La hipertensión portal es el aumento de la presión en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el sistema venoso portal. Este aumento de la presión puede provocar vasodilatación esplácnica, flujo sanguíneo colateral a través de anastomosis portosistémicas y aumento de la presión hidrostática. Hay una serie de etiologías, que incluyen cirrosis, insuficiencia cardíaca derecha, esquistosomiasis, trombosis de la vena porta, hepatitis y síndrome de Budd-Chiari. La mayoría de los LOS Neisseria individuos son asintomáticos hasta que surgen complicaciones, como várices esofágicas, gastropatía hipertensiva portal, ascitis e hiperesplenismo. El diagnóstico es clínico, pero puede apoyarse en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria hallazgos del ultrasonido (y la medición del gradiente de presión venoso hepático en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum casos poco claros). El tratamiento requiere tratar la etiología subyacente y tratar las complicaciones. Esto puede incluir beta-bloqueadores no selectivos para prevenir el sangrado por várices, diuréticos y restricción de sodio para la ascitis, y derivación portosistémica intrahepática transyugular para complicaciones refractarias.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Las etiologías de la hipertensión portal se pueden clasificar según la ubicación del aumento de la resistencia al AL Amyloidosis flujo sanguíneo a través del hígado.
Etiologías prehepáticas:
Etiologías hepáticas:
Etiologías posthepáticas:
Anatomía:
Hipertensión portal:
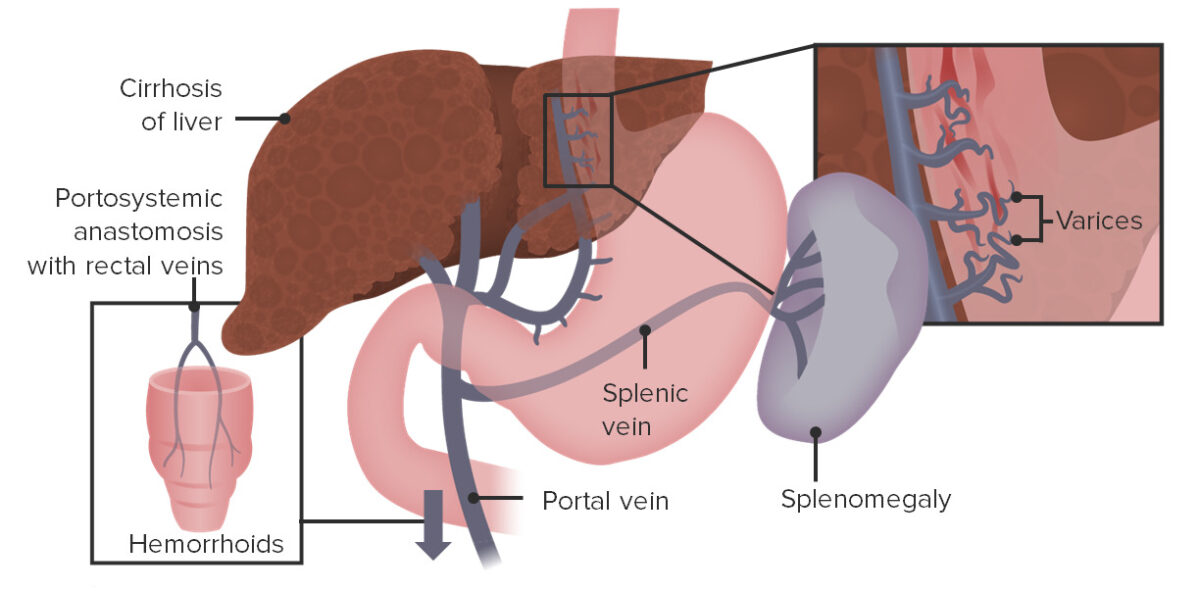
Várices esofágicas, esplenomegalia y várices rectales resultantes del reflujo de sangre debido a presiones elevadas dentro de la vena porta
Imagen por Lecturio.La hipertensión portal en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum sí no suele presentar síntomas. Las manifestaciones clínicas surgen como resultado de la etiología subyacente y/o de las complicaciones.
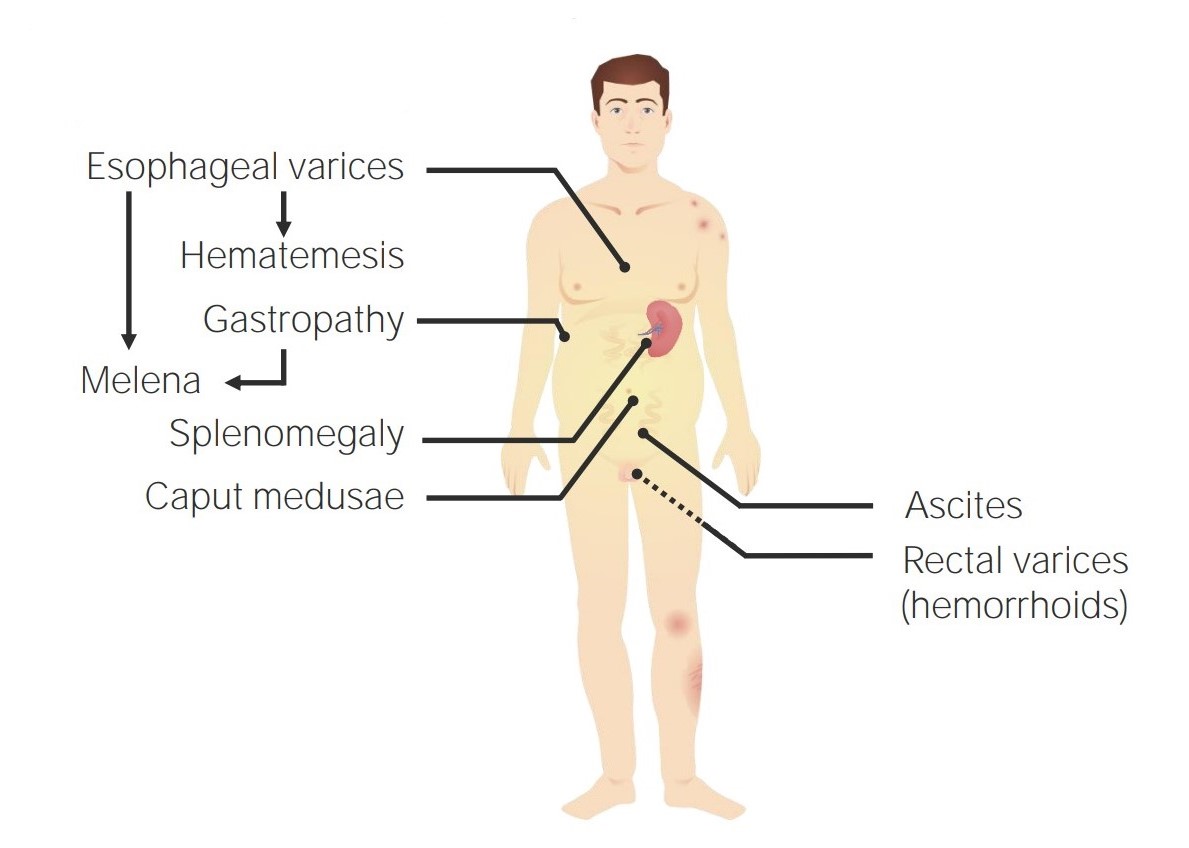
Síntomas derivados de la hipertensión portal
Imagen por Lecturio.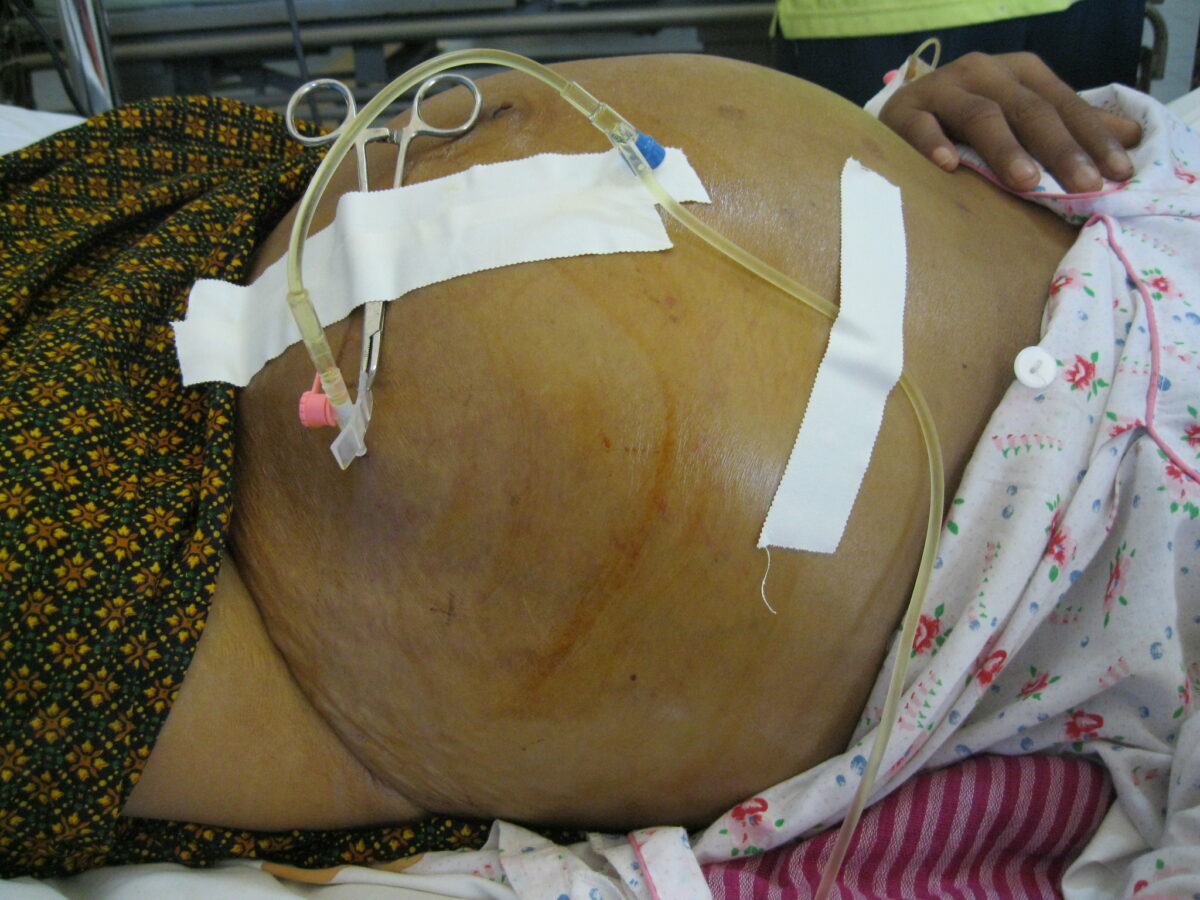
Ascitis secundaria a cirrosis hepática
Imagen: “Draining ascites, secondary to hepatic cirrhosis” por John Campbell. Licencia: Dominio PúblicoEl diagnóstico de hipertensión portal generalmente se basa en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la evaluación clínica, pero puede estar respaldado por:
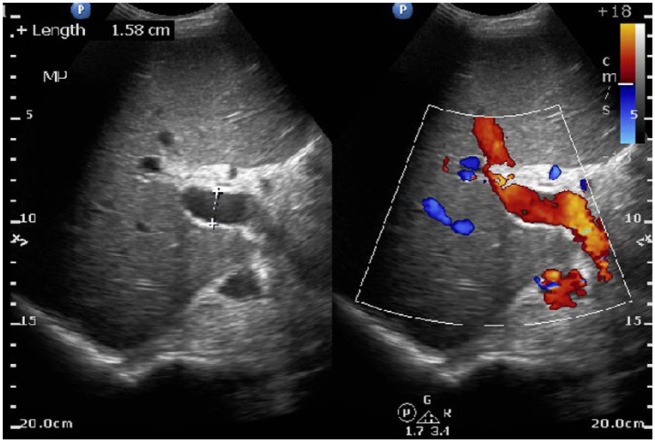
Ultrasonido del hígado que identifica una vena porta grande, compatible con hipertensión portal.
Imagen: “Ultrasound abdomen: ultrasound of liver dentifies a patent portal vein, 158 mm in diameter, indicative of portal hypertension in this noncirrhotic patient.” por Ratnayake S. et al. Licencia: CC BY 3.0Se pueden realizar estudios adicionales en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum función de la presentación clínica y la presencia de complicaciones.
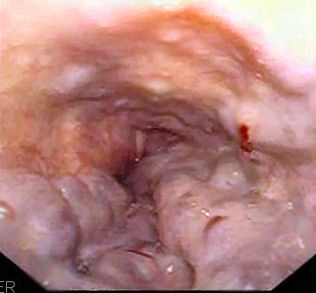
Vista endoscópica de las várices esofágicas:
Los parches rojos indican una hemorragia reciente.
El enfoque de la terapia es prevenir y tratar las complicaciones de la trombosis de la vena porta. También es importante tratar la etiología subyacente (cuando sea posible).