O vírus Ébola e o vírus Marburg são membros da família Filoviridae Filoviridae A family of RNA viruses, of the order mononegavirales, containing filamentous virions. Although they resemble rhabdoviridae in possessing helical nucleocapsids, filoviridae differ in the length and degree of branching in their virions. There are two genera: ebolavirus and marburgvirus. Ebolavirus and Marburgvirus. São vírus de RNA RNA A polynucleotide consisting essentially of chains with a repeating backbone of phosphate and ribose units to which nitrogenous bases are attached. RNA is unique among biological macromolecules in that it can encode genetic information, serve as an abundant structural component of cells, and also possesses catalytic activity. RNA Types and Structure de cadeia simples, de sentido negativo, com uma morfologia filamentosa e pleomórfica característica. A transmissão ocorre principalmente através do contacto com secreções de um indivíduo infetado. Estes vírus causam doenças similares, com sintomas semelhantes aos da gripe, diarreia, hemorragia, disfunção multiorgânica e choque. O diagnóstico pode ser feito por PCR PCR Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a technique that amplifies DNA fragments exponentially for analysis. The process is highly specific, allowing for the targeting of specific genomic sequences, even with minuscule sample amounts. The PCR cycles multiple times through 3 phases: denaturation of the template DNA, annealing of a specific primer to the individual DNA strands, and synthesis/elongation of new DNA molecules. Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR), deteção de antigénios e serologia. O tratamento é principalmente de suporte, embora a terapia com anticorpos monoclonais tem sido promissora para o tratamento da doença do vírus Ébola.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025

Identificação do vírus RNA:
Os vírus podem ser classificados de várias maneiras. A maioria dos vírus, no entanto, terá um genoma formado por DNA ou RNA. Os vírus de genoma de RNA podem ser ainda caracterizados por um RNA de cadeia simples ou dupla. Os vírus “envelopados” são cobertos por uma fina camada de membrana celular (geralmente retirada da célula hospedeira). Se a camada estiver ausente, os vírus são chamados de vírus “nus”. Os vírus com genomas de cadeia simples são vírus de “sentido positivo” se o genoma for usado diretamente como RNA mensageiro (mRNA), que é traduzido em proteínas. Os vírus de “sentido negativo” de cadeia simples usam a RNA polimerase dependente de RNA, uma enzima viral, para transcrever o seu genoma em RNA mensageiro.
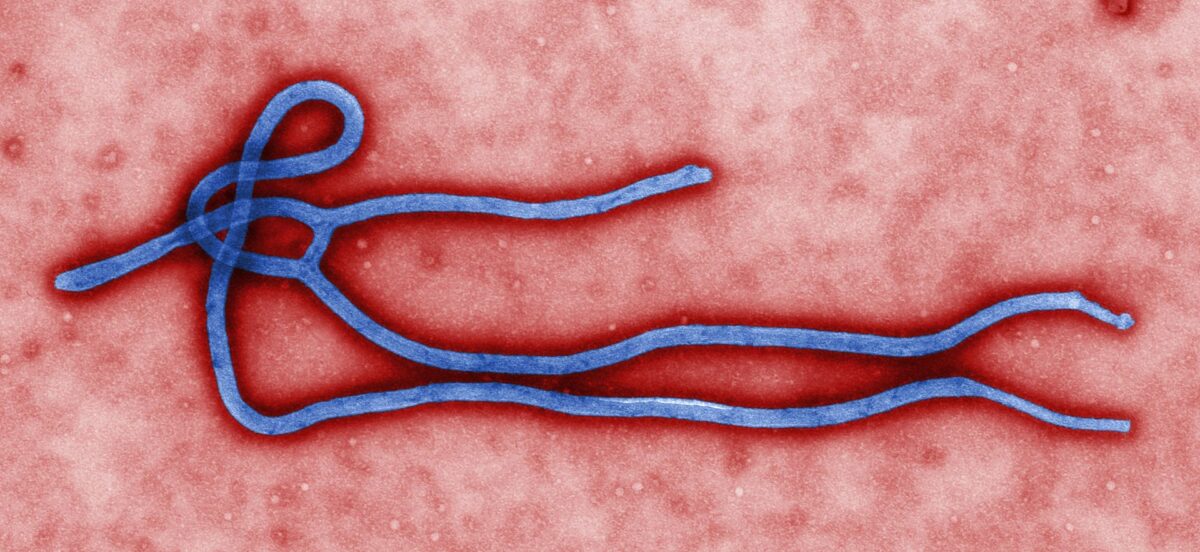
Micrografia eletrónica de um vírion do vírus Ébola:
Observar a estrutura filamentosa.
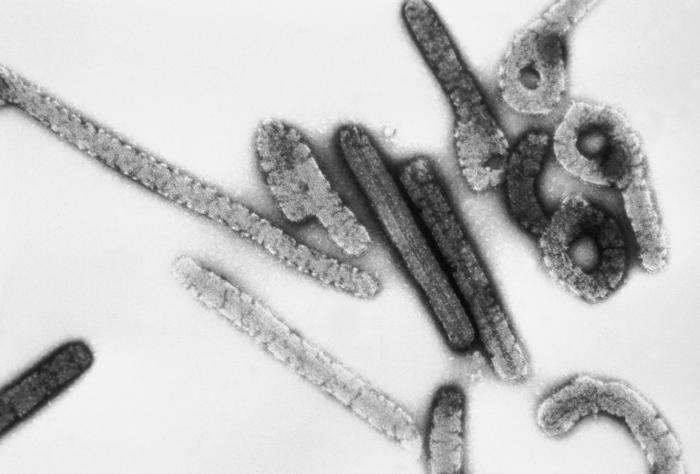
Micrografia eletrónica de vírions do vírus Marburg
Imagem: “Marburg virus” por Erskine Palmer, Russell Regnery. Licença: Public Domain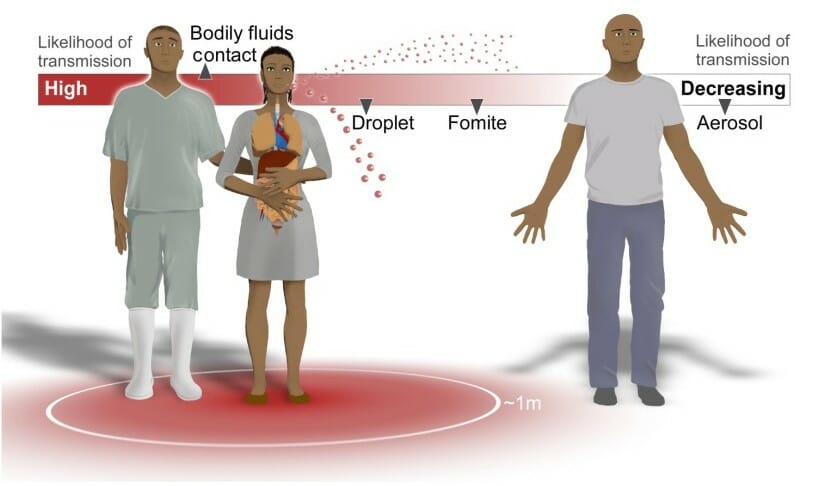
Vias de transmissão do vírus Ébola:
O contacto com fluídos corporais como sangue, fezes, sémen, leite materno e saliva tem o maior risco de transmissão. Os fluídos infecciosos também se podem formar em gotículas de aerossóis, que possuem um menor risco de transmissão.
A doença do vírus Ébola e a MVD têm apresentações muito semelhantes e podem ser difíceis de distinguir.
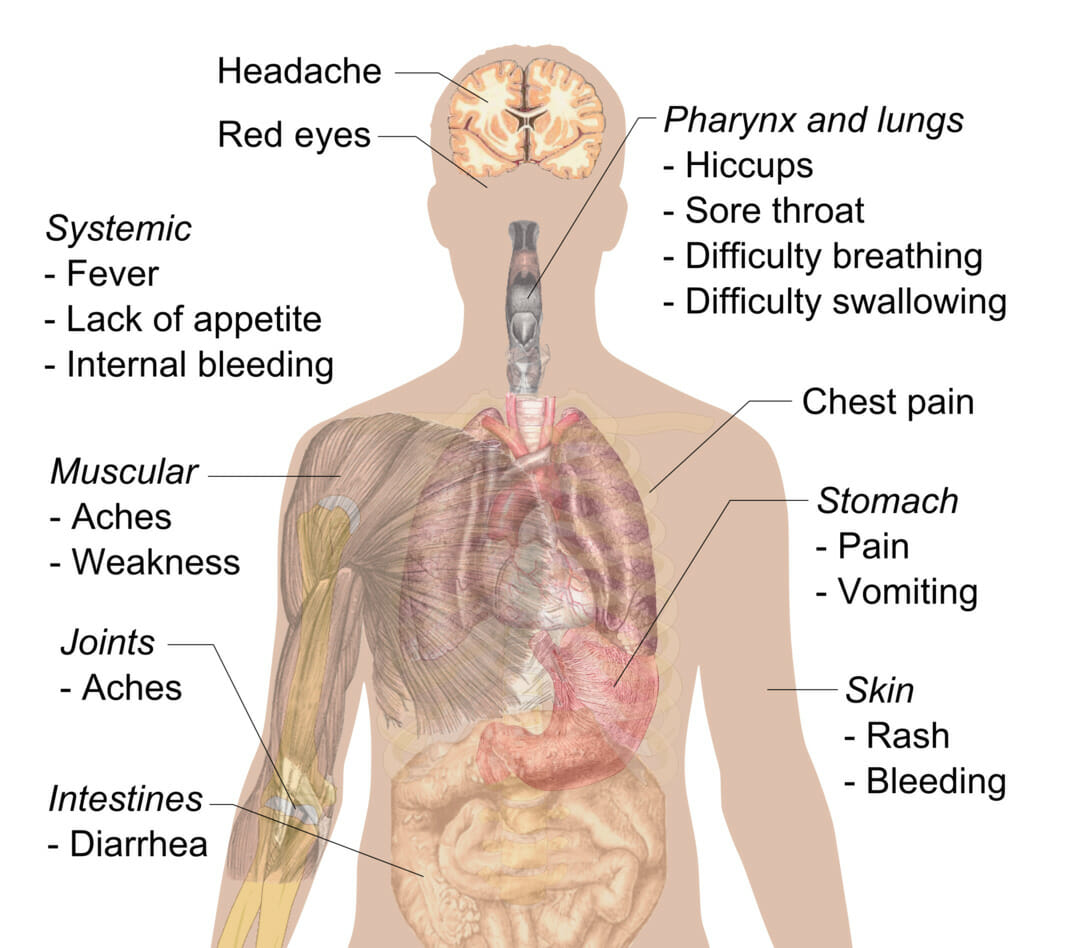
Sinais e sintomas da doença do vírus Ébola
Imagem: “Symptoms of ebola” por Mikael Häggström. Licença: CC0 1.0O diagnóstico de EVD e MVD no início do curso da doença pode ser difícil (os primeiros sintomas mimetizam outras doenças mais MAIS Androgen Insensitivity Syndrome comuns). É necessário um alto grau de suspeição, uma vez que o isolamento precoce dos pacientes em que há suspeita de EVD ou MVC é essencial para controlar o surto.
A tabela a seguir compara e diferencia as várias causas virais de febre hemorrágica:
| Organismo | Vírus Ébola | Vírus da Febre Amarela | Hantavírus | Vírus Lassa |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Família | Filoviridae Filoviridae A family of RNA viruses, of the order mononegavirales, containing filamentous virions. Although they resemble rhabdoviridae in possessing helical nucleocapsids, filoviridae differ in the length and degree of branching in their virions. There are two genera: ebolavirus and marburgvirus. Ebolavirus and Marburgvirus | Flaviviridae Flaviviridae A family of RNA viruses, many of which cause disease in humans and domestic animals. There are three genera flavivirus; pestivirus; and hepacivirus, as well as several unassigned species. Hepatitis C Virus | Bunyaviridae Bunyaviridae A family of viruses, mainly arboviruses, consisting of a single strand of RNA. Virions are enveloped particles 90-120 nm diameter. The complete family contains over 300 members arranged in five genera: orthobunyavirus; hantavirus; nairovirus; phlebovirus; and tospovirus. Bunyavirales | Arenaviridae Arenaviridae A family of RNA viruses naturally infecting rodents and consisting of one genus (arenavirus) with two groups: old world arenaviruses and new world arenaviruses. Infection in rodents is persistent and silent. Vertical transmission is through milk-, saliva-, or urine-borne routes. Horizontal transmission to humans, monkeys, and other animals is important. Lassa Virus |
| Características |
|
|
|
|
| Transmissão |
|
Vetor: mosquito |
|
|
| Apresentação clínica |
|
|
|
|
| Diagnóstico |
|
|
|
|
| Tratamento |
|
Suporte | Suporte |
|