Las oxazolidinonas ( linezolid Linezolid An oxazolidinone and acetamide derived anti-bacterial agent and protein synthesis inhibitor that is used in the treatment of gram-positive bacterial infections of the skin and respiratory tract. Oxazolidinones y tedizolid Tedizolid Oxazolidinones) son inhibidores de la síntesis proteica bacteriana. El sitio de unión único en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el ARN ribosomal 23S del ribosoma 50S impide que las bacterias desarrollen una resistencia cruzada cuando se exponen a otros antibióticos. Estos medicamentos se absorben fácilmente y se distribuyen ampliamente en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el organismo y están indicados para las infecciones por Gram-positivos, incluidos el Staphylococcus aureus Staphylococcus aureus Potentially pathogenic bacteria found in nasal membranes, skin, hair follicles, and perineum of warm-blooded animals. They may cause a wide range of infections and intoxications. Brain Abscess resistente a la meticilina ( MRSA MRSA A strain of Staphylococcus aureus that is non-susceptible to the action of methicillin. The mechanism of resistance usually involves modification of normal or the presence of acquired penicillin binding proteins. Staphylococcus, por sus siglas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum inglés) y el enterococo resistente a la vancomicina. Los LOS Neisseria efectos secundarios incluyen malestar gastrointestinal, mielosupresión, neuropatía periférica u óptica y acidosis Acidosis A pathologic condition of acid accumulation or depletion of base in the body. The two main types are respiratory acidosis and metabolic acidosis, due to metabolic acid build up. Respiratory Acidosis láctica. El linezolid Linezolid An oxazolidinone and acetamide derived anti-bacterial agent and protein synthesis inhibitor that is used in the treatment of gram-positive bacterial infections of the skin and respiratory tract. Oxazolidinones es un inhibidor débil de la monoamino oxidasa, por lo tanto, puede aumentar el riesgo de síndrome serotoninérgico cuando se coadministra con otros medicamentos serotoninérgicos.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
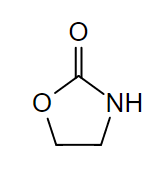
Estructura química de 2 oxazolidinonas:
Tanto el linezolid como el tedizolid contienen este anillo en su estructura química.
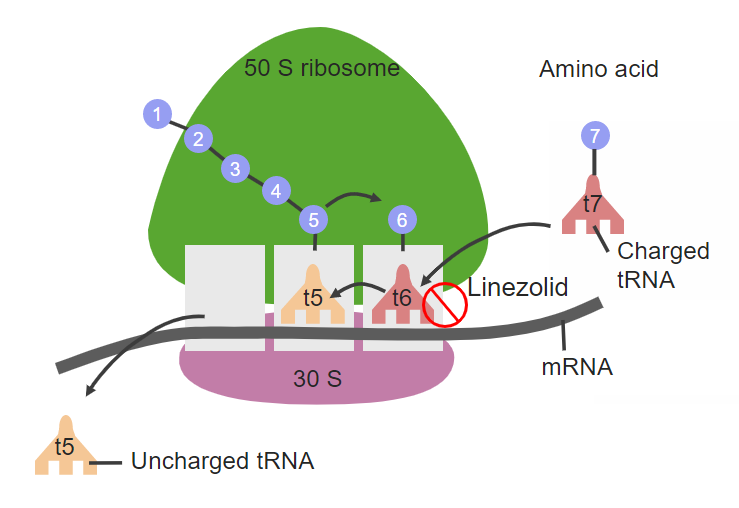
Sitio de acción de linezolid en la subunidad ribosomal 50S:
Esta construcción inhibe el inicio de la síntesis proteica e impide la replicación bacteriana.
Estos medicamentos están aprobados por la administración de medicamentos y alimentos (FDA, por sus siglas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum inglés) para:
El linezolid Linezolid An oxazolidinone and acetamide derived anti-bacterial agent and protein synthesis inhibitor that is used in the treatment of gram-positive bacterial infections of the skin and respiratory tract. Oxazolidinones puede causar una crisis hipertensiva en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum las siguientes condiciones:
| Clase de medicamento | Mecanismo de acción | Cobertura | Efectos secundarios |
|---|---|---|---|
| Anfenicoles |
|
|
|
| Lincosamidas |
|
|
|
| Macrólidos |
|
|
|
| Oxazolidinonas |
|
Cocos Gram-positivos:
|
|
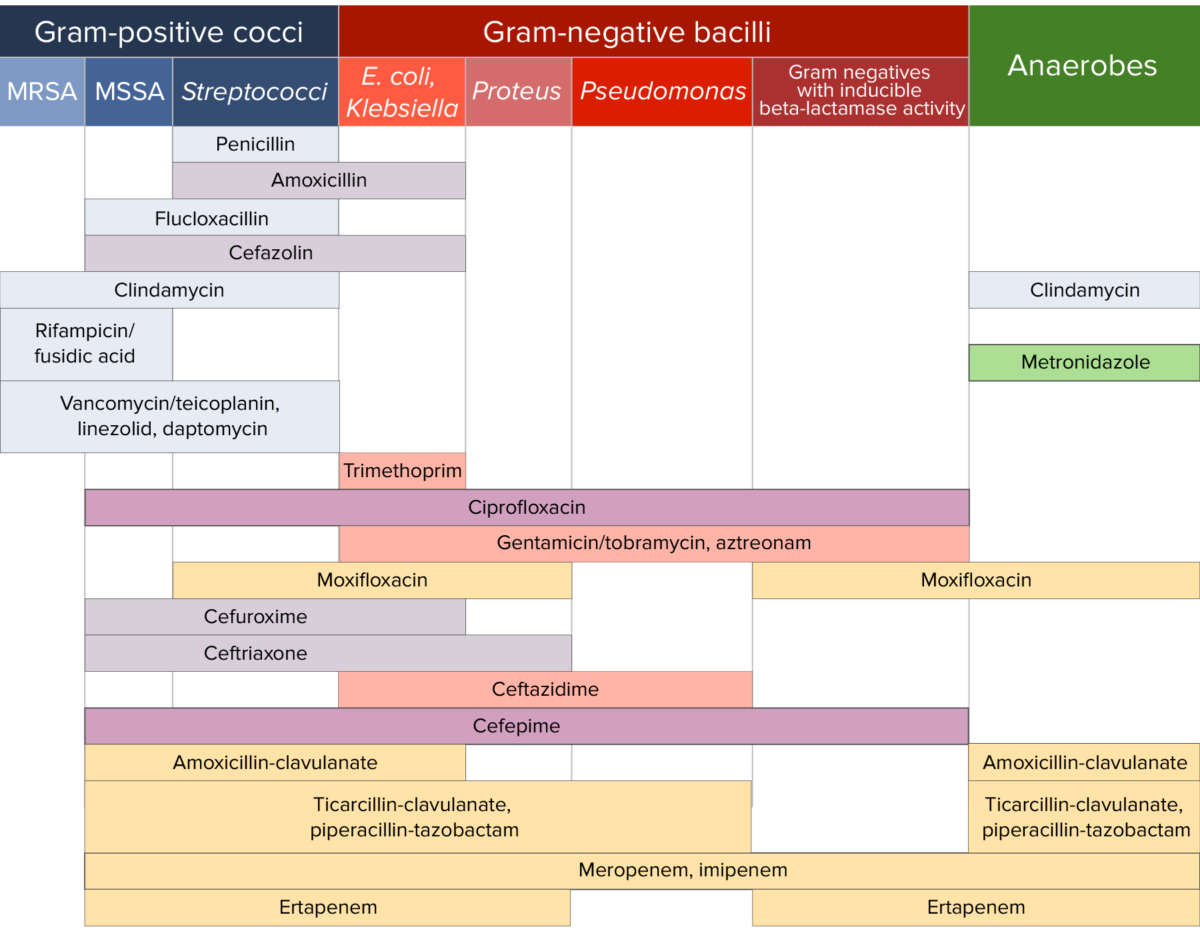
Sensibilidad a los antibióticos:
Gráfico que compara la cobertura microbiana de diferentes antibióticos para cocos Gram-positivos, bacilos Gram-negativos y anaerobios.