La pancreatitis Pancreatitis Inflammation of the pancreas. Pancreatitis is classified as acute unless there are computed tomographic or endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatographic findings of chronic pancreatitis. The two most common forms of acute pancreatitis are alcoholic pancreatitis and gallstone pancreatitis. Acute Pancreatitis aguda es una enfermedad inflamatoria del páncreas debida a la autodigestión. Las etiologías más comunes son los LOS Neisseria cálculos biliares y el consumo excesivo de alcohol. Los LOS Neisseria pacientes suelen presentar un dolor Dolor Inflammation epigástrico que se irradia a la espalda. El diagnóstico requiere 2 de 3 criterios, incluyendo: el dolor Dolor Inflammation abdominal característico, amilasa y lipasa séricas 3 veces el límite superior de la normalidad, o hallazgos radiológicos característicos. Los LOS Neisseria criterios de Ranson se utilizan habitualmente para evaluar la gravedad. El tratamiento incluye hidratación intravenosa agresiva, analgesia Analgesia Methods of pain relief that may be used with or in place of analgesics. Anesthesiology: History and Basic Concepts, apoyo nutricional y tratamiento de la causa subyacente.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
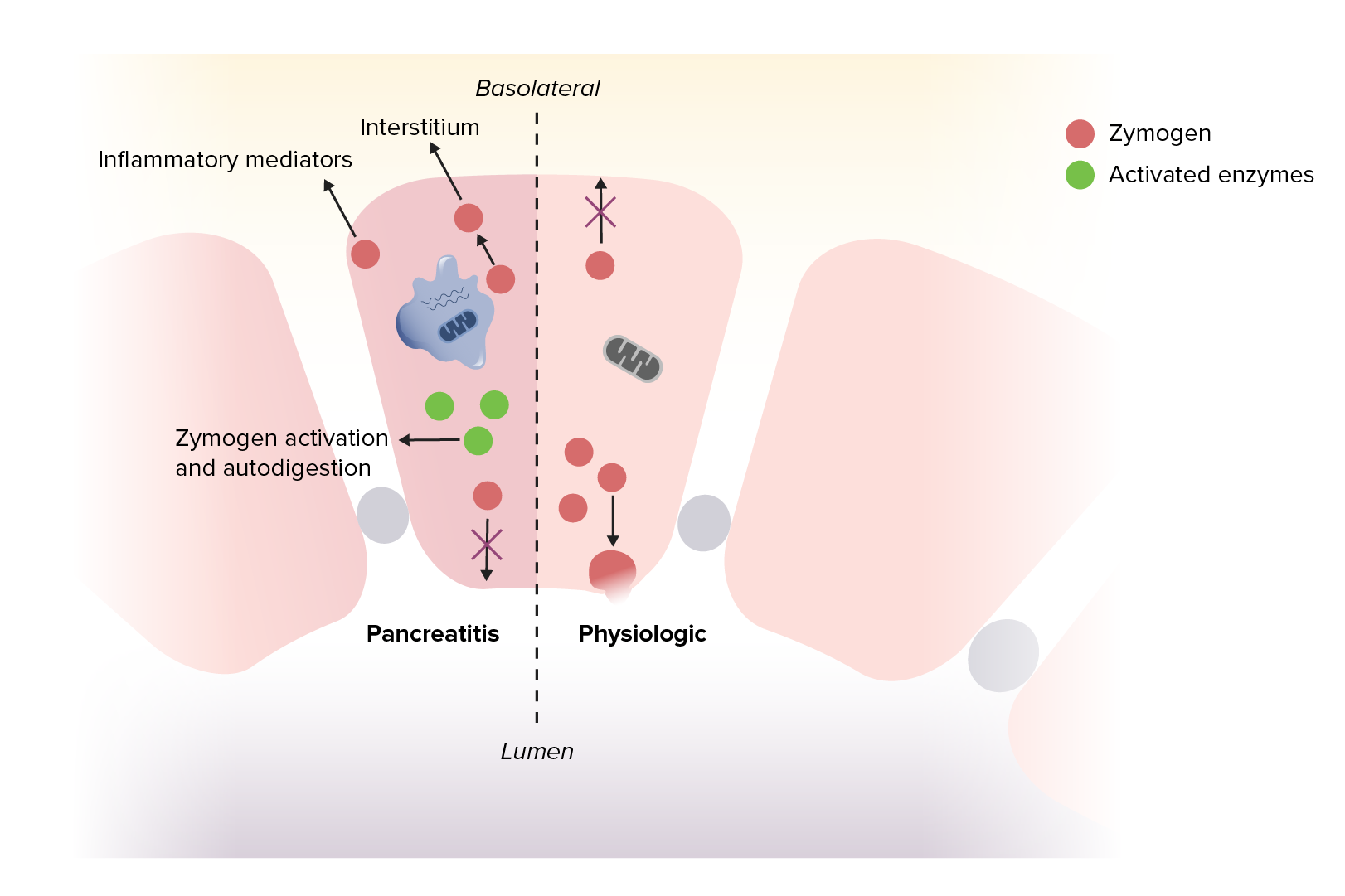
Pancreatitis aguda
Imagen por Lecturio.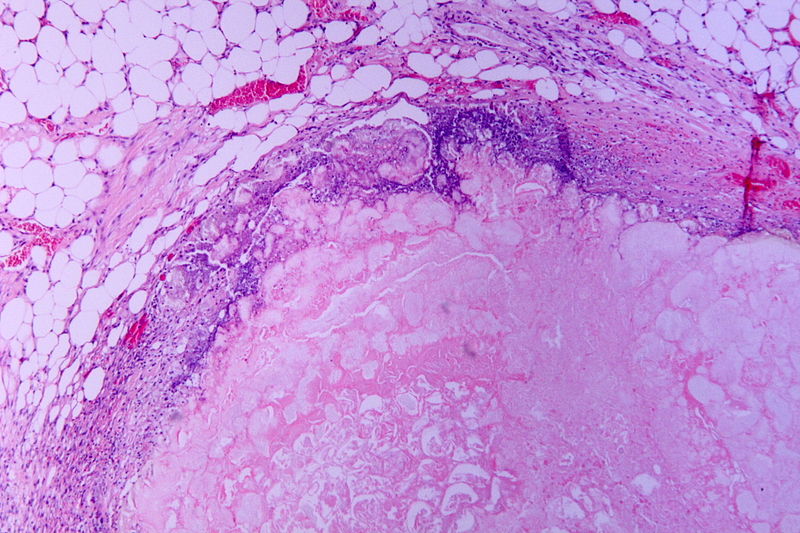
Tinción de hematoxilina y eosina (H&E) de una pancreatitis necrótica (área eosinofílica sin arquitectura: necrosis), rodeada de células inflamatorias basófilas y células grasas normales
Imagen: “Tryptic fat tissue necrosis in severe pancreatitis” por Patho. Licencia: CC BY-SA 3.0.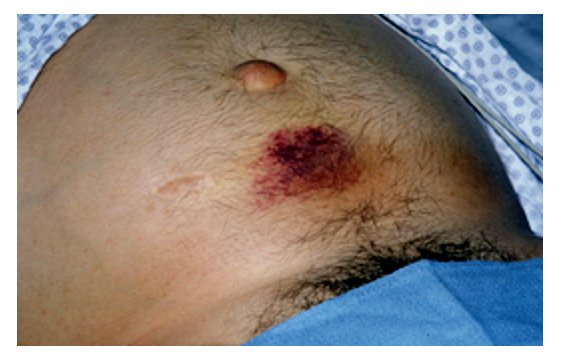
El signo de Cullen, que señala sangre en el peritoneo
Imagen: “Cullen’s sign” por Herbert L. Fred, MD. Licencia: CC BY 2.0.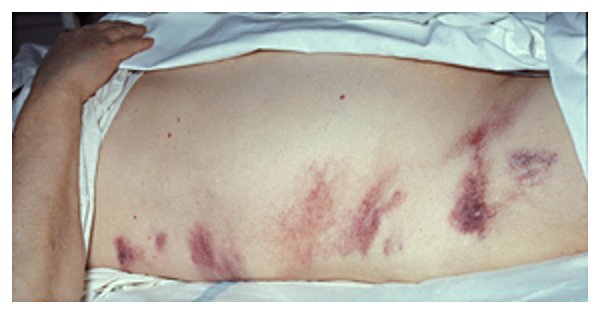
Signo de Grey-Turner por pancreatitis hemorrágica
Imagen: por Herbert L. Fred, MD y Hendrik A. van Dijk. Licencia: CC BY 2.0.El diagnóstico de pancreatitis Pancreatitis Inflammation of the pancreas. Pancreatitis is classified as acute unless there are computed tomographic or endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatographic findings of chronic pancreatitis. The two most common forms of acute pancreatitis are alcoholic pancreatitis and gallstone pancreatitis. Acute Pancreatitis aguda requiere al AL Amyloidosis menos 2 de los LOS Neisseria siguientes elementos:
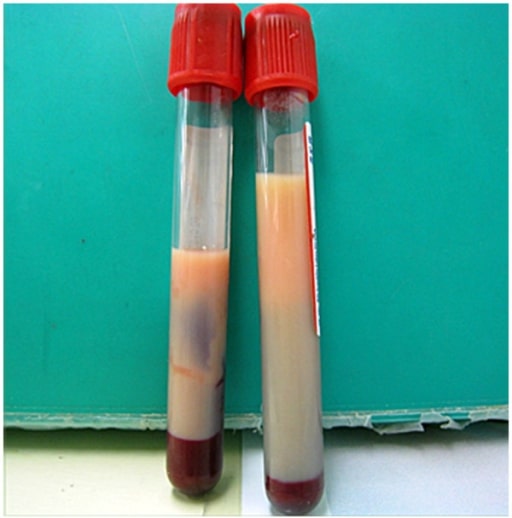
Plasma lechoso observado en un paciente con hipertrigliceridemia: Si se observa, el plasma lechoso debe considerarse como una causa potencial de pancreatitis aguda.
Imagen: “Milky plasma” por Department of Emergency and Critical Care Medicine, Ohta Nishinouchi Hospital, 2-5-20 Nishinouchi, Koriyama, Fukushima, 963-8558, Japan. Licencia: CC BY 2.0.El diagnóstico imagenológico puede no ser necesario si se cumplen los LOS Neisseria 2 primeros criterios diagnósticos, pero puede utilizarse para evaluar la causa subyacente y las complicaciones:
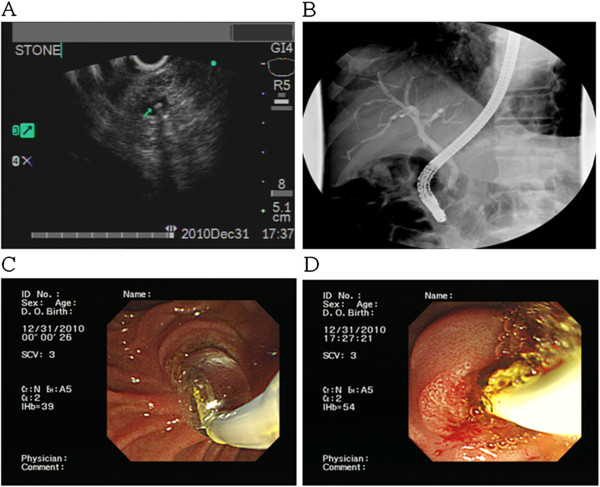
Un pequeño cálculo del conducto biliar común se evidencia usando ultrasonido. Estos cálculos deben considerarse una etiología potencial en un paciente que presenta una pancreatitis aguda.
Imagen: “F2” por Division of Gastroenterology, Department of Internal Medicine, Kaohsiung Veterans General Hospital, 386 Ta-Chung 1st Road, Kaohsiung 81362, Taiwan. Licencia: CC BY 2.0, editado por Lecturio.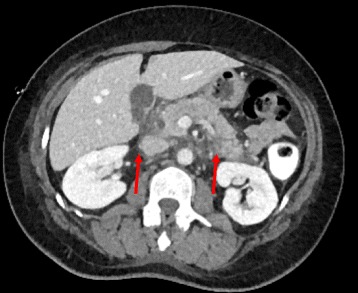
Pancreatitis aguda vista en la TC, mostrando edema alrededor del páncreas
Imagen: “Arterial phase contrast CT showing an acute pancreatitis” por Benoît Bédat et al. Licencia: CC BY 4.0.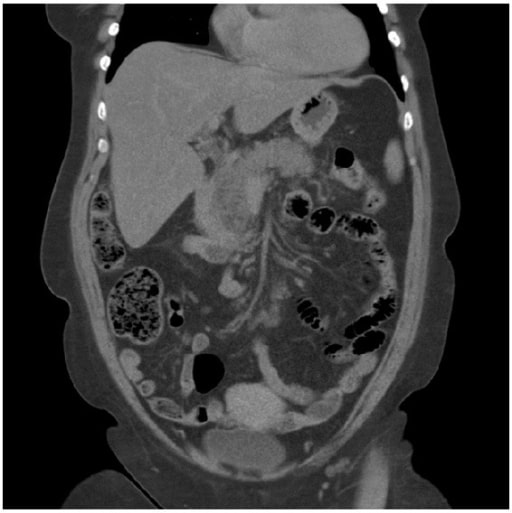
Pancreatitis aguda: Una TC que muestra los cambios de la pancreatitis, que aparece agrandada y edematosa.
Imagen: “A computed tomography scan” por Department of Surgery, Helsingborg Hospital, 25187 Helsingborg, Sweden. Licencia: CC BY 3.0Identificar la gravedad de la pancreatitis Pancreatitis Inflammation of the pancreas. Pancreatitis is classified as acute unless there are computed tomographic or endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatographic findings of chronic pancreatitis. The two most common forms of acute pancreatitis are alcoholic pancreatitis and gallstone pancreatitis. Acute Pancreatitis aguda es útil para garantizar que el paciente reciba el tratamiento adecuado:
| Al AL Amyloidosis momento del ingreso | A las 48 horas del ingreso |
|---|---|
| Edad > 55 años | Disminución del hematocrito > 10% |
| Leucocitos > 16 000/μL | Aumento del BUN por > 5 mg/dL |
| Glicemia > 200 mg/dL | Calcio sérico < 8 mg/dL |
| LDH LDH Osteosarcoma sérico > 350 IU/L | PaO2 < 60 mm Hg |
| Aspartato aminotransferasa ( AST AST Enzymes of the transferase class that catalyze the conversion of l-aspartate and 2-ketoglutarate to oxaloacetate and l-glutamate. Liver Function Tests) > 250 IU/L | Déficit de base > 4 mEq/L |
| Secuestro de fluidos estimado > 6 L |
| BUN | > 25 mg/dL |
|---|---|
| Alteración del estado mental | GCS GCS A scale that assesses the response to stimuli in patients with craniocerebral injuries. The parameters are eye opening, motor response, and verbal response. Coma < 15 |
| Síndrome de respuesta inflamatoria sistémica (SIRS, por sus siglas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum inglés) | Evidencia de SIRS |
| Edad | > 60 años |
| Derrame pleural | Hallazgos positivos en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria estudios imagenológicos |
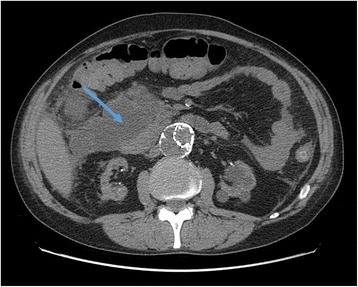
TC abdominal que muestra la zona inicial de necrosis en parches alrededor de la cabeza del páncreas
Imagen: “Abdominal CT scan” por Francesco Fontana. Licencia: CC BY 4.0.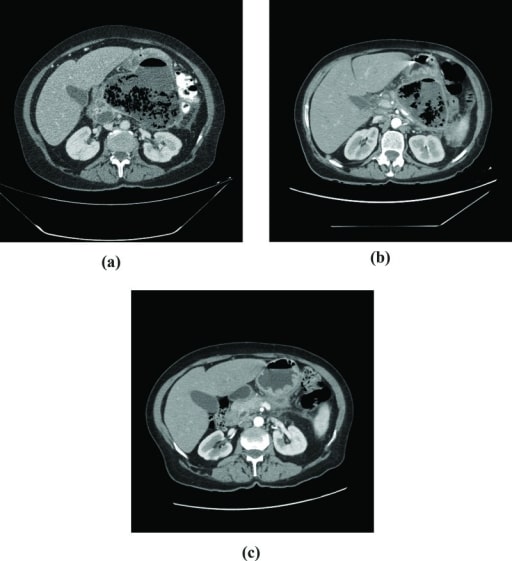
TC en un paciente que desarrolló una necrosis pancreática infectada.
A: Se observa una extensa necrosis pancreática con gran cantidad de gas en el cuerpo y la cola del páncreas.
B: Tras 60 días de seguimiento, se observa una pequeña disminución en la colección de gas.
C: Cuatro meses después del alta hospitalaria: atrofia del parénquima pancreático.
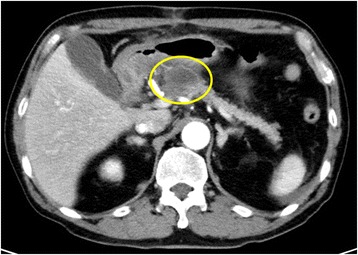
La pancreatitis aguda se produjo repetidamente un mes después de la 1era operación, y se desarrolló un pseudoquiste pancreático en el mismo lugar. La TC con contraste mostró un quiste de 29 mm de diámetro en el cuerpo del páncreas.
Imagen: “Pancreatic pseudocyst” por Department of Gastroenterological Surgery, Kumamoto University Graduate School of Medical Sciences, 1-1-1 Honjo, Kumamoto, 860-8556 Japan. Licencia: CC BY 4.0.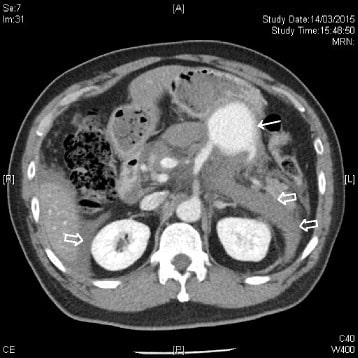
TC de abdomen con contraste intravenoso que muestra una masa con realce (flecha sólida) en la arteria esplénica (ramificación de la arteria mesentérica superior) compatible con un pseudoaneurisma de la arteria esplénica. Se evidencian el hemoretroperitoneo y el hemoperitoneo (flechas huecas).
Imagen: “CT scan of the abdomen” por Accident and Emergency Department, Ruttonjee Hospital, Wanchai, Hong Kong. Licencia: CC BY 4.0.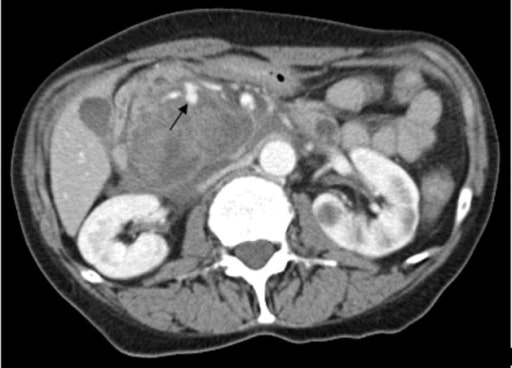
La TC de abdomen con contraste revela una masa quística compleja de 5 × 6 × 7 cm en la región del proceso unciforme de la cabeza del páncreas con una cápsula realzada y una pequeña hiperdensidad consistente con un pseudoaneurisma de un vaso peripancreático con hemorragia activa hacia el pseudoquiste pancreático.
Imagen: “Contrast-enhanced CT scan” por Rohan Mandaliya. Licencia: CC BY 2.0.