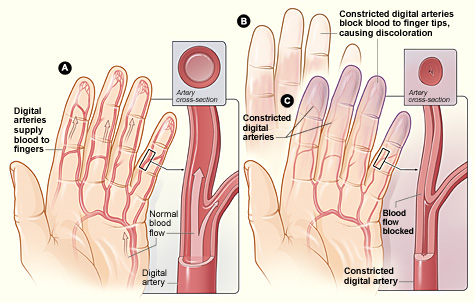
Raynaud Phenomenon
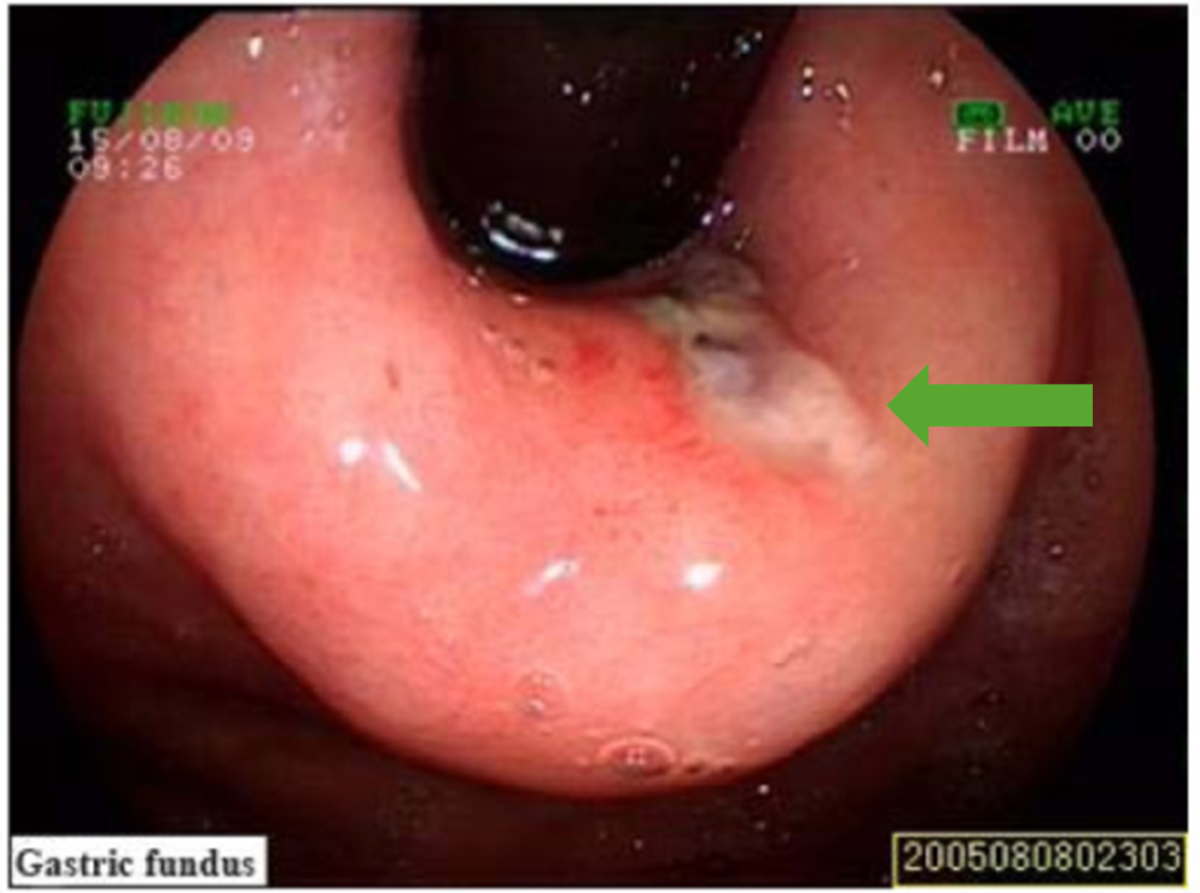
Mallory-Weiss Syndrome (Mallory-Weiss Tear)
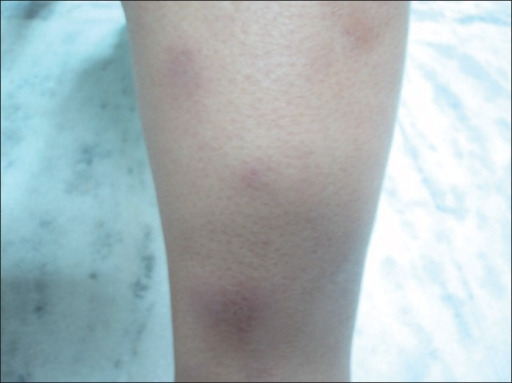
Erythema Nodosum
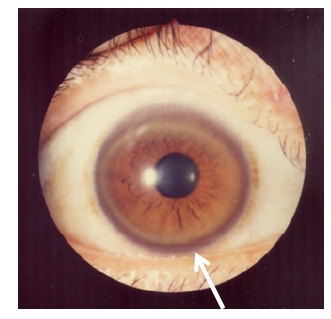
Wilson Disease
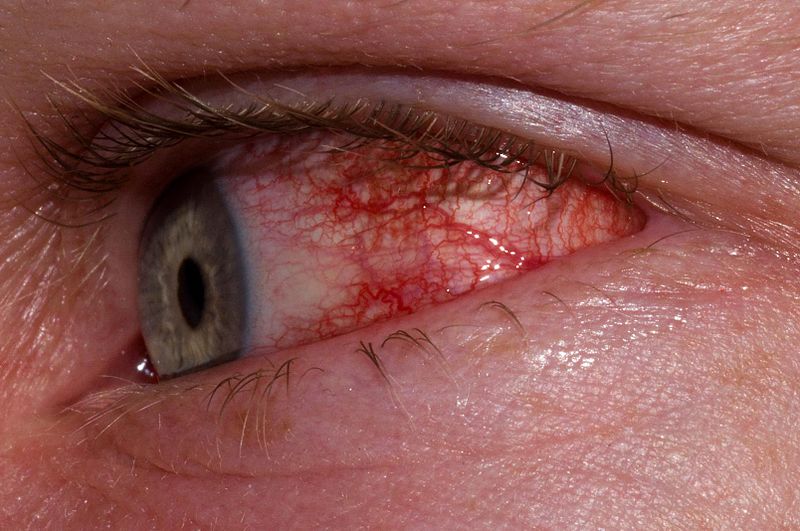
Conjunctivitis
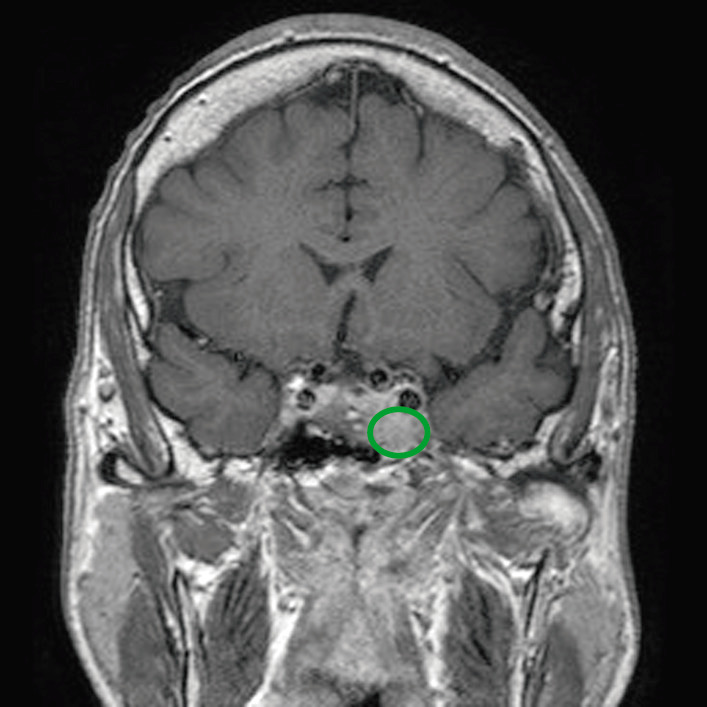
Pituitary Adenomas
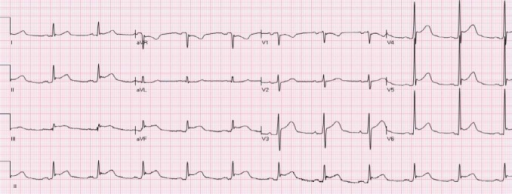
Pericarditis
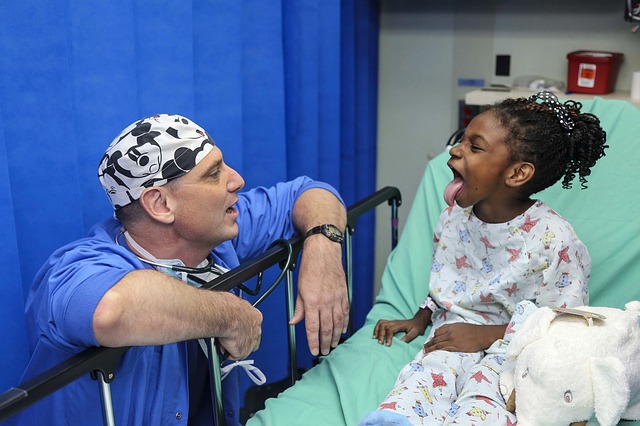
Epiglottitis
Croup
Study with Lecturio for
USMLE™ is a joint program of the Federation of State Medical Boards (FSMB®) and National Board of Medical Examiners (NBME®). MCAT is a registered trademark of the Association of American Medical Colleges (AAMC). NCLEX®, NCLEX-RN®, and NCLEX-PN® are registered trademarks of the National Council of State Boards of Nursing, Inc (NCSBN®). None of the trademark holders are endorsed by nor affiliated with Lecturio.
Lecturio Premium gives you full access to all content & features
Verify your email now to get a free trial.
Lecturio Premium gives you full access to all contents and features—including Lecturio’s Qbank with up-to-date board-style questions.