Acute Coronary Syndrome (Myocardial Infarction and Unstable Angina) (Clinical)
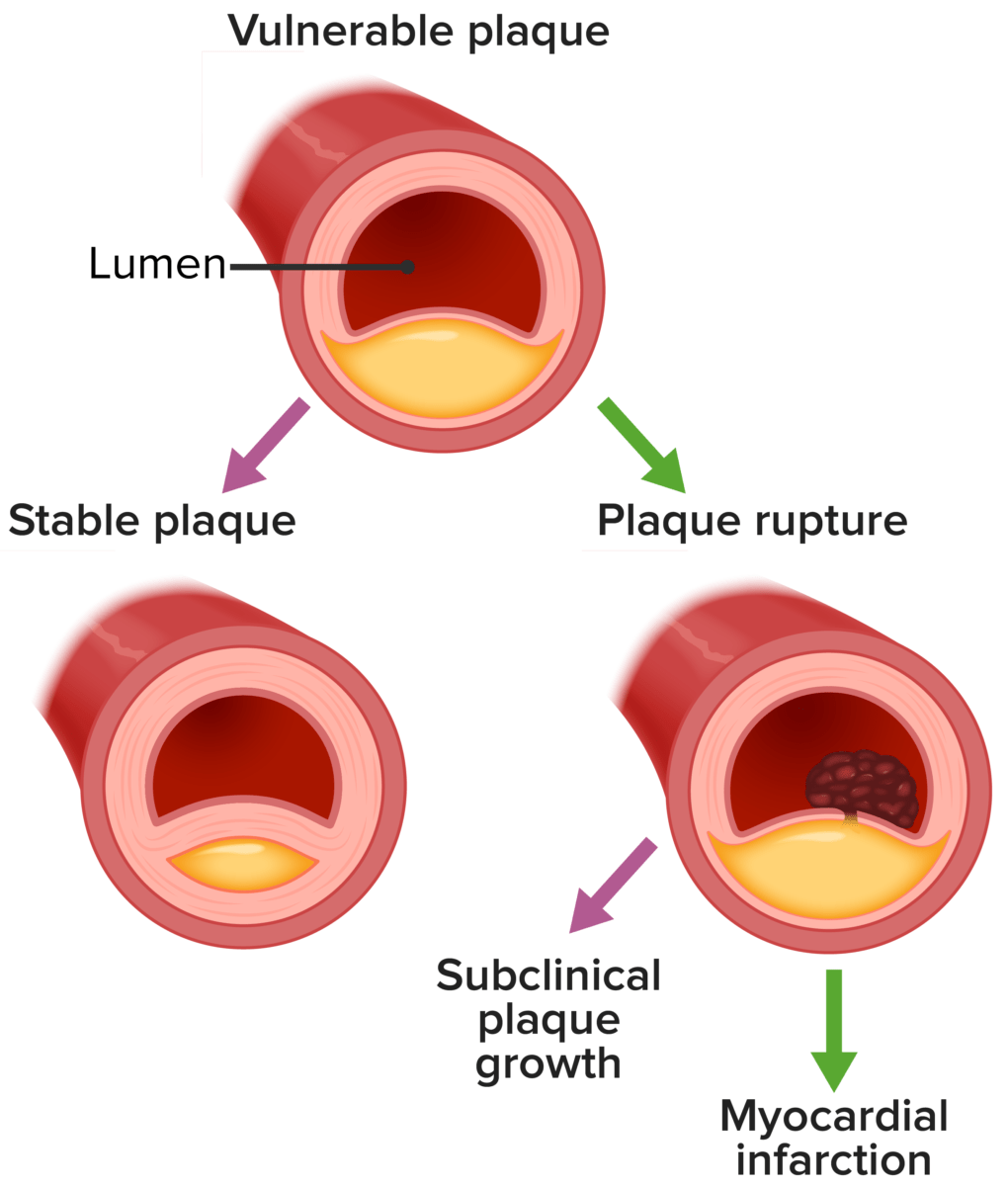
Overview Definitions[2,12,18] Myocardial infarction (MI): MI, commonly known as a “heart attack,” is defined as acute myocardial injury and tissue death resulting from ischemia. Acute coronary syndrome (ACS): ACS is a broad term defined by a condition in which myocardial ischemia or infarction is suspected or confirmed; it includes: Epidemiology[10,12,24] Risk factors[6,7,10] The risks of […]
Tachyarrhythmias
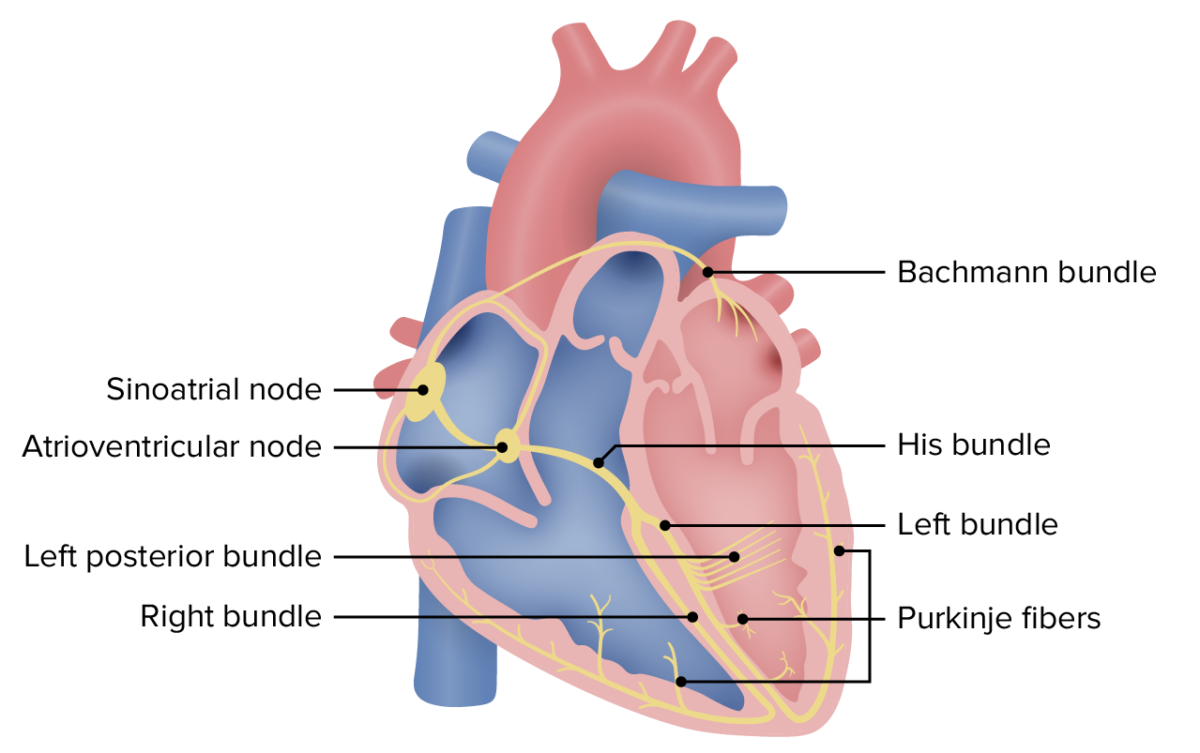
Overview Definition A tachyarrhythmia is a rapid heart rhythm, regular or irregular, with a rate > 100 beats/min. Classification Narrow QRS complex (< 120 msec) tachycardia: Wide QRS complex (≥ 120 msec) tachycardia: Etiology Anatomy and Physiology Anatomy Physiology Sequential events of a cardiac cycle (numbers correlate to the 6 images below): 1. SA node […]
Bundle Branch and Fascicular Blocks
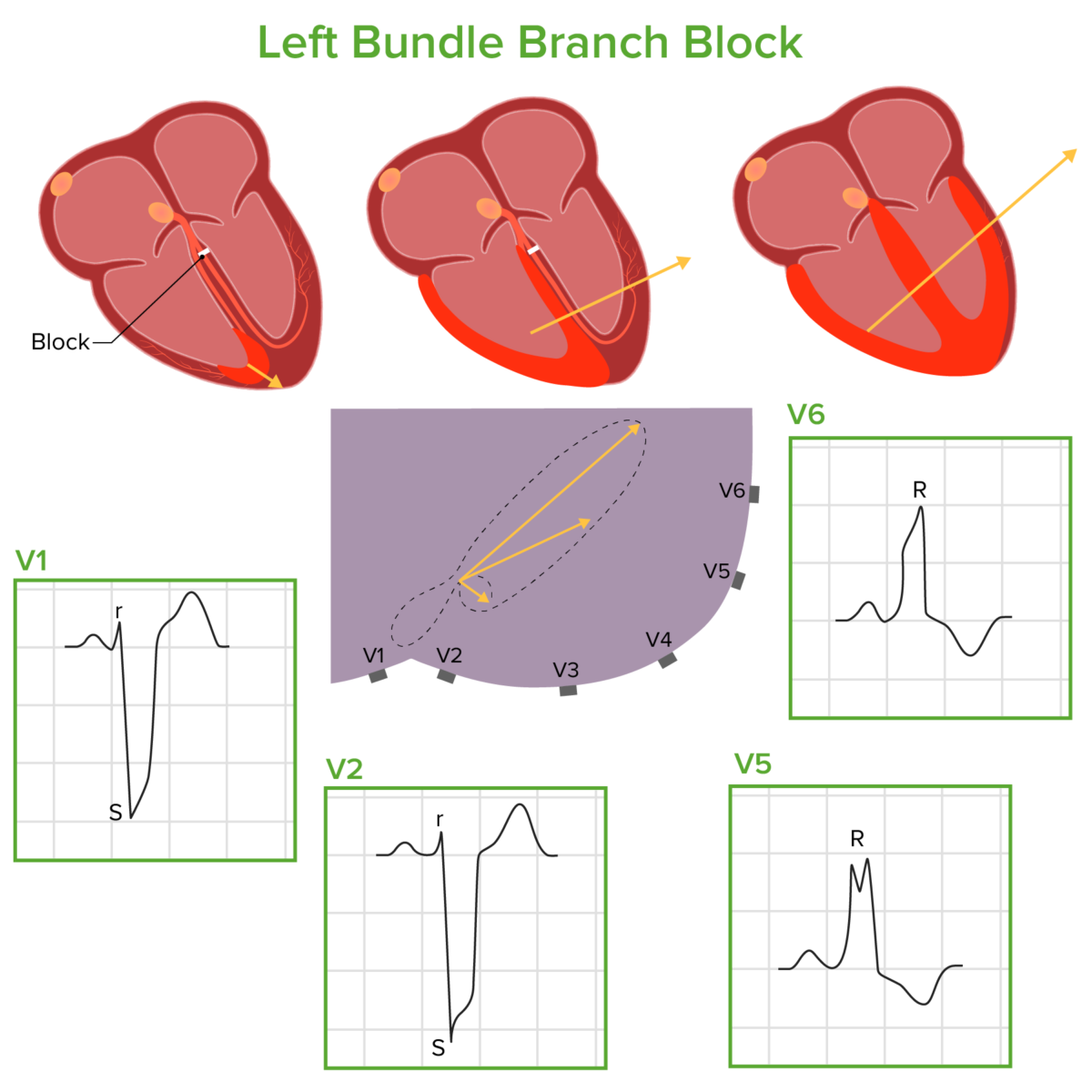
Classification and Epidemiology Classification Bundle branch and fascicular blocks are classified on the basis of where the disruption occurs within the His-Purkinje system. Epidemiology Etiology RBBB LBBB LAFB and LPFB These fascicular blocks can occur because of many of the same causes of RBBB or LBBB, most notably: Pathophysiology Normal physiology Bundle branch blocks Fascicular […]
Chest Pain

Overview Anatomy The anatomy of the chest and thorax includes: heart, lungs, breasts, and chest wall. History Description of chest pain: Typical chest pain descriptions and their clinical significance: Risk factors: Physical examination Vital sign abnormalities and their possible diseases: Examples of important findings in the physical exam: Diagnostic workup Differential Diagnosis Cardiovascular causes Gastrointestinal […]
Ventricular Tachycardia
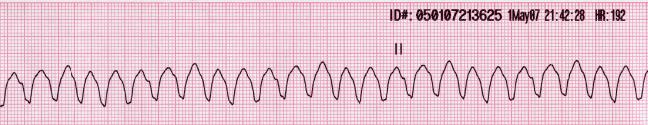
Epidemiology and Etiology Epidemiology Etiology Pathophysiology Clinical Presentation Family history Symptoms Exam Diagnosis Diagnosis is by ECG or cardiac monitoring. There are 2 primary types of ventricular tachycardia: Management Management of ventricular tachycardia is based on whether a pulse is present and, if it is, whether the individual is hemodynamically stable. For pulseless ventricular tachycardia […]
Hypokalemia
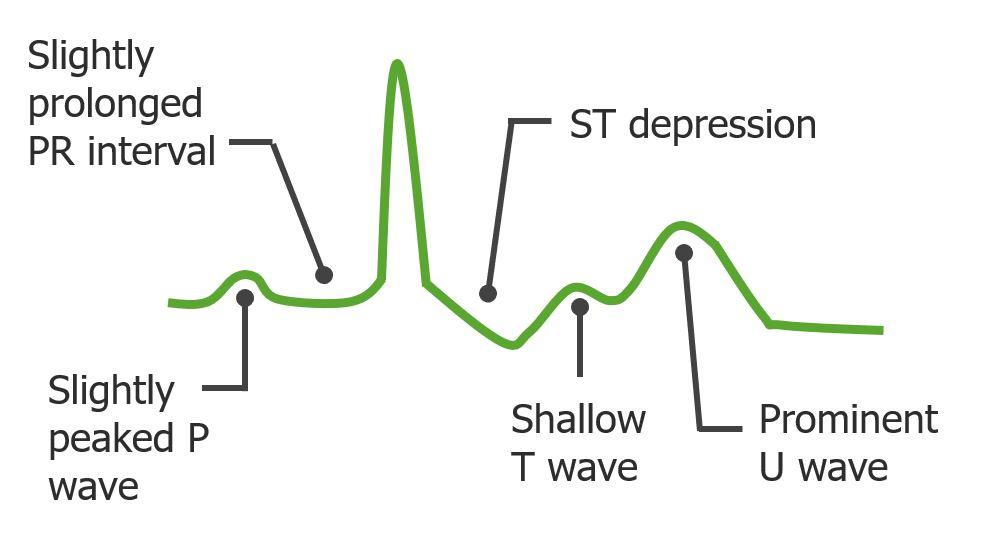
Overview Introduction Potassium (K+) is the main intracellular cation in all cells and is distributed unevenly between the intracellular fluid (98%) and extracellular fluid (2%). The large disparity is necessary for maintaining the resting membrane potential of cells. Definition Hypokalemia is defined as plasma K+ concentration < 3.5 mEq/L. Sites of action in the kidney […]
Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Cardiomyopathy
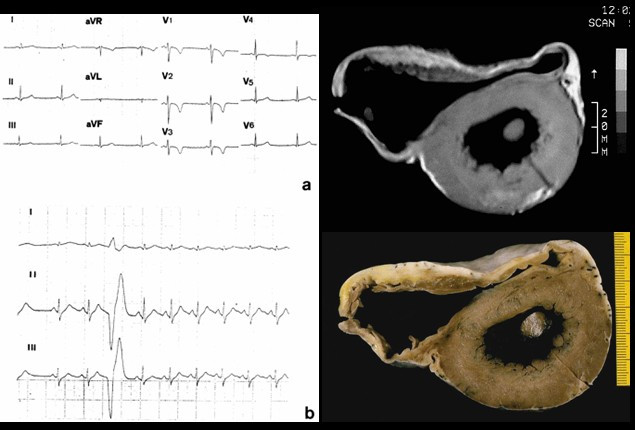
Overview Definition Arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy (ARVC) is a genetic disease of the heart muscle characterized by the fibrofatty replacement of the right ventricular myocardium. Epidemiology The prevalence is 1:2000 to 1:5000. In 11% of cases: sudden cardiac death (SCD) Mean age at presentation is 30 years. Men-to-women predominance is almost 3:1. Presentation is most […]
Hypertension
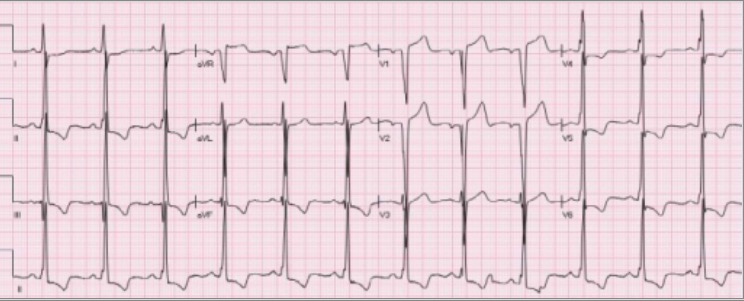
Overview Definition Hypertension is defined as a BP > 130/80 mm Hg. Epidemiology Etiology Primary hypertension: The pathogenesis of primary hypertension is poorly understood but is most likely the result of numerous genetic and environmental factors affecting cardiovascular and kidney structure and function. Risk factors: Secondary hypertension: Classification Table: Classification of hypertension (2017 JNC 8 […]
Myocardial Infarction

Overview Definition Myocardial infarction (MI), commonly known as a “heart attack,” is defined as acute myocardial injury and tissue death resulting from ischemia. Epidemiology Risk factors The risks of MI increase proportionately with increases in risk factors for coronary atherosclerosis (also known as coronary artery disease (CAD)). Classification Classification of MI according to the assumed […]
Stable and Unstable Angina

Overview Definition Epidemiology Stable angina: Unstable angina: Etiology Angina results from coronary artery disease (CAD): Risk factors Cardiac risk factors include: Pathophysiology Angina is a result of mismatched myocardial oxygen demand and oxygen supply. Myocardial oxygen demand Myocardial oxygen supply Pathogenesis of angina Ischemia results when oxygen demand is greater than supply: Clinical Presentation Stable […]