El mieloma múltiple ( MM MM Multiple myeloma (MM) is a malignant condition of plasma cells (activated B lymphocytes) primarily seen in the elderly. Monoclonal proliferation of plasma cells results in cytokine-driven osteoclastic activity and excessive secretion of IgG antibodies. Multiple Myeloma) es una condición maligna de las células plasmáticas (linfocitos B activados) que se observa principalmente en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria ancianos. La proliferación monoclonal de células plasmáticas da como resultado una actividad osteoclástica impulsada por citoquinas y una secreción excesiva de anticuerpos IgG IgG The major immunoglobulin isotype class in normal human serum. There are several isotype subclasses of igg, for example, igg1, igg2a, and igg2b. Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis. La actividad osteoclástica da como resultado reabsorción ósea, dolor Dolor Inflammation óseo, fracturas patológicas y alteraciones metabólicas. La secreción excesiva de anticuerpos da como resultado proteinuria Proteinuria The presence of proteins in the urine, an indicator of kidney diseases. Nephrotic Syndrome in Children y daño renal asociado, así como producción y depósito tisular de fibrillas de amiloide. Las alteraciones metabólicas combinadas con el depósito de amiloide tisular provocan daños en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria órganos diana. El diagnóstico se establece mediante electroforesis en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum plasma Plasma The residual portion of blood that is left after removal of blood cells by centrifugation without prior blood coagulation. Transfusion Products y biopsia de médula ósea. Hay tratamientos disponibles para retrasar la progresión de la enfermedad; sin embargo, no existe una cura para el MM MM Multiple myeloma (MM) is a malignant condition of plasma cells (activated B lymphocytes) primarily seen in the elderly. Monoclonal proliferation of plasma cells results in cytokine-driven osteoclastic activity and excessive secretion of IgG antibodies. Multiple Myeloma. La mediana de supervivencia es de aproximadamente 3 años.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
El mieloma múltiple ( MM MM Multiple myeloma (MM) is a malignant condition of plasma cells (activated B lymphocytes) primarily seen in the elderly. Monoclonal proliferation of plasma cells results in cytokine-driven osteoclastic activity and excessive secretion of IgG antibodies. Multiple Myeloma) es una neoplasia maligna de la médula ósea que surge de las células plasmáticas monoclonales.
Características de MM MM Multiple myeloma (MM) is a malignant condition of plasma cells (activated B lymphocytes) primarily seen in the elderly. Monoclonal proliferation of plasma cells results in cytokine-driven osteoclastic activity and excessive secretion of IgG antibodies. Multiple Myeloma: “CRAB” ( en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum inglés)
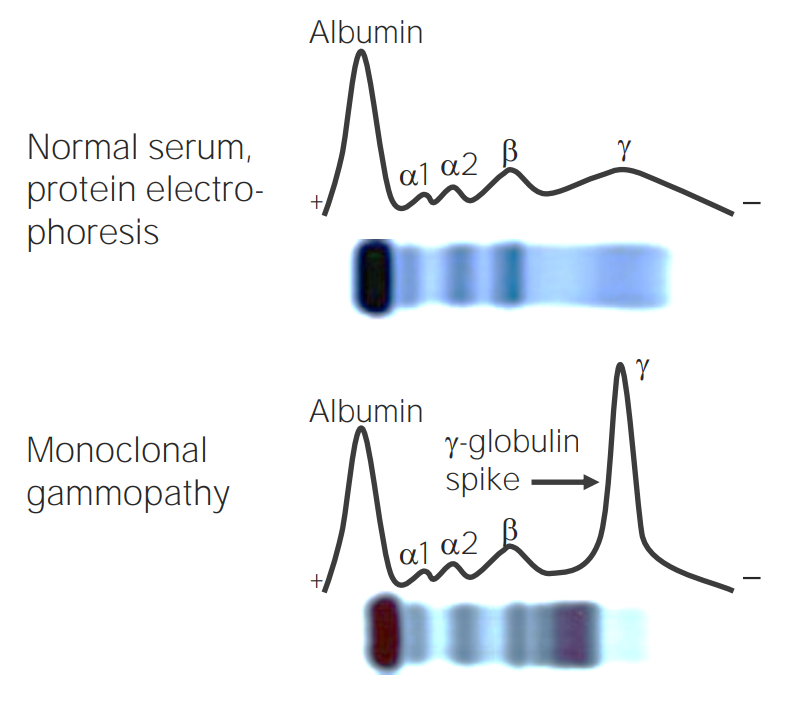
Electroforesis de proteínas en suero que muestra el pico M en pacientes con MM
Imagen por Lecturio.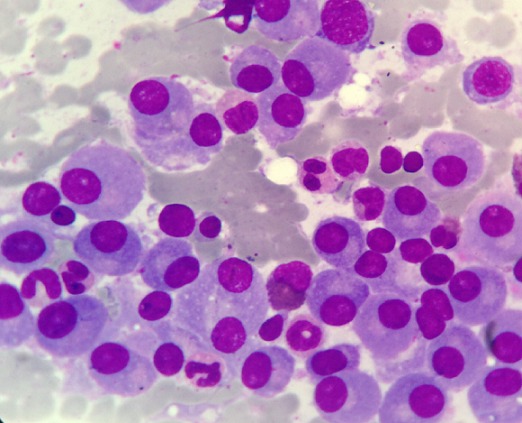
Mieloma múltiple:
Infiltración de médula ósea con células plasmáticas maduras: observe los núcleos excéntricos y las zonas pálidas perinucleares.
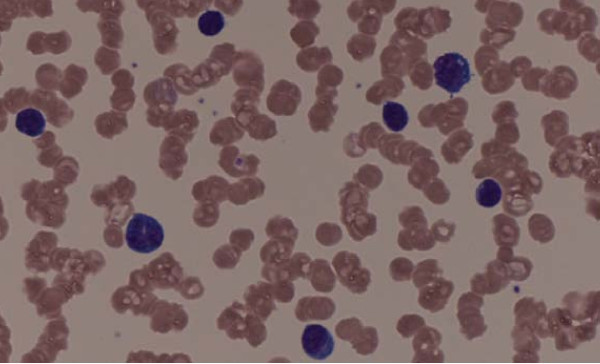
El frotis de sangre periférica muestra formación de rouleaux
Imagen: “Rouleaux formation” por Michail Charakidis, David Joseph Russell. Licencia: CC BY 2.0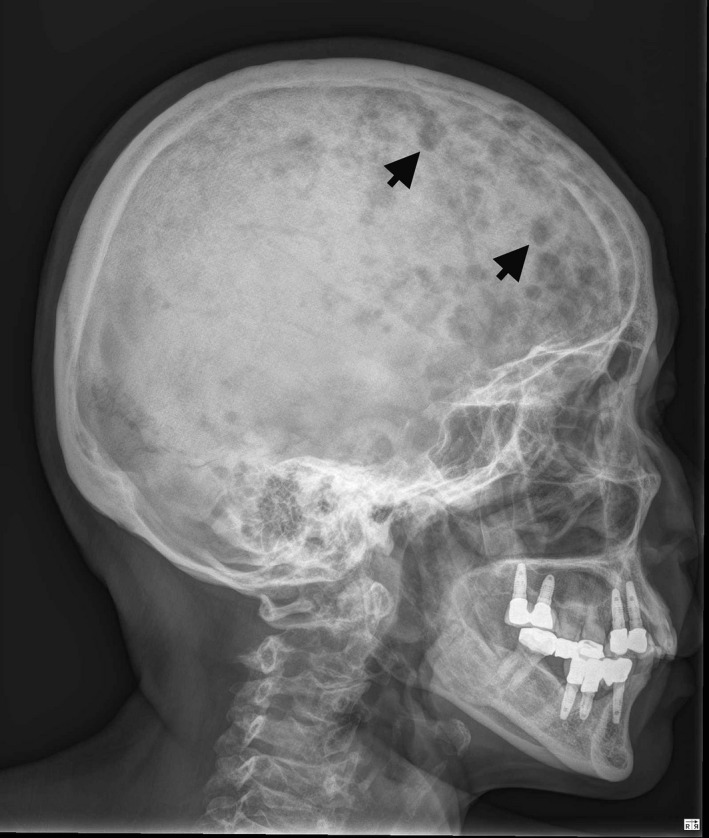
Múltiples lesiones líticas (flechas) en el cráneo
Imagen: “X‐ray of skull bone shows multiple punched‐out lesions (arrows)” por Ya‐Ting Hsu and Kung‐Chao Chang. Licencia: CC BY 4.0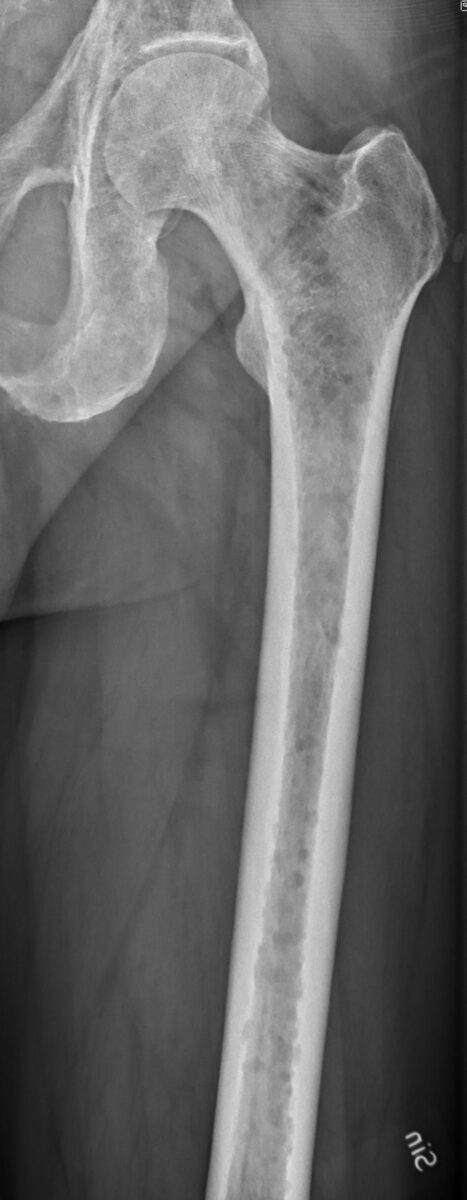
Mieloma múltiple:
La radiografía de fémur izquierdo muestra lesiones líticas con osteopenia.