Las infecciones congénitas se adquieren en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el útero o durante el paso por el canal del parto al AL Amyloidosis nacer y pueden estar asociadas con una morbilidad y mortalidad significativas para el lactante. Las infecciones TORCH son un grupo de infecciones congénitas agrupadas por su presentación similar. El acrónimo TORCH surge de los LOS Neisseria nombres de los LOS Neisseria agentes infecciosos causantes de las enfermedades incluidas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum este grupo: toxoplasmosis Toxoplasmosis Toxoplasmosis is an infectious disease caused by Toxoplasma gondii, an obligate intracellular protozoan parasite. Felines are the definitive host, but transmission to humans can occur through contact with cat feces or the consumption of contaminated foods. The clinical presentation and complications depend on the host's immune status. Toxoplasma/Toxoplasmosis, otros agentes (sífilis, virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology varicela-zóster (VZV, por sus siglas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum inglés), parvovirus B19 Parvovirus B19 Primate erythroparvovirus 1 (generally referred to as parvovirus B19, B19 virus, or sometimes erythrovirus B19) ranks among the smallest DNA viruses. Parvovirus B19 is of the family Parvoviridae and genus Erythrovirus. In immunocompetent humans, parvovirus B19 classically results in erythema infectiosum (5th disease) or "slapped cheek syndrome." Parvovirus B19 y VIH), rubéola, CMV y herpes simple.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Un grupo de infecciones congénitas específicas adquiridas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el útero o durante el parto:
El tamizaje prenatal es importante en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la identificación.
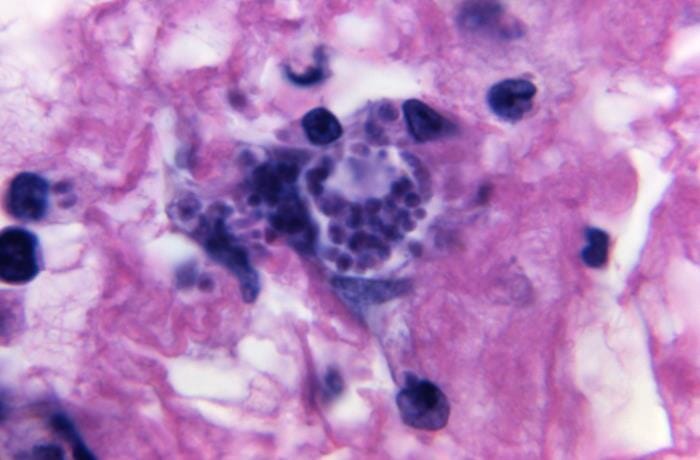
Toxoplasma gondii: con un aumento de 1 125x, esta microfotografía de una muestra de tejido revela una vista cercana de un quiste de Toxoplasma gondii teñido de oscuro, que contiene una cantidad de bradizoítos esféricos.
Imagen: “21122” por CDC/Dr. Green. Licencia: Dominio Público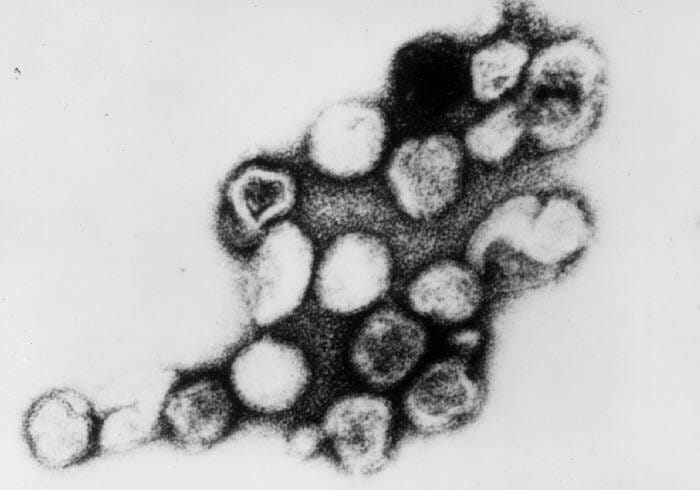
Micrografía electrónica de transmisión del virus de la rubeola
Imagen: “Rubella virus” por CDC/Dr. Erskine Palmer. Licencia: Dominio Público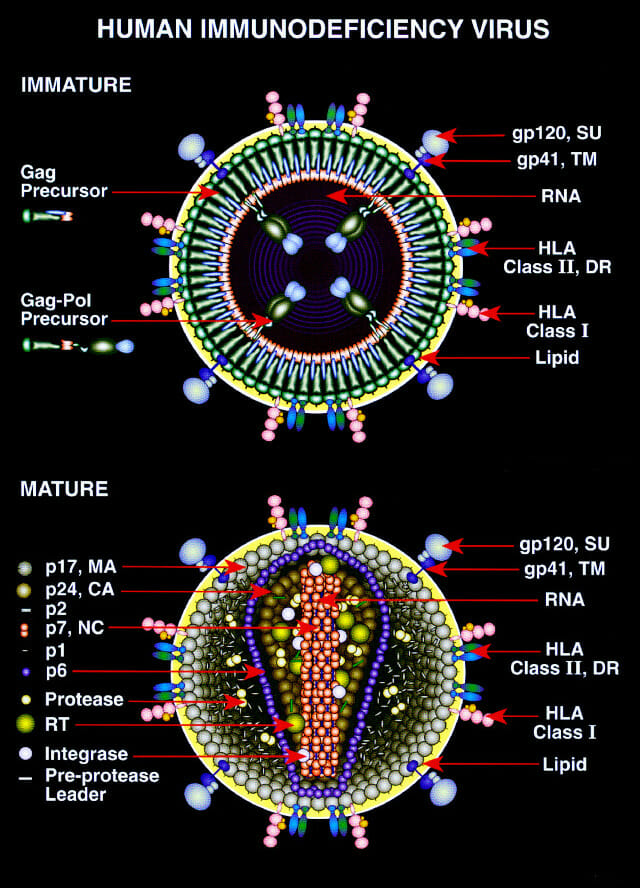
Diagrama de las formas inmaduras y maduras del VIH
Imagen: “Diagram of the immature and mature forms of HIV” por Drs. Louis E. Henderson and Larry Arthur. Licencia: Dominio PúblicoLa tríada de toxoplasmosis Toxoplasmosis Toxoplasmosis is an infectious disease caused by Toxoplasma gondii, an obligate intracellular protozoan parasite. Felines are the definitive host, but transmission to humans can occur through contact with cat feces or the consumption of contaminated foods. The clinical presentation and complications depend on the host’s immune status. Toxoplasma/Toxoplasmosis congénita en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum lactantes incluye:
Las manifestaciones tempranas de la sífilis congénita pueden afectar varios sistemas:
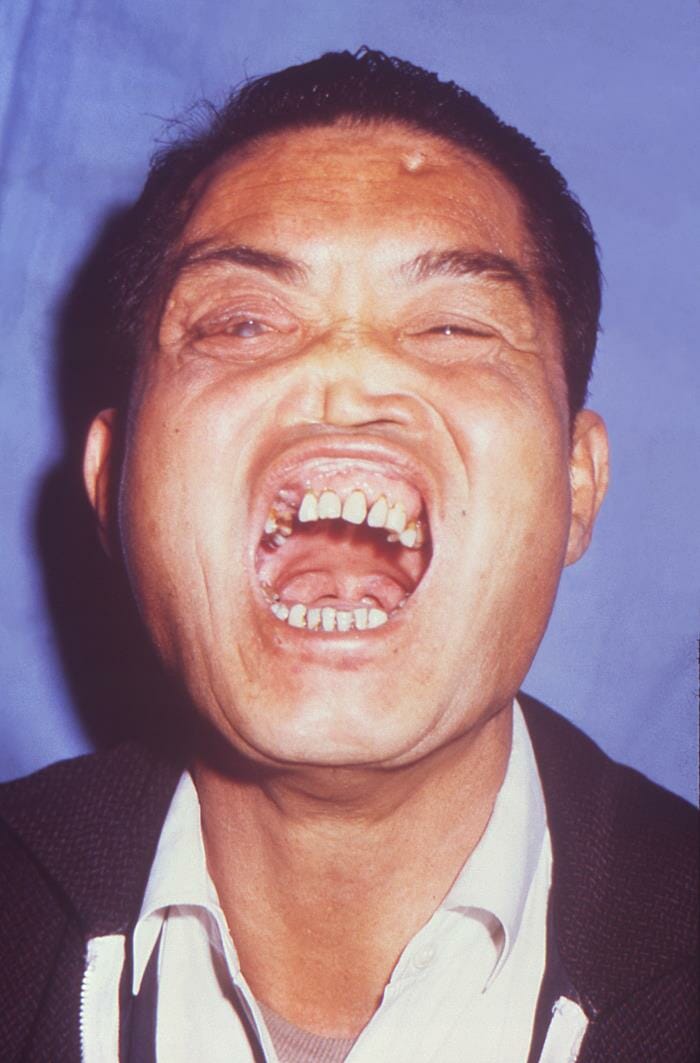
Estigmas de sífilis congénita, incluyendo protuberancia frontal, molares de mora, dientes de Hutchinson, nariz en silla de montar y una catarata en el ojo derecho.
Imagen: “16463” por Centers for Disease Control and Prevention CDC/ Brian Hill. Licencia: Dominio Público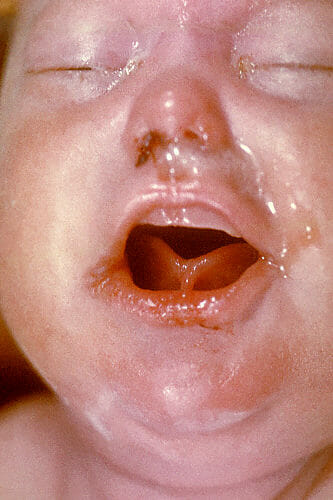
Un recién nacido muestra ronquidos, lo que indica una sífilis congénita.
Imagen: “2246” por Centers for Disease Control and Prevention CDC/ Dr. Norman Cole. Licencia: Dominio PúblicoLa presentación más común del síndrome de varicela congénita incluye:
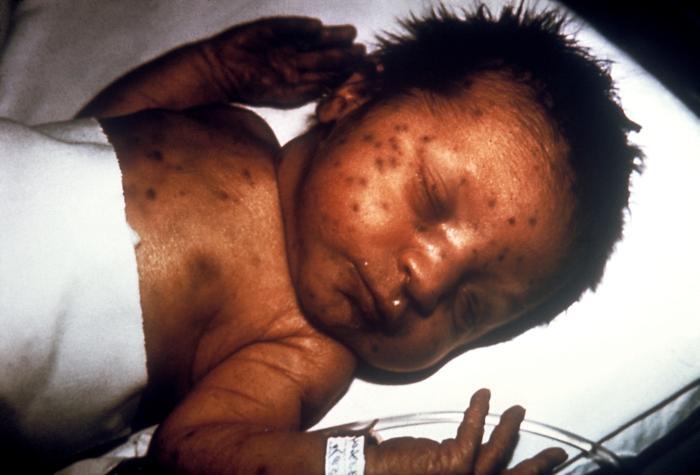
Lactante con una erupción en muffin de arándanos por rubéola congénita
Imagen: “Infant presented with ‘blueberry muffin’ skin lesions indicative of congenital rubella” por CDC. Licencia: Dominio Público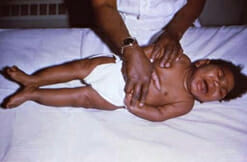
Un bebé con infección congénita por citomegalovirus presenta microcefalia y espasticidad de los miembros inferiores
Imagen: “fig5.4.2” por CDC Public Health Image Library. Licencia: Dominio PúblicoLos LOS Neisseria síntomas generalmente comienzan dentro del 1er día de vida, pero pueden retrasarse hasta 1 semana después del nacimiento.
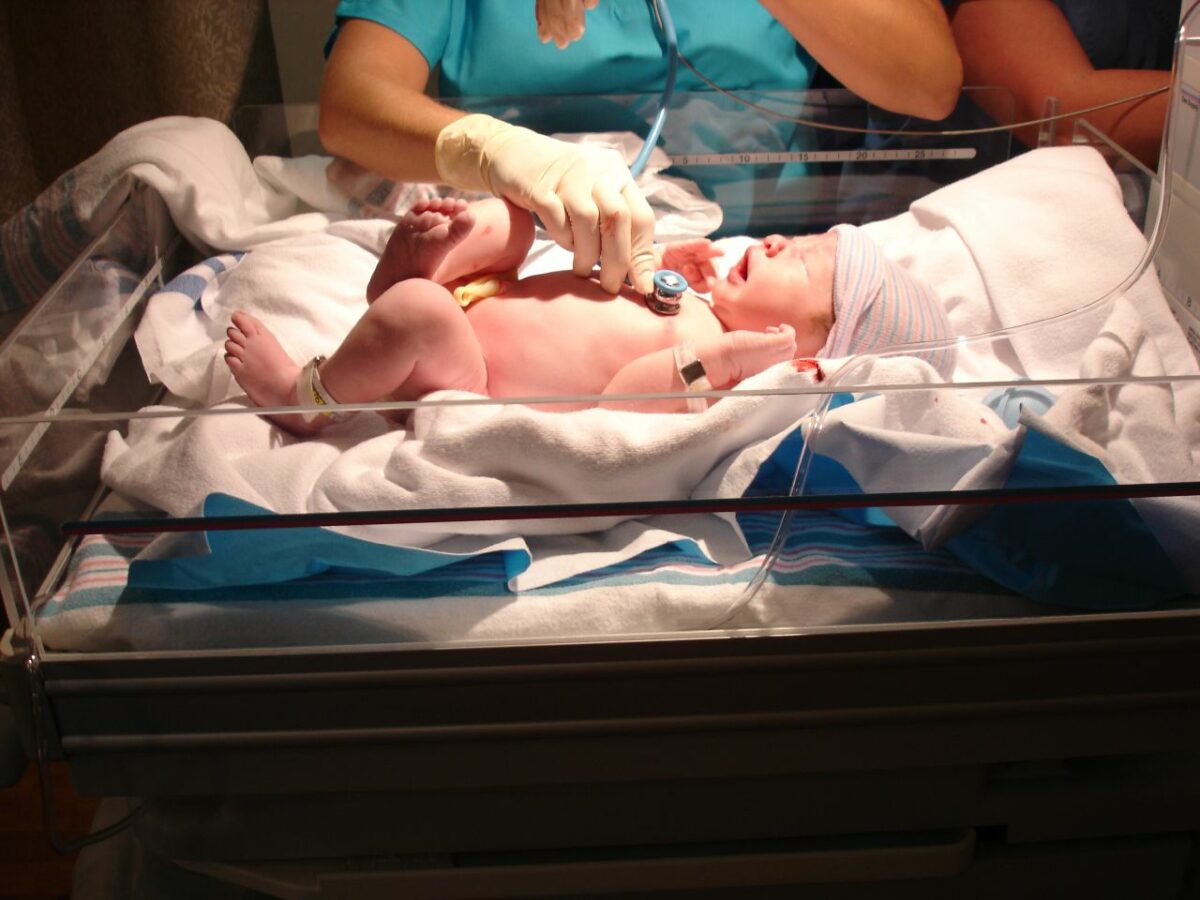
Bebé normal en el examen:
La frecuencia respiratoria es de 30–60/min; se observan patrones de respiración periódica en bebés a término y pretérmino tardíos. La piel normalmente es rosada (lo que indica una oxigenación adecuada), tanto las extremidades superiores como las inferiores tienen un tono flexor y el bebé responde con la estimulación.
El tratamiento depende de la severidad: