El síndrome de Sjögren es una afección inflamatoria autoinmune en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la que los LOS Neisseria linfocitos infiltran los LOS Neisseria tejidos glandulares, como las glándulas salivales y lagrimales, lo que da como resultado una disminución de la producción de lágrimas y saliva Saliva The clear, viscous fluid secreted by the salivary glands and mucous glands of the mouth. It contains mucins, water, organic salts, and ptyalin. Salivary Glands: Anatomy. La enfermedad afecta principalmente a mujeres de mediana edad y está asociada a otras enfermedades autoinmunes. Los LOS Neisseria pacientes pueden experimentar síntomas y complicaciones relacionadas con ojos y boca secos. Existe una amplia gama de manifestaciones extraglandulares, incluyendo el fenómeno de Raynaud, la neuropatía y la vasculitis Vasculitis Inflammation of any one of the blood vessels, including the arteries; veins; and rest of the vasculature system in the body. Systemic Lupus Erythematosus cutánea. Los LOS Neisseria pacientes también tienen un mayor riesgo de desarrollar linfoma no Hodgkin. El diagnóstico se basa en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la presencia de síntomas y se válida mediante el examen clínico, estudios serológicos y biopsia de glándulas salivales. Se necesita un enfoque multidisciplinario para el tratamiento de estos pacientes. Dicho tratamiento se enfoca en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el alivio sintomático, reservando la terapia inmunosupresora para los LOS Neisseria síntomas graves.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
El síndrome de Sjögren, también conocido como síndrome sicca, es una condición autoinmune e inflamatoria crónica que conduce a una disminución de la función de las glándulas lagrimales y salivales, lo que provoca sequedad en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria ojos (xeroftalmía) y en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la boca (xerostomía).
Síndrome de Sjögren primario:
Síndrome de Sjögren secundario:
Se presenta en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum asociación con otra enfermedad autoinmune:
El mecanismo general en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el síndrome de Sjögren no está claro:
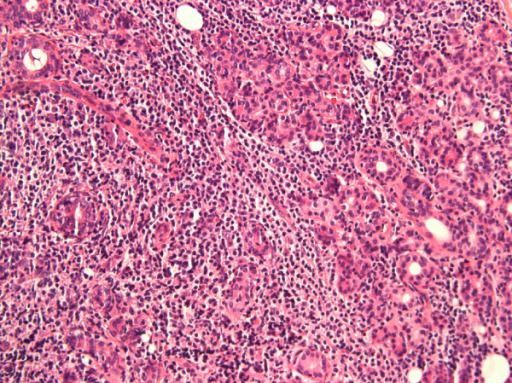
Infiltración linfocítica de la glándula parótida en un paciente con síndrome de Sjögren
Imagen: “Anti-salivary gland protein 1 antibodies in two patients with Sjogren’s syndrome: Two case reports” por Vishwanath S, Shen L, Suresh L, Ambrus JL. Licencia: CC BY 2.0.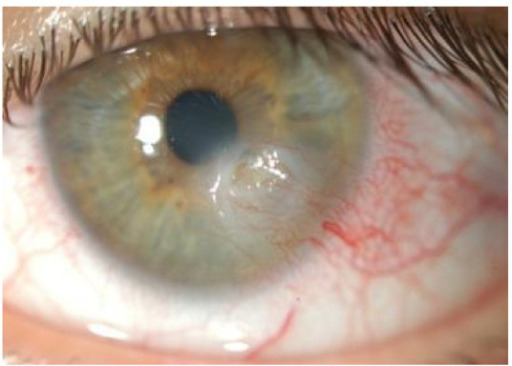
Queratoconjuntivitis sicca con ulceración corneal en paciente con síndrome de Sjögren
Imagen:“Novel aspects of Sjögren’s syndrome in 2012” por Tincani A, Andreoli L, Cavazzana I, Doria A, Favero M, Fenini MG, Franceschini F, Lojacono A, Nascimbeni G, Santoro A, Semeraro F, Toniati P, Shoenfeld Y Licencia: CC BY 2.0.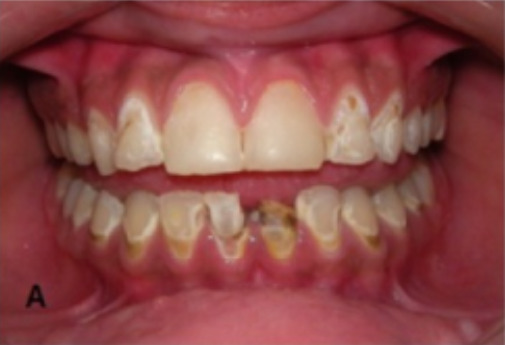
Caries dentales en un paciente con síndrome de Sjögren secundario
Imagen: “Oral Rehabilitation and Management for Secondary Sjögren’s Syndrome in a Child” por Case Reports in Dentistry. Licencia: CC BY 4.0, editada por Lecturio.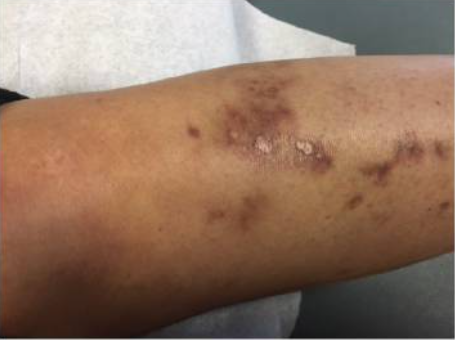
Cambios vasculíticos en la piel y ulceración observados en un paciente con síndrome de Sjögren
Imagen: “Skin Findings in a Patient with Sjogren’s Syndrome” por Case Reports in Rheumatology. Licencia: CC BY 4.0, editada por Lecturio.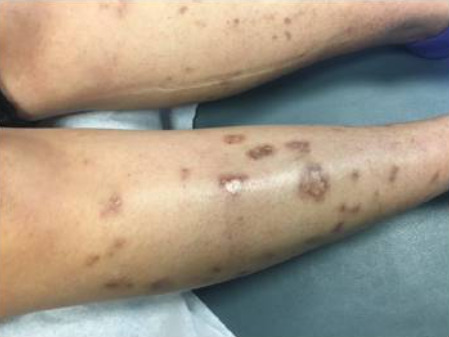
Cambios vasculíticos en la piel y ulceración observados en un paciente con síndrome de Sjögren
Imagen: “Skin Findings in a Patient with Sjogren’s Syndrome” por Case Reports in Rheumatology. Licencia: CC BY 4.0, editada por Lecturio.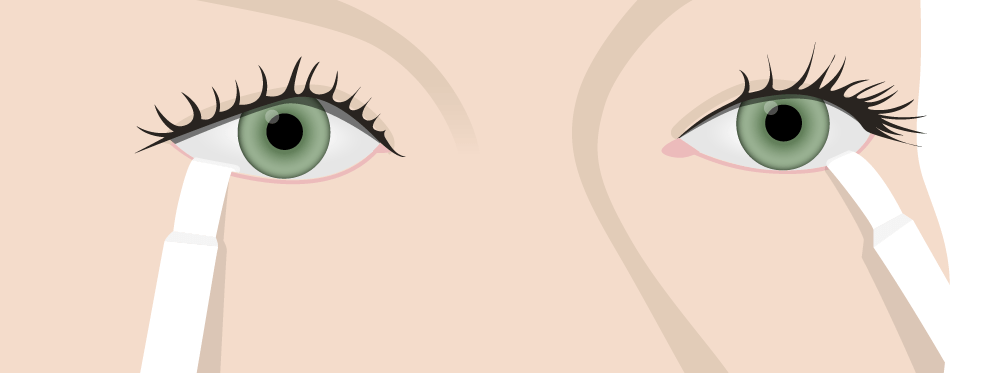
Prueba de Schirmer para la producción de lágrimas:
Para evaluar el síndrome de Sjögren, se colocan tiras reactivas en el párpado inferior y se mide el grado de humedad después de 5 minutos.
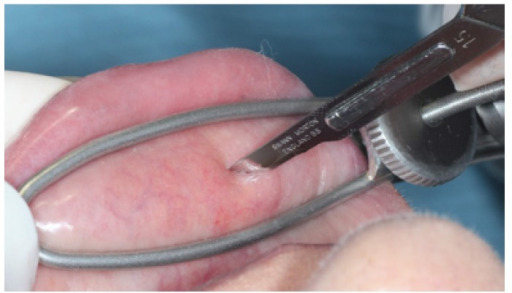
Biopsia de una glándula salival menor en el labio de un paciente
Tal biopsia se puede hacer como parte de la evaluación de síndrome de Sjögren.
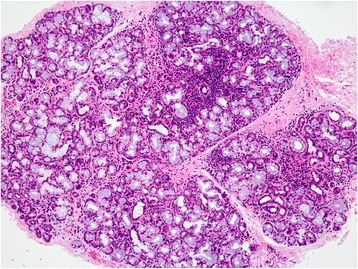
Hallazgos histológicos de una glándula salival menor en un paciente con síndrome de Sjögren
Se observa agregación linfocítica focal en toda la glándula con atrofia glandular leve.
Se han propuesto varios criterios para ayudar en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el diagnóstico de síndrome de Sjögren. Lo siguiente es del American-European Consensus Group (requiere 4 de 6 criterios, incluyendo una biopsia o autoanticuerpos positivos):
El diagnóstico diferencial del síndrome de Sjögren incluye otras patologías basadas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria síntomas de presentación, así como otros trastornos autoinmunes: