La trombosis venosa profunda (TVP) es un coágulo de sangre en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum las venas profundas, normalmente en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum las extremidades inferiores (aunque también pueden producirse en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum las extremidades superiores, en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum las venas mesentéricas y en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum las cerebrales). Las venas afectadas suelen ser las poplíteas, femorales, ilíacas y pélvicas. Los LOS Neisseria tres factores principales (conocidos como la tríada de Virchow) que contribuyen a la formación de la TVP son: estasis venosa, hipercoagulabilidad y daño endotelial vascular. Cualquier condición que empeore 1 (o más) de estos 3 factores aumenta el riesgo de formación de TVP. Las personas pueden presentar dolor Dolor Inflammation unilateral en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum las extremidades, hinchazón y/o enrojecimiento alrededor de la TVP; sin embargo, la mayoría de los LOS Neisseria casos son asintomáticos. El ultrasonido puede visualizar el trombo. La anticoagulación es el principal modo de tratamiento; el objetivo principal es prevenir un tromboembolismo pulmonar (TEP).
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Los LOS Neisseria 3 factores primarios (conocidos como tríada de Virchow) que contribuyen a la formación de TVP incluyen: estasis venosa, hipercoagulabilidad y daño endotelial vascular. Cualquier condición que empeore uno (o más) de estos tres factores aumenta el riesgo de formación de TVP.
Factores que resultan en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum daño endotelial:
Factores que resultan en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum estasis venosa:
Factores que resultan en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum hipercoagulabilidad:
Otros factores de riesgo y/o condiciones que afectan múltiples componentes de la triada de Virchow:
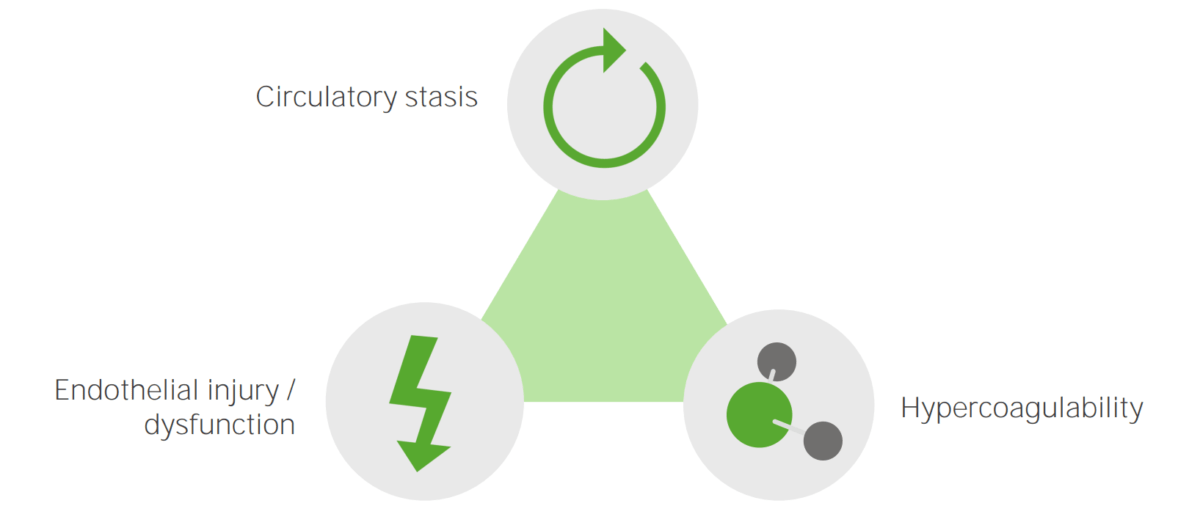
Los principales factores etiológicos que causan la TVP: estasis circulatoria, lesión o disfunción endotelial e hipercoagulabilidad
Imagen por Lecturio.Para recordar los LOS Neisseria factores de riesgo de la TVP, piense THROMBOSIS Thrombosis Formation and development of a thrombus or blood clot in the blood vessel. Epidemic Typhus.
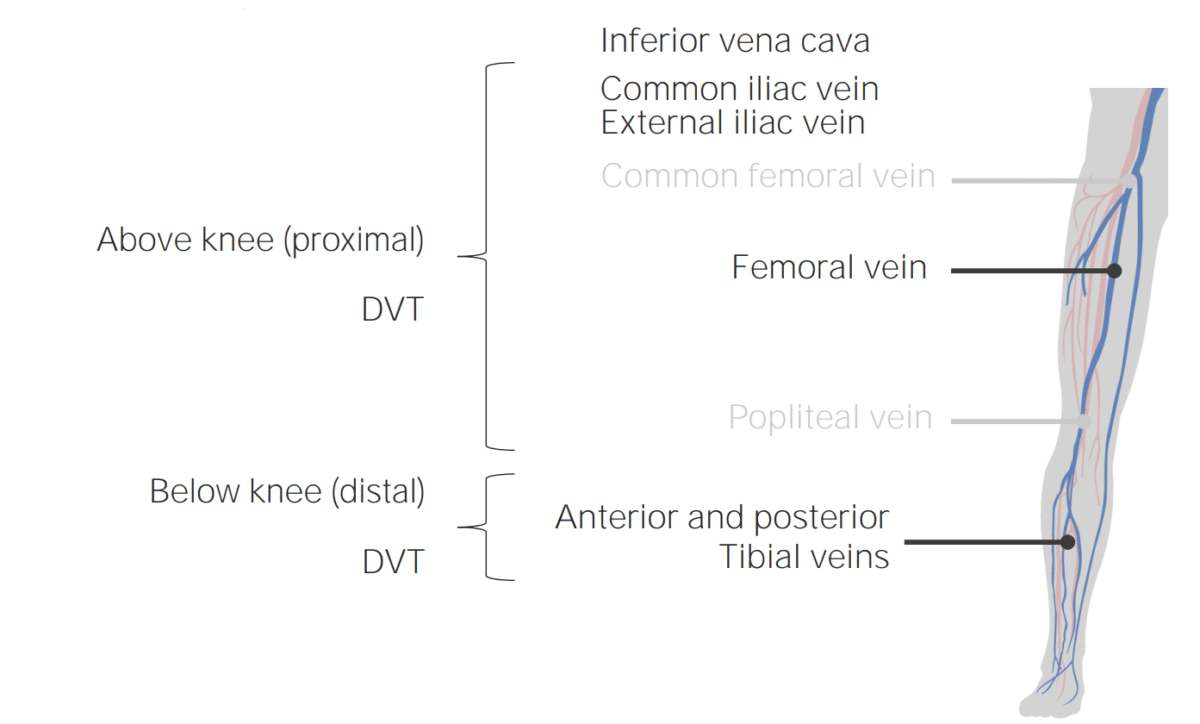
Localizaciones comunes de TVP.
Imagen por Lecturio.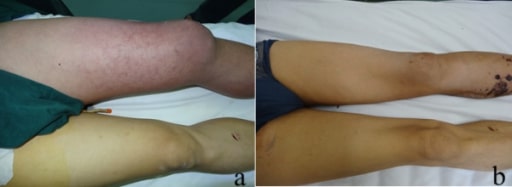
La imagen muestra eritema, inflamación y cianosis en un paciente con flegmasia cerulea dolens “pierna dolorosa azul”.
a) Aspecto inicial de la pierna izquierda, que muestra una importante inflamación y cianosis
b) Aspecto de la pierna izquierda 35 días después de la cirugía, en el momento del alta del paciente
| Sensibilidad/ Dolor Dolor Inflammation a lo largo del sistema venoso profundo | +1 |
| Edema Edema Edema is a condition in which excess serous fluid accumulates in the body cavity or interstitial space of connective tissues. Edema is a symptom observed in several medical conditions. It can be categorized into 2 types, namely, peripheral (in the extremities) and internal (in an organ or body cavity). Edema con fóvea unilateral | +1 |
| Hinchazón de toda la pierna | +1 |
| Hinchazón de la pantorrilla ≥ 3 cm ( en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum comparación con la pantorrilla asintomática) | +1 |
| Venas colaterales superficiales no varicosas | +1 |
| Cáncer activo | +1 |
| TVP anterior | +1 |
| Parálisis o inmovilización por yeso | +1 |
| En EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum cama ≥ 3 días o cirugía mayor en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum las últimas 4 semanas | +1 |
| Diagnóstico alternativo tan probable/más probable que TVP | -2 |
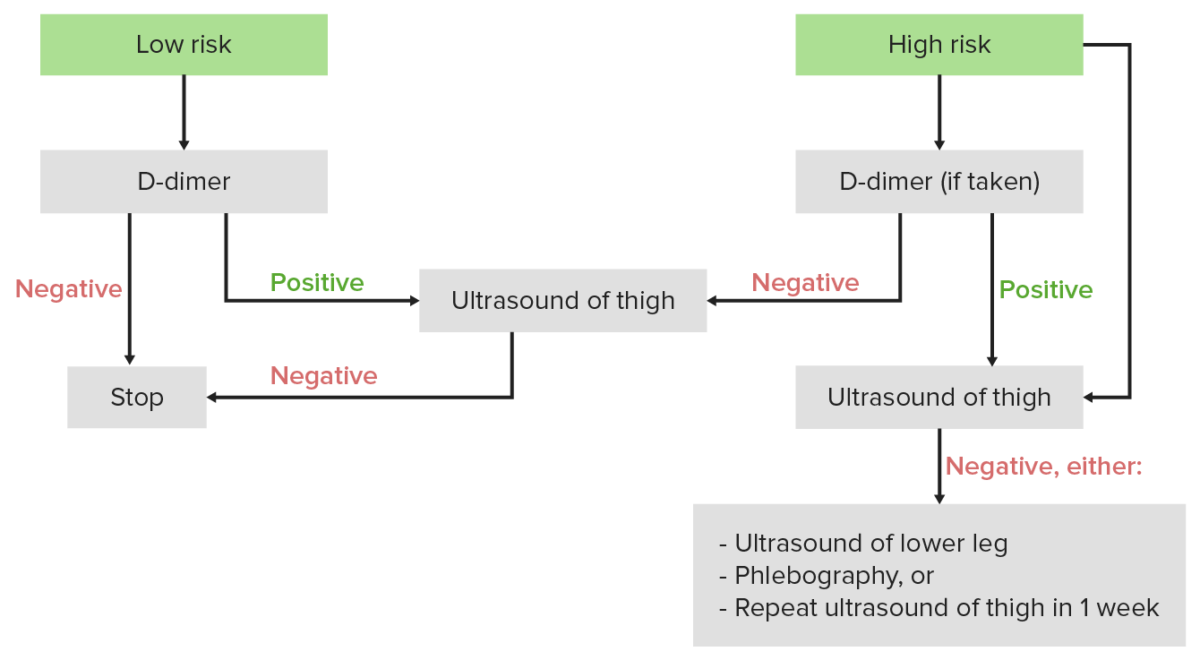
Algoritmo diagnóstico de la TVP: Si la puntuación de Wells es < 2, se considera al individuo como de bajo riesgo, y la 1era prueba debe ser el dímero D. Si la puntuación de Wells es ≥ 2, se considera al individuo como de alto riesgo, y la 1era prueba debe ser un ultrasonido.
Imagen por Lecturio.La anticoagulación es el pilar del tratamiento de las TVP. Dependiendo de la situación, algunos individuos pueden requerir trombólisis, un procedimiento invasivo y/o anticoagulación de por vida.
Tratamiento inicial
Prevención secundaria de la TVP
Otras medidas preventivas
Las siguientes condiciones pueden presentarse similarmente a la TVP: