La osteomielitis es una infección de hueso que resulta de la propagación de microorganismos desde la sangre (hematógena), el tejido infectado cercano o heridas abiertas (no hematógena). Las infecciones suelen ser causadas por Staphylococcus aureus, pero se han relacionado diversos organismos con la osteomielitis. La mayoría de los pacientes presentan dolor, enrojecimiento y edema del lugar afectado, y pueden tener síntomas asociados como fiebre y escalofríos. Los valores de laboratorio demostrarán un aumento de leucocitos, PCR y velocidad de eritrosedimentación (VES) en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la mayoría de los LOS Neisseria casos. La modalidad de imagenología más sensible y específica para diagnosticar la osteomielitis es la RM. El tratamiento puede requerir antibióticos a largo plazo y un posible desbridamiento quirúrgico.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
La osteomielitis se clasifica en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum función de la vía de infección.
Osteomielitis no hematógena (80% de los LOS Neisseria casos):
Osteomielitis hematógena (20% de los LOS Neisseria casos):
| Factores de riesgo | Agentes infecciosos |
|---|---|
| Ningún factor de riesgo específico | S. aureus S. aureus Potentially pathogenic bacteria found in nasal membranes, skin, hair follicles, and perineum of warm-blooded animals. They may cause a wide range of infections and intoxications. Staphylococcus |
| Prótesis articulares de reemplazo |
|
| Enfermedades de células falciformes |
|
| Enfermedad granulomatosa crónica |
|
| Osteomielitis vertebral |
|
| Actividad sexual, sin otros factores de riesgo | N. gonorrhoeae N. gonorrhoeae A species of gram-negative, aerobic bacteria primarily found in purulent venereal discharges. It is the causative agent of gonorrhea. Neisseria (más probable que cause artritis séptica que osteomielitis) |
| Mordedura de gato o de perro | Pasteurella multocida Pasteurella Multocida A species of gram-negative, facultatively anaerobic, rod-shaped bacteria normally found in the flora of the mouth and respiratory tract of animals and birds. It causes shipping fever; hemorrhagic bacteremia; and intestinal disease in animals. In humans, disease usually arises from a wound infection following a bite or scratch from domesticated animals. Dog and Cat Bites |
| Uso de drogas por vía intravenosa o inmunocompromiso |
|
La osteomielitis es una infección de hueso que resulta de la propagación hematógena o no hematógena de organismos infecciosos.
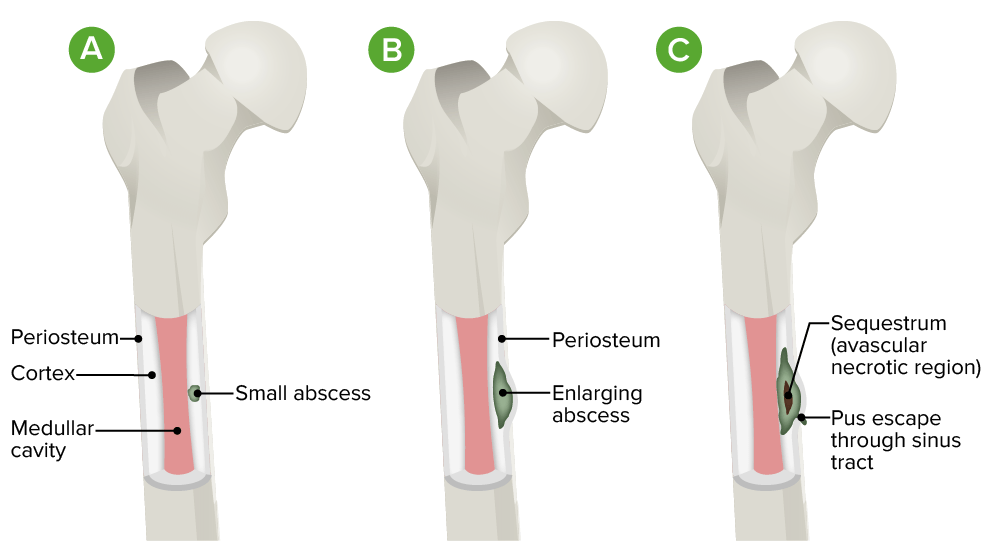
Fisiopatología de la osteomielitis:
A. La infección inicial se localiza en la región cortical.
B. Hay progresión hacia el espacio subperióstico con levantamiento del periostio.
C. Se produce una infección difusa con secuestro (región necrótica avascular) y formación de tracto sinusal.
Osteomielitis vertebral:
Osteomielitis esternoclavicular y pélvica:
Osteomielitis de los LOS Neisseria huesos largos:
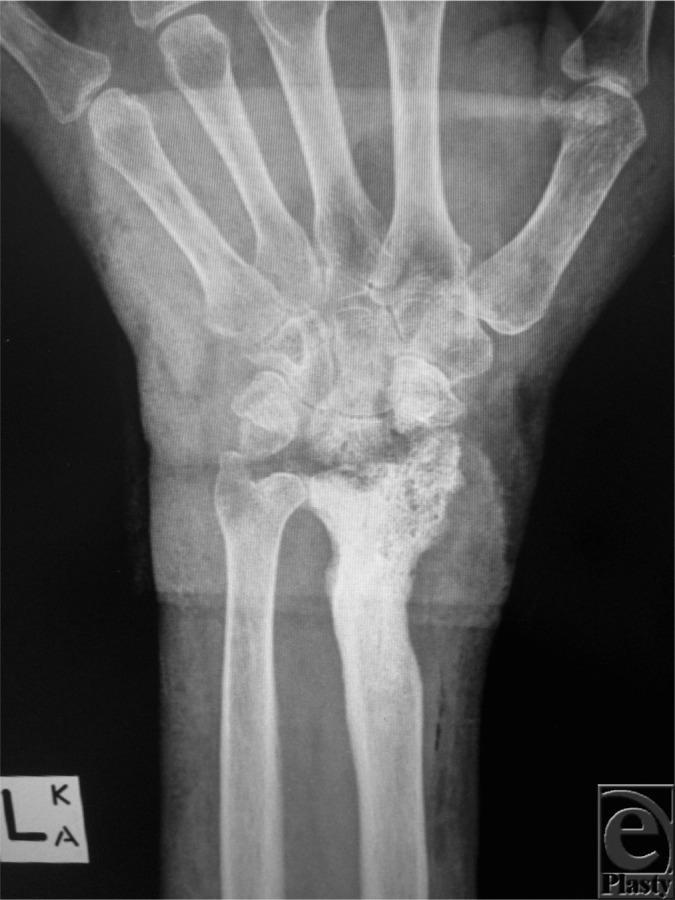
Radiografía de una mano que muestra una osteomielitis crónica:
Obsérvese la destrucción ósea en la articulación radiocarpiana.
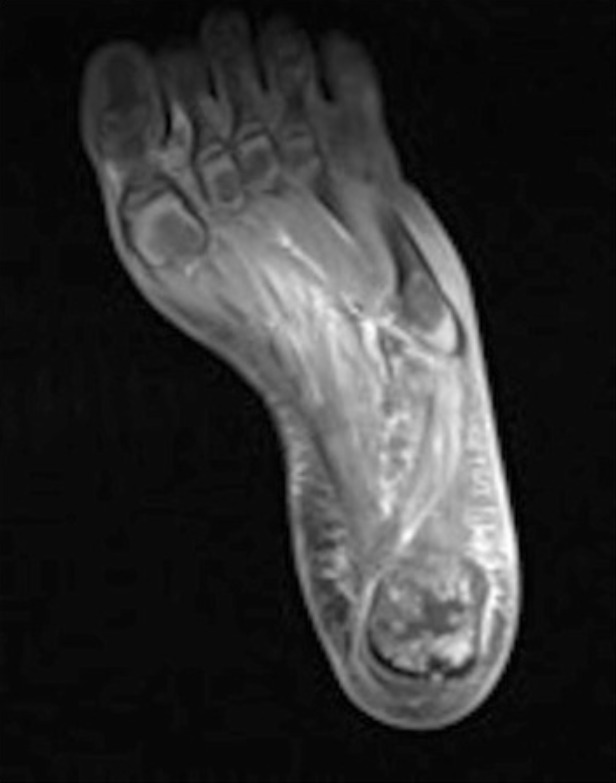
Una RM del pie izquierdo con cambios óseos del calcáneo compatibles con una osteomielitis
Imagen: “Delayed recognition of pediatric calcaneal osteomyelitis: a case report” por Mallia AJ, Ashwood N, Arealis G, Bindi F, Zamfir G, Galanopoulos I. Licencia: CC BY 4.0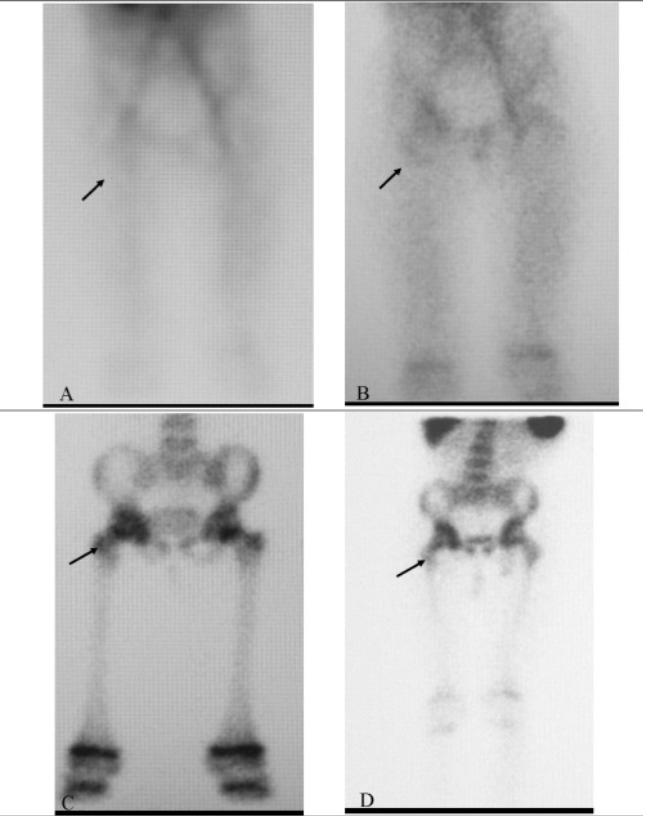
Una gammagrafía ósea trifásica que muestra una captación positiva en la región de la cadera derecha (flecha) en un paciente con osteomielitis
Imagen: “Tc-99m Labeled HMPAO white Blood Cell Scintigraphy in Pediatric Patients” por Aydın F, Kın Cengiz A, Güngör F. Licencia: CC BY 2.5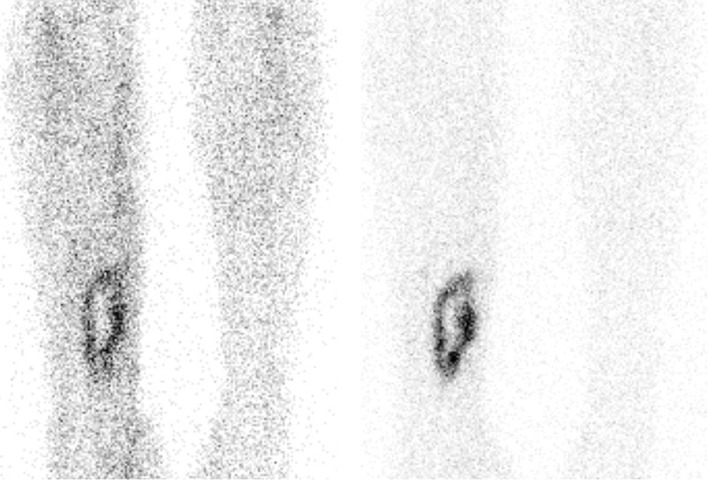
Ejemplo de una gammagrafía con leucocitos marcados positiva en un paciente con osteomielitis de la tibia derecha.
Se observa una mayor captación en la tibia derecha, en comparación con la captación de fondo.
Imagen izquierda: vista anterior 4 horas después de la inyección
Imagen derecha: vista anterior 24 horas después de la inyección.