capable of invading surrounding tissues and metastasizing to distant sites. Epidemiology Endometrial cancer is the most common gynecologic cancer in the developed world […]
Vaginal Cancer
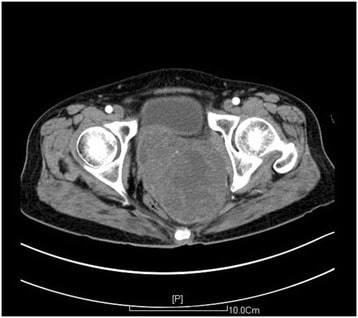
Overview Definition Primary vaginal cancer is a malignant tumor arising from tissue of the vagina. Anatomy review The vagina is: Histologic classification Vaginal malignancies may be either primary (originating from the vagina itself) or metastatic to the vagina from other primary sites. Primary vaginal cancers: The most common subtypes of primary vaginal cancer (originating in […]
Vulvar Cancer
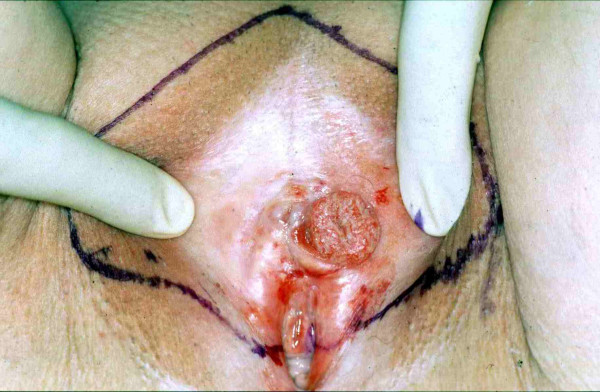
Overview Definition Vulvar cancer is a malignancy of the vulva, which includes structures of the external female genitalia: Epidemiology Vulvar cancer is a rare cancer that constitutes only 0.3% of new cancer diagnoses. Risk factors Classification Classification by histologic subtype Histologic subtypes of vulvar cancer include: Staging Vulvar cancer is staged on the basis of […]
Exocrine Pancreatic Cancer
Overview Classification Epidemiology Etiology Table: Hereditary/genetic factors of exocrine pancreatic cancer Hereditary/genetic factors Germ-line mutations Maximum increased lifetime risk (approximate) Peutz-Jeghers syndrome (PJS) STKII 132 Hereditary pancreatitis PRSS1, others 53 Familial atypical multiple mole melanoma (FAMMM) p16/CDKN2A 38 Family history (increases with the number of 1st-degree relatives and if cancer < 55 years) Unknown 32 […]