Os antivirais para o tratamento da hepatite C englobam várias classes de fármacos. O regime de tratamento anterior incluía a combinação de interferão alfa (IFN-α) com ribavirina, que induzem a entrada do vírus na célula, regulação imune e replicação viral. Os novos agentes antivirais de ação direta (DAV, pela sigla em inglês) têm como alvo proteínas não estruturais (NS, pela sigla em inglês) específicas do vírus da hepatite C (VHC), importantes para a replicação viral. Estes agentes incluem os inibidores da protease Protease Enzyme of the human immunodeficiency virus that is required for post-translational cleavage of gag and gag-pol precursor polyproteins into functional products needed for viral assembly. HIV protease is an aspartic protease encoded by the amino terminus of the pol gene. HIV Infection and AIDS NS3A/4A, inibidores da NS5A e inibidores da polimerase NS5B. Os DAVs são frequentemente administrados em terapêutica combinada e são o tratamento de primeira linha da hepatite C, devido à sua alta taxa de sucesso e perfil de efeitos adversos pouco significativos.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
O RNA RNA A polynucleotide consisting essentially of chains with a repeating backbone of phosphate and ribose units to which nitrogenous bases are attached. RNA is unique among biological macromolecules in that it can encode genetic information, serve as an abundant structural component of cells, and also possesses catalytic activity. RNA Types and Structure do vírus da hepatite C codifica:
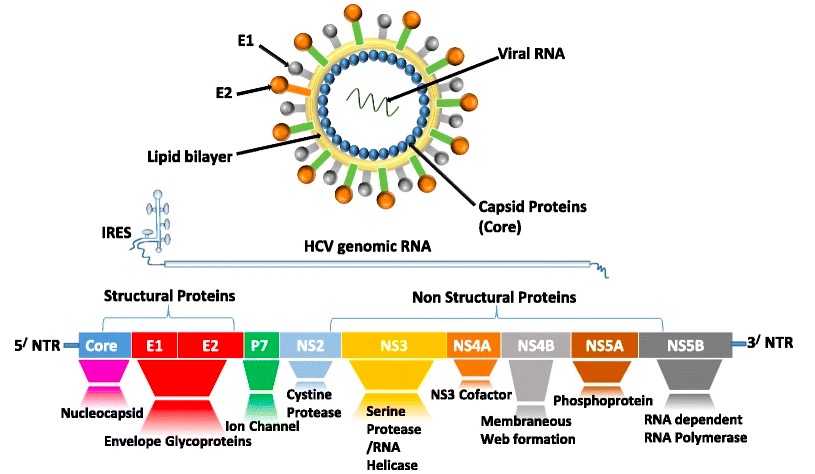
Estrutura viral da hepatite C e proteínas traduzidas do seu genoma:
As proteínas estruturais contêm núcleo, envelope 1 (E1) e E2. NS2, NS3, NS4A, NS4B, NS5A e NS5B são proteínas não estruturais (NS, pela singla em inglês), a maioria das quais são alvos da terapêutica antiviral de ação direta.
O interferão é uma proteína de sinalização pertencente à família das citocinas.
O IFN-α atua através de vários mecanismos:
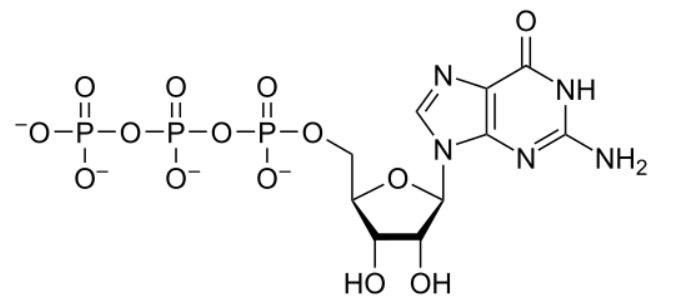
Estrutura química do trifosfato de guanosina (GTP, pela sigla em inglês)
Imagem: “GTP chemical structure” por Hbf878. Licença: CC0 1.0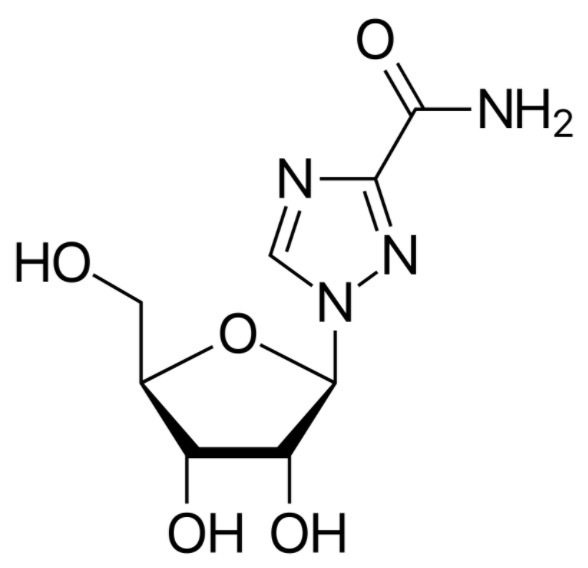
Estrutura química da ribavirina:
É muito semelhante à da guanosina, que desempenha um papel importante na sua ação antiviral.
Os inibidores da protease Protease Enzyme of the human immunodeficiency virus that is required for post-translational cleavage of gag and gag-pol precursor polyproteins into functional products needed for viral assembly. HIV protease is an aspartic protease encoded by the amino terminus of the pol gene. HIV Infection and AIDS NS3A/4A são uma classe de fármacos que inibe a protease Protease Enzyme of the human immunodeficiency virus that is required for post-translational cleavage of gag and gag-pol precursor polyproteins into functional products needed for viral assembly. HIV protease is an aspartic protease encoded by the amino terminus of the pol gene. HIV Infection and AIDS de serina NS3/4A, necessária para a replicação do VHC.
Os inibidores da protease Protease Enzyme of the human immunodeficiency virus that is required for post-translational cleavage of gag and gag-pol precursor polyproteins into functional products needed for viral assembly. HIV protease is an aspartic protease encoded by the amino terminus of the pol gene. HIV Infection and AIDS NS3A/4A são utilizados (geralmente em terapêutica combinada com outro DAV) no tratamento da hepatite C crónica.
Estes fármacos são utilizados (geralmente em terapêutica combinada com outro DAV) no tratamento da hepatite C crónica.
Os inibidores da RNA RNA A polynucleotide consisting essentially of chains with a repeating backbone of phosphate and ribose units to which nitrogenous bases are attached. RNA is unique among biological macromolecules in that it can encode genetic information, serve as an abundant structural component of cells, and also possesses catalytic activity. RNA Types and Structure polimerase dependente de RNA RNA A polynucleotide consisting essentially of chains with a repeating backbone of phosphate and ribose units to which nitrogenous bases are attached. RNA is unique among biological macromolecules in that it can encode genetic information, serve as an abundant structural component of cells, and also possesses catalytic activity. RNA Types and Structure NS5B têm como alvo a NS5B (uma polimerase de RNA RNA A polynucleotide consisting essentially of chains with a repeating backbone of phosphate and ribose units to which nitrogenous bases are attached. RNA is unique among biological macromolecules in that it can encode genetic information, serve as an abundant structural component of cells, and also possesses catalytic activity. RNA Types and Structure dependente de RNA RNA A polynucleotide consisting essentially of chains with a repeating backbone of phosphate and ribose units to which nitrogenous bases are attached. RNA is unique among biological macromolecules in that it can encode genetic information, serve as an abundant structural component of cells, and also possesses catalytic activity. RNA Types and Structure).
Os inibidores da RNA RNA A polynucleotide consisting essentially of chains with a repeating backbone of phosphate and ribose units to which nitrogenous bases are attached. RNA is unique among biological macromolecules in that it can encode genetic information, serve as an abundant structural component of cells, and also possesses catalytic activity. RNA Types and Structure polimerase dependente de RNA RNA A polynucleotide consisting essentially of chains with a repeating backbone of phosphate and ribose units to which nitrogenous bases are attached. RNA is unique among biological macromolecules in that it can encode genetic information, serve as an abundant structural component of cells, and also possesses catalytic activity. RNA Types and Structure NS5B são utilizados (geralmente em terapêutica combinada com outro DAV) no tratamento da hepatite C crónica.