Las infecciones por clamidias son un grupo de enfermedades infecciosas causadas por una pequeña bacteria Bacteria Bacteria are prokaryotic single-celled microorganisms that are metabolically active and divide by binary fission. Some of these organisms play a significant role in the pathogenesis of diseases. Bacteriology intracelular gramnegativa obligada perteneciente a la familia Chlamydiaceae. Las tres especies que pueden infectar al AL Amyloidosis ser humano son Chlamydia trachomatis Chlamydia trachomatis Type species of Chlamydia causing a variety of ocular and urogenital diseases. Chlamydia, C. pneumoniae y C. psittaci. La infección más común es una ITS, causada por los LOS Neisseria serotipos D hasta la K de C. trachomatis, que es la infección bacteriana de transmisión sexual más frecuente en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum Estados Unidos. Puede causar cervicitis Cervicitis Inflammation of the uterine cervix. Gonorrhea, uretritis, enfermedad pélvica inflamatoria, laringitis, epididimitis, proctitis Proctitis Inflammation of the mucous membrane of the rectum, the distal end of the large intestine. Chronic Granulomatous Disease y linfogranuloma venéreo. Los LOS Neisseria serotipos A, B, Ba y C de C. trachomatis causan el tracoma, una queratoconjuntivitis crónica que sigue siendo la principal causa infecciosa de ceguera en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum todo el mundo. Las otras especies de Chlamydia Chlamydia Chlamydiae are obligate intracellular gram-negative bacteria. They lack a peptidoglycan layer and are best visualized using Giemsa stain. The family of Chlamydiaceae comprises 3 pathogens that can infect humans: Chlamydia trachomatis, Chlamydia psittaci, and Chlamydia pneumoniae. Chlamydia causan principalmente infecciones respiratorias. El diagnóstico se basa en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum pruebas de amplificación de ácidos nucleicos. El tratamiento consiste en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum antibióticos. Las infecciones por clamidia no tratadas pueden tener consecuencias graves, como esterilidad, embarazos ectópicos, abortos espontáneos e infertilidad debida a enfermedad pélvica inflamatoria crónica.
Last updated: Jan 15, 2026
Las infecciones por clamidia son enfermedades infecciosas causadas por bacterias pertenecientes a la familia Chlamydiaceae.
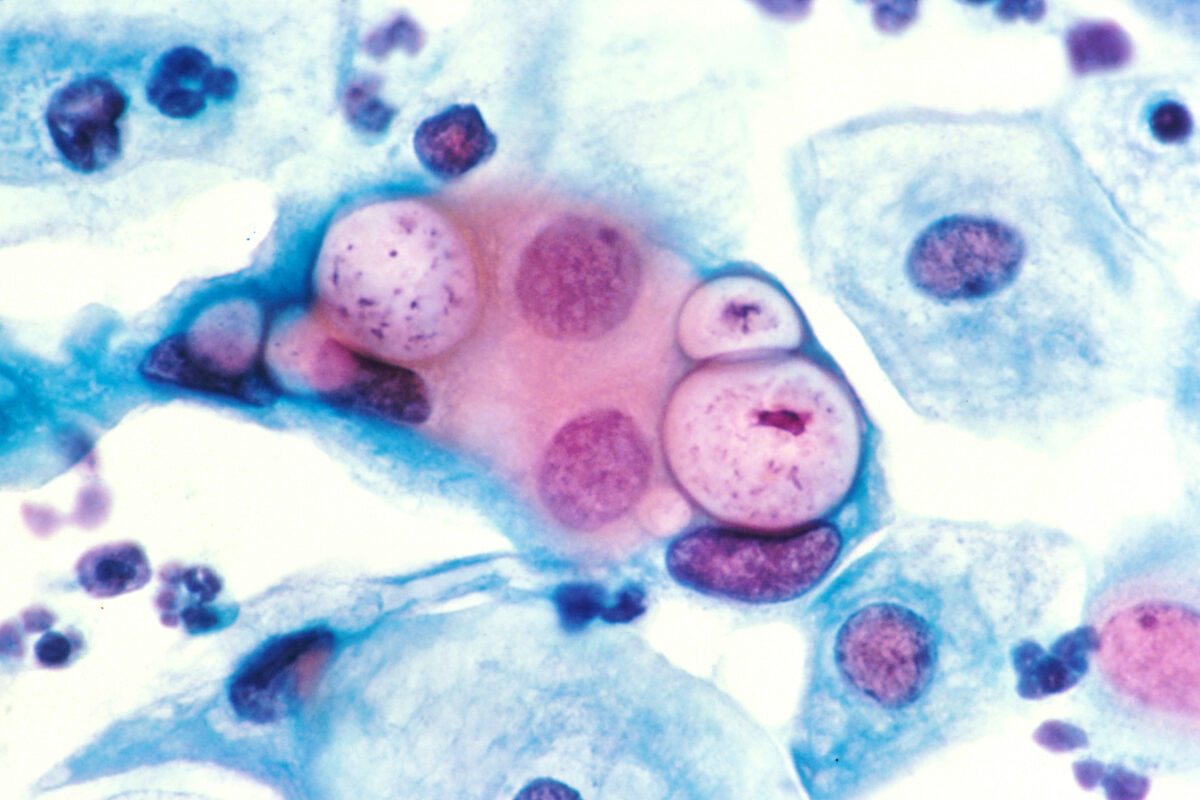
Tinción de Papanicolaou de una preparación citológica cervicovaginal que muestra 3 inclusiones intranucleares clamidiales dentro de células epiteliales escamosas que están junto a varias células epiteliales normales
Imagen: “Pap smear showing Chlamydia in the vacuoles 500x H&E” por Dr. Lance Liotta Laboratory. Licencia: Dominio público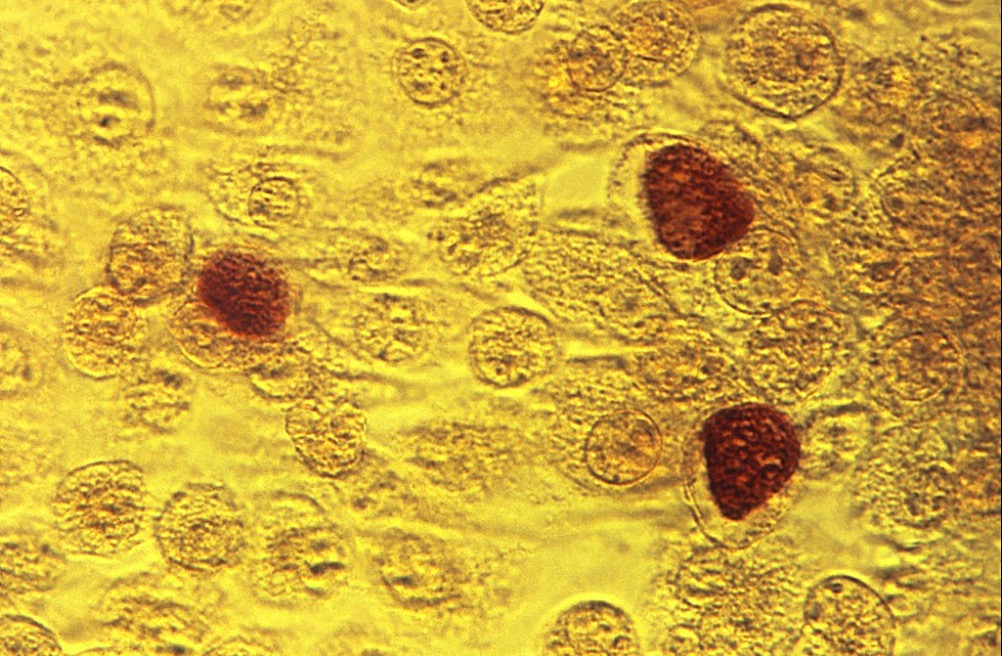
Fotomicrografía que muestra monocapas de células McCoy con cuerpos de inclusión de Chlamydia trachomatis
Imagen: “Chlamydia trachomatis inclusion bodies” por CDC/Dr. E. Arum. Licencia: Dominio públicoEnfermedad genital (serovares D–K):
Enfermedad del lactante:
Enfermedad ocular (serovares A–C):
Linfogranuloma venéreo (serovares L1–L3):
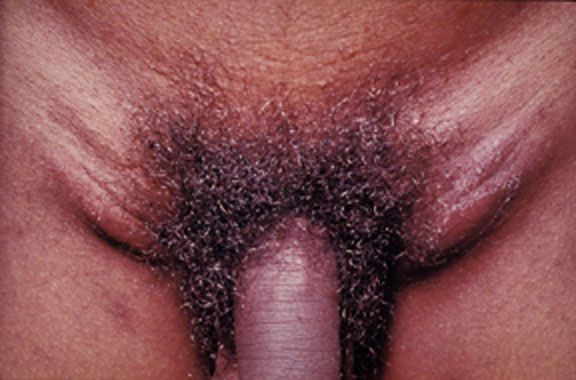
Linfogranuloma venéreo causado por los serovares invasivos L1, L2 o L3 de Chlamydia trachomatis. Este joven adulto experimentó una aparición aguda de ganglios linfáticos sensibles y agrandados en ambas ingles.
Imagen: “Lymphogranuloma venerum: lymph nodes” por Herbert L. Fred, Hendrik A. van Dijk. Licencia: CC BY 2.0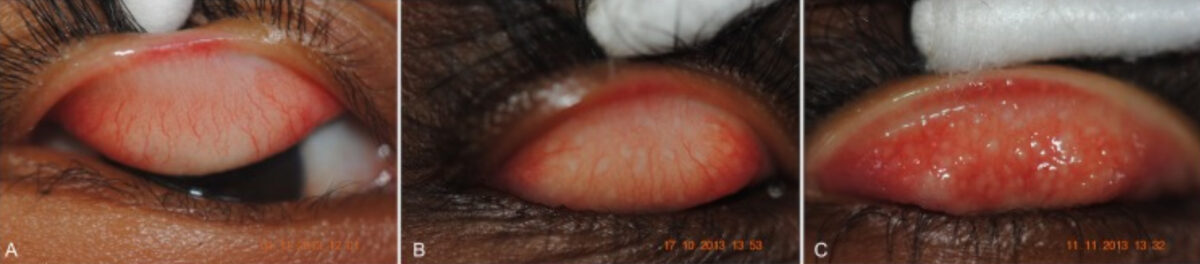
Fotografías de conjuntivas que muestran (A) no hay evidencia de tracoma activo, (B) inflamación tracomatosa folicular (TF) leve, y (C) TF más grave
Imagen: “Baja prevalencia de la infección conjuntival por Chlamydia trachomatis en una región endémica de tracoma sin tratamiento en las Islas Salomón” por PLoS Neglected Tropical Diseases. Licencia: CC BY 4.0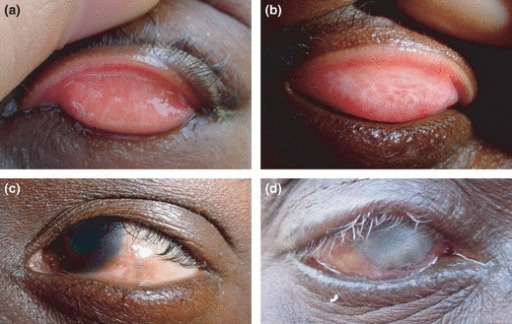
Tracoma
Los episodios recurrentes de infección por los serovares A–C de Chlamydia trachomatis causan inflamación conjuntival en los niños, que acaban desarrollando cicatrices y ceguera en la edad adulta.
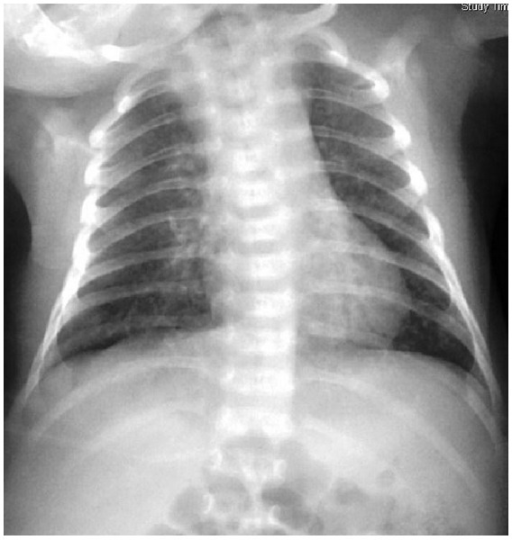
Neumonía neonatal porChlamydia trachomatis: parches difusos en una radiografía de tórax
Imagen: “Chlamydial pneumonitis: a creepy neonatal disease” por Hon KL, Leung AK. Licencia: CC BY 3.0Antecedentes clínicos:
Examen físico:
Estudios de laboratorio:
Enfoque general:
Antibióticos:
Tracoma:
Neumonía:
| C. trachomatis | C. psittaci | C. pneumoniae |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|