What is asystole?
Definition and meaning
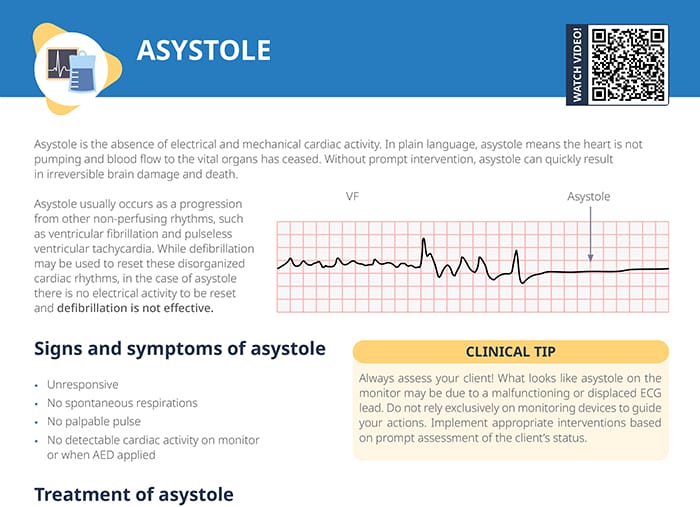
Asystole is defined as the absence of electrical and mechanical cardiac activity.
In plain language, asystole means the heart is not pumping and blood flow to the vital organs has ceased.
“A-” means “without”, “-systole” is the phase of the heartbeat when the heart muscle contracts, and blood pumps from the chambers into the arteries.
Without prompt intervention, asystole can quickly result in irreversible brain damage and death.
Common causes
Common causes of cardiac arrest can be remembered by the “Hs and Ts” mnemonic:
- Hypoxia
- Hypovolemia
- Hydrogen ion (→ acidosis)
- Hypo/hyperkalemia
- Hypothermia
- Tension pneumothorax
- Tamponade (cardiac)
- Toxins (such as drug overdose)
- Thrombosis (pulmonary or coronary)
How to recognize asystole on an ECG strip
On an ECG strip, asystole shows up as a “flatline” with no P waves and no QRS complexes indicating atrial and ventricular activity.
Important: Always assess the client and do not solely rely on the ECG strip to guide your actions. An isoelectric line on the ECG may have other reasons than asystole, such as a malfunctioning or displaced ECG.
Signs and symptoms of asystole
- Unresponsive
- No spontaneous respirations
- No palpable pulse
- No detectable cardiac activity on monitor or when AED applied
Asystole treatment and nursing tasks
How to treat asystole
The first step in treating asystole is to call for help and initiate CPR.
If possible, seek advanced cardiac life support after 2 minutes of high quality CPR with no return of spontaneous circulation. If trained personnel are available, implement the advanced cardiac life support algorithm. Epinephrine may be administered every 3 to 5 minutes.
Is asystole shockable?
Asystole is not a shockable rhythm because, by definition, there is no electrical activity in asystole that could be reset by defibrillation, making defibrillation ineffective.
Other non-perfusing rhythms that may lead to asystole can be reset by defibrillation (such as ventricular fibrillation (V Fib) or pulseless ventricular tachycardia (V Tach)), but not once they have progressed to asystole.
Further nursing tasks
- Perform rhythm check every 2 minutes
- Defibrillate if conversion to shockable rhythm is detected
- Establish an advanced airway if client remains unresponsive
- Work to identify and reverse underlying cause of cardiac arrest
Pulseless electrical activity (PEA) vs asystole
PEA is a condition where the ECG shows organized electrical activity, but the heart fails to contract effectively, leading to no palpable pulse. Like in asystole, defibrillation is not indicated, and CPR is the first step.
Agonal rhythm vs asystole
Agonal rhythm is a slow, irregular heart rhythm often seen in dying clients, indicating severe cardiac dysfunction. Unlike in asystole, there is electrical activity, though inadequate for effective circulation.
V Fib vs asystole
Differentiating ventricular fibrillation and asystole can be difficult, but the treatment options are very different.
Both are life-threatening conditions with no identifiable QRS complexes or P waves on the ECG, but V fib is characterized by chaotic, irregular electrical activity which can show up like small, squiggly lines on the strip. Immediate defibrillation and CPR are required.