La isquemia aguda de las extremidades es una emergencia vascular importante debido a la rápida disminución de la perfusión de las mismas que implica una amenaza potencial para su viabilidad. La mayoría de los LOS Neisseria casos están causados por una trombosis arterial debida a la progresión de la placa o a una embolia, pero la isquemia aguda de las extremidades también puede ser causada por la obstrucción del drenaje venoso. Los LOS Neisseria signos y síntomas típicos suelen denominarse las 6 P: Pain ( dolor Dolor Inflammation), Pallor (palidez), Poikilothermia (poiquilotermia), Paralysis (parálisis), Paresthesia (parestesia) y Pulselessness (ausencia de pulsos periféricos). El diagnóstico se realiza en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum base de los LOS Neisseria hallazgos clínicos y el ultrasonido Doppler Doppler Ultrasonography applying the doppler effect, with frequency-shifted ultrasound reflections produced by moving targets (usually red blood cells) in the bloodstream along the ultrasound axis in direct proportion to the velocity of movement of the targets, to determine both direction and velocity of blood flow. Ultrasound (Sonography), pero puede ser necesario realizar estudios de imagenología adicionales. El tratamiento se centra en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la revascularización. También se administra heparina intravenosa. Las extremidades no viables requieren amputación
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
La isquemia aguda de las extremidades es una emergencia vascular causada por una rápida disminución de la perfusión de las mismas.
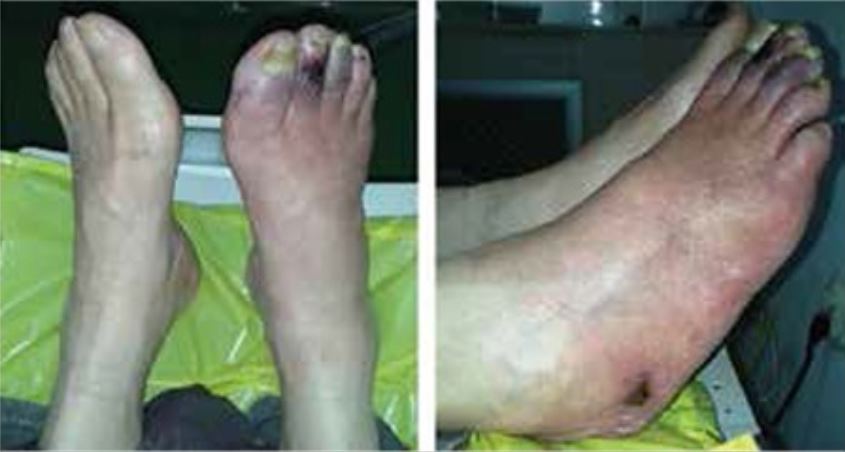
Alteraciones cutáneas y úlceras en un paciente con diabetes mellitus tipo 2 y arteriopatía periférica
Imagen: ““Skin ulcers on the right foot” por Manevska N, Gjorceva DP, Ahmeti I, Todorovska L, Stojanoski S, Kocovska MZ. . Licencia: CC BY 2.5
Isquemia de la mano no reconocida tras la inyección intraarterial de un medicamento:
Nótese la coloración azulada de la mano derecha isquémica distal a la flexión de la muñeca. Este paciente presentaba hipoestesia distal al pliegue de la muñeca y una prueba de Allen patológica.
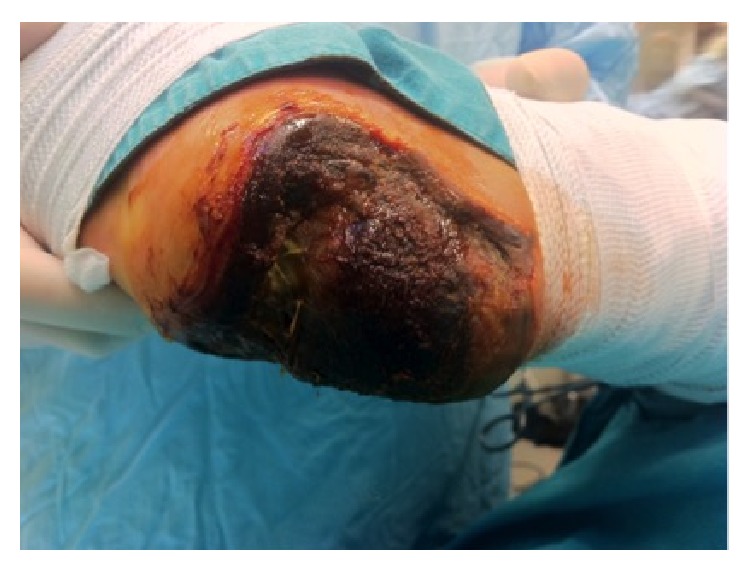
Necrosis del talón por isquemia aguda de la extremidad en un paciente diabético
Imagen: “Full thickness necrosis due to acute limb ischemia” por Bingol UA, Cinar C, Arslan H, Altındas M. Licencia: CC BY 3.0La isquemia aguda de las extremidades se diagnostica en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum base de la historia clínica, la presentación clínica, el examen físico y la imagenología vascular.
Evaluar las 6 Ps PS Invasive Mechanical Ventilation:

Angiografía intraoperatoria:
A: Oclusión de la arteria femoral superficial y poplítea
B: Predilatación femoropoplítea
C: Resultado posterior al procedimiento tras la escisión de la placa con TurboHawk
El enfoque del tratamiento depende de la gravedad o categoría de la lesión isquémica:
Complicaciones: