La lactancia materna suele ser la principal fuente de nutrición del recién nacido. Durante el embarazo, la estimulación hormonal hace HACE Altitude Sickness que el número y el tamaño de las glándulas mamarias aumenten considerablemente. Después del parto, la prolactina estimula la producción de leche, mientras que la oxitocina estimula la expulsión de la leche a través de los LOS Neisseria conductos galactóforos, donde el lactante la succiona a través del pezón. La lactancia materna tiene muchos beneficios para la madre y el bebé, como la disminución del riesgo de infecciones, trastornos gastrointestinales y enfermedades atópicas para el niño, y la disminución del riesgo de anemia Anemia Anemia is a condition in which individuals have low Hb levels, which can arise from various causes. Anemia is accompanied by a reduced number of RBCs and may manifest with fatigue, shortness of breath, pallor, and weakness. Subtypes are classified by the size of RBCs, chronicity, and etiology. Anemia: Overview and Types, enfermedades cardiovasculares y cáncer de mama y ovarios para la madre. Existen contraindicaciones absolutas para la lactancia materna, pero son bastante raras. Entre las afecciones clínicas importantes asociadas a la lactancia materna se encuentran la congestión mamaria, la mastitis Mastitis Mastitis is inflammation of the breast tissue with or without infection. The most common form of mastitis is associated with lactation in the first few weeks after birth. Non-lactational mastitis includes periductal mastitis and idiopathic granulomatous mastitis (IGM). Mastitis, el galactocele Galactocele Benign Breast Conditions, el absceso mamario y la ictericia infantil.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
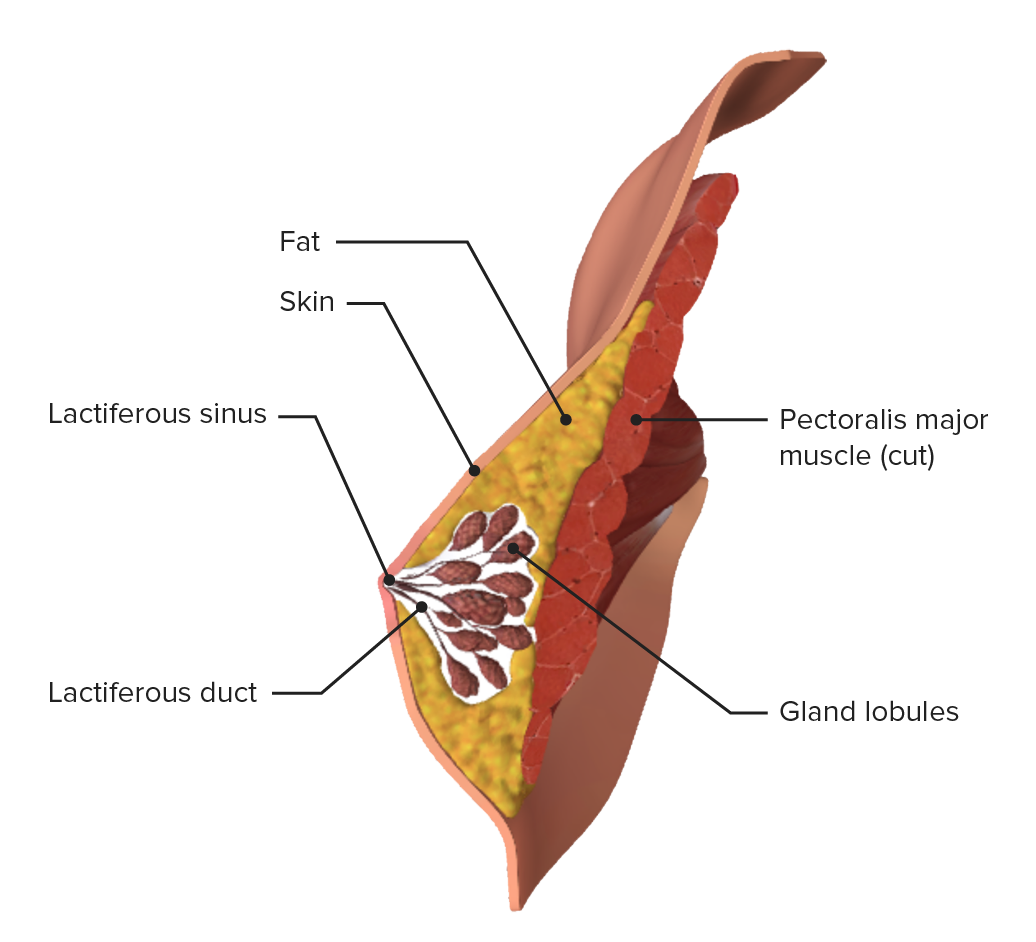
Diagrama de un corte sagital de la mama
Imagen de Lecturio.Durante el embarazo se produce un importante crecimiento y maduración de las mamas como consecuencia de la secreción hormonal de la placenta Placenta A highly vascularized mammalian fetal-maternal organ and major site of transport of oxygen, nutrients, and fetal waste products. It includes a fetal portion (chorionic villi) derived from trophoblasts and a maternal portion (decidua) derived from the uterine endometrium. The placenta produces an array of steroid, protein and peptide hormones (placental hormones). Placenta, Umbilical Cord, and Amniotic Cavity.
La eyección de leche requiere la hormona hipofisaria oxitocina.
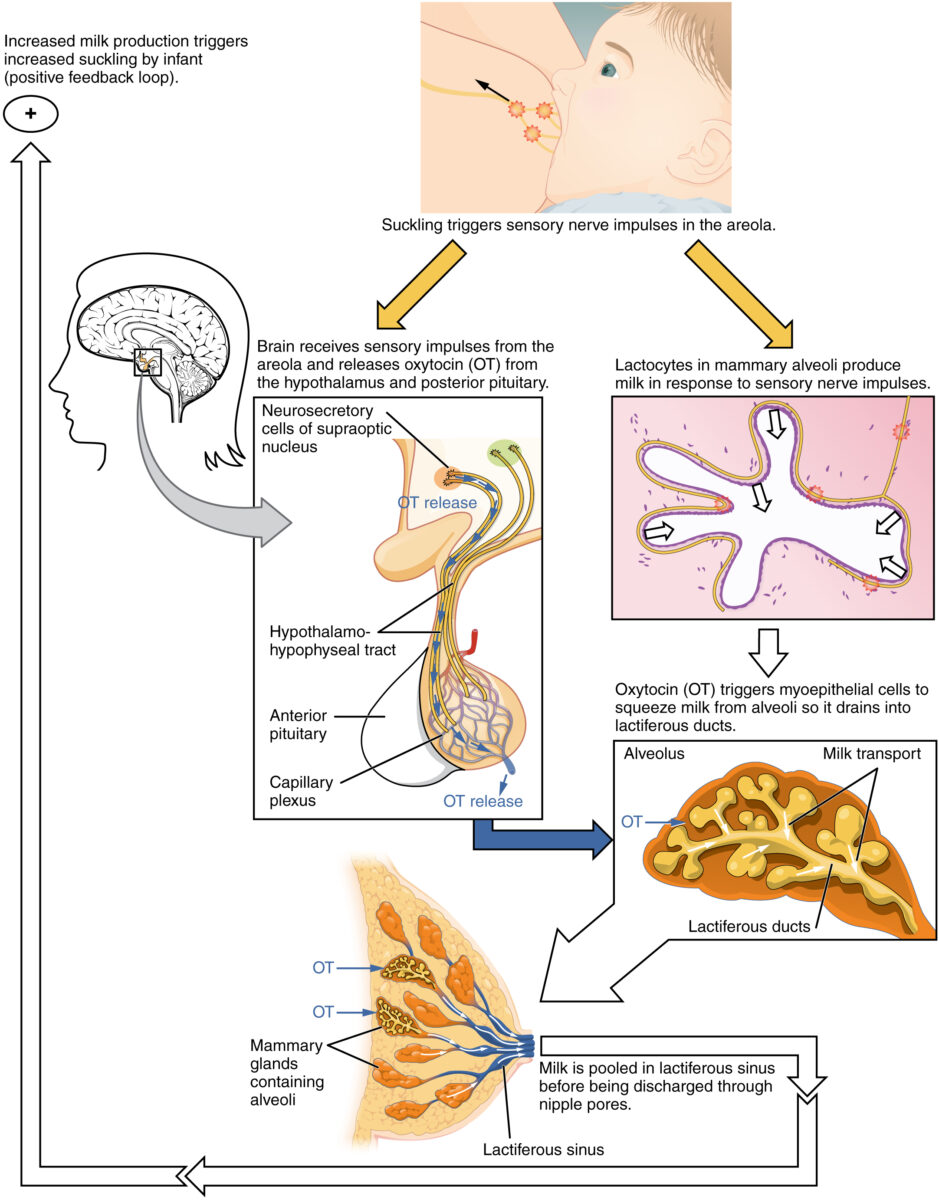
El reflejo de bajada
Imagen: “A positive feedback loop ensures continued milk production as long as the infant continues to breastfeed” por OpenStax College. Licencia: CC BY 4.0Hay 2 estadios de la lactogénesis:
Aunque generalmente “lo mejor es la lactancia”, hay casos en los que no se recomienda la lactancia materna, en cuyo caso, “lo mejor es la fórmula”. Estos casos incluyen:
Las contraindicaciones absolutas para la lactancia son raras, pero incluyen:
La lactancia materna es recomendada por la World Health Organization (WHO, por sus siglas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum inglés), la Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC, por sus siglas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum inglés) de EE. UU. y el Fondo Internacional de Emergencia de las Naciones Unidas para la Infancia (UNICEF, por sus siglas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum inglés). En EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum concreto, estas organizaciones recomiendan lo siguiente:
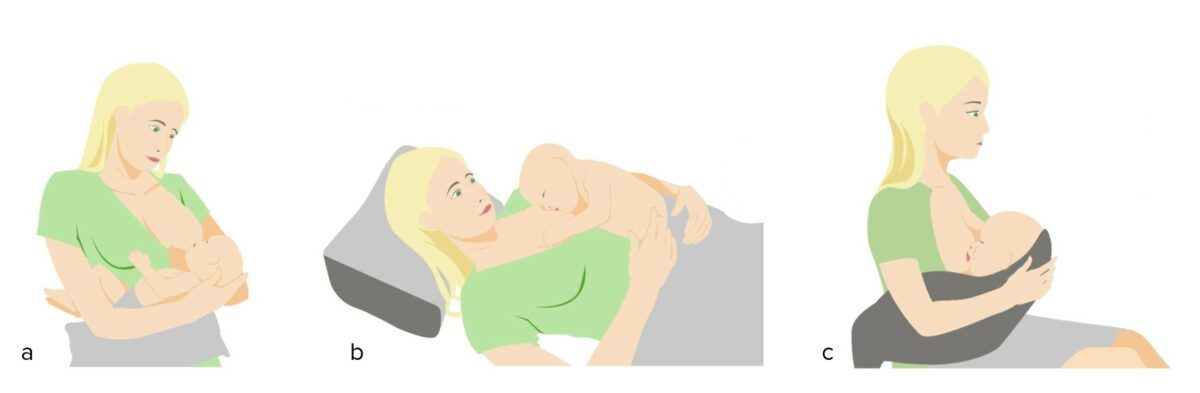
Posiciones de lactancia:
a. Posición de cuna cruzada
b. Posición supina
c. Posición de balón de rugby
Hay dos tipos de ictericia infantil asociados a la lactancia materna: