Los LOS Neisseria antibióticos glucopéptidos vancomicina y teicoplanina son inhibidores de la síntesis de la pared celular bacteriana y se consideran como último recurso para el tratamiento de infecciones graves debidas a bacterias Gram-positivas como Staphylococcus aureus Staphylococcus aureus Potentially pathogenic bacteria found in nasal membranes, skin, hair follicles, and perineum of warm-blooded animals. They may cause a wide range of infections and intoxications. Brain Abscess, Enterococcus Enterococcus Enterococcus is a genus of oval-shaped gram-positive cocci that are arranged in pairs or short chains. Distinguishing factors include optochin resistance and the presence of pyrrolidonyl arylamidase (PYR) and Lancefield D antigen. Enterococcus is part of the normal flora of the human GI tract. Enterococcus spp. y Clostridiodes difficile. La vancomicina es el único antibiótico glucopéptido disponible en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria Estados Unidos. Este medicamento tiene una pobre absorción en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el tracto gastrointestinal; por lo tanto, la vancomicina oral se utiliza para las infecciones de la luz intestinal, incluido el C. difficile. La vancomicina intravenosa está indicada para las infecciones graves por Gram-positivos, como la endocarditis Endocarditis Endocarditis is an inflammatory disease involving the inner lining (endometrium) of the heart, most commonly affecting the cardiac valves. Both infectious and noninfectious etiologies lead to vegetations on the valve leaflets. Patients may present with nonspecific symptoms such as fever and fatigue. Endocarditis, neumonía y la bacteriemia. Los LOS Neisseria efectos secundarios significativos incluyen anafilaxia, reacciones de hipersensibilidad, síndrome del hombre rojo (relacionado con la infusión rápida), nefrotoxicidad y ototoxicidad.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Los LOS Neisseria antibióticos glucopéptidos son péptidos no ribosomales derivados de actinomicetos, glucosilados, que se dirigen contra bacterias Gram-positivas mediante la inhibición de la síntesis de la pared celular:
Tanto la vancomicina como la teicoplanina son heptapéptidos, pero los LOS Neisseria grupos de carbohidratos de cada medicamento difieren.
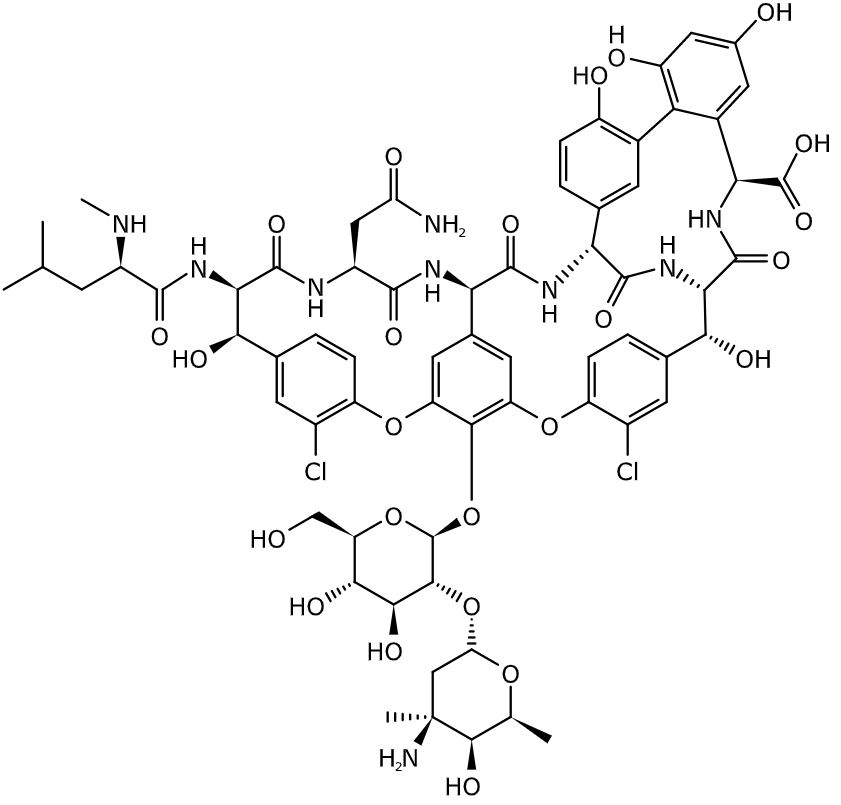
Estructura química de la vancomicina
Imagen: “Vancomycin” por BartVL71. Licencia: Dominio Público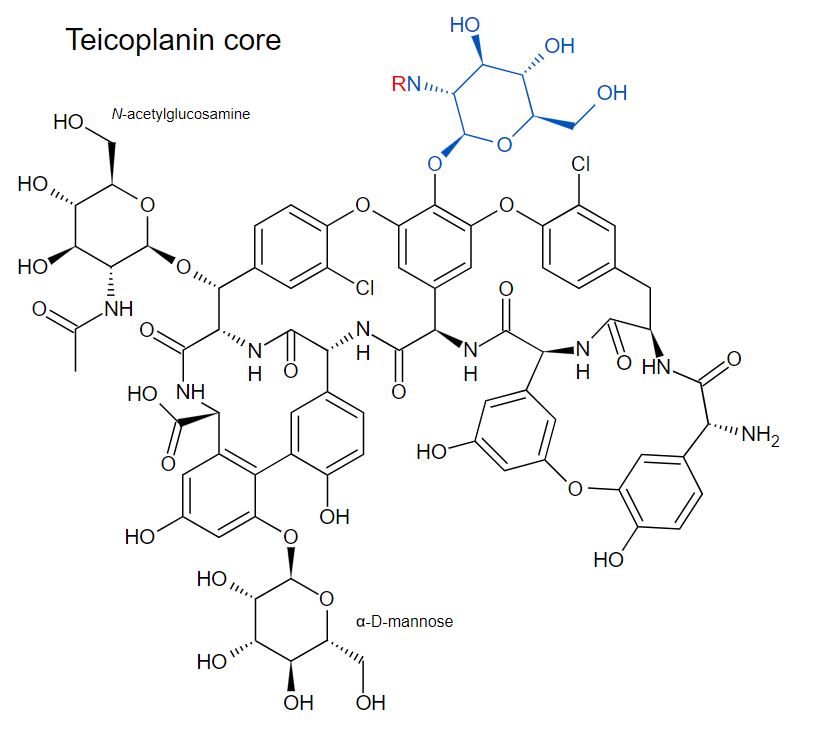
Estructura química de la teicoplanina
Imagen: “Teicoplanin core and major components” por Fvasconcellos. Licencia: Dominio público, recortado por Lecturio.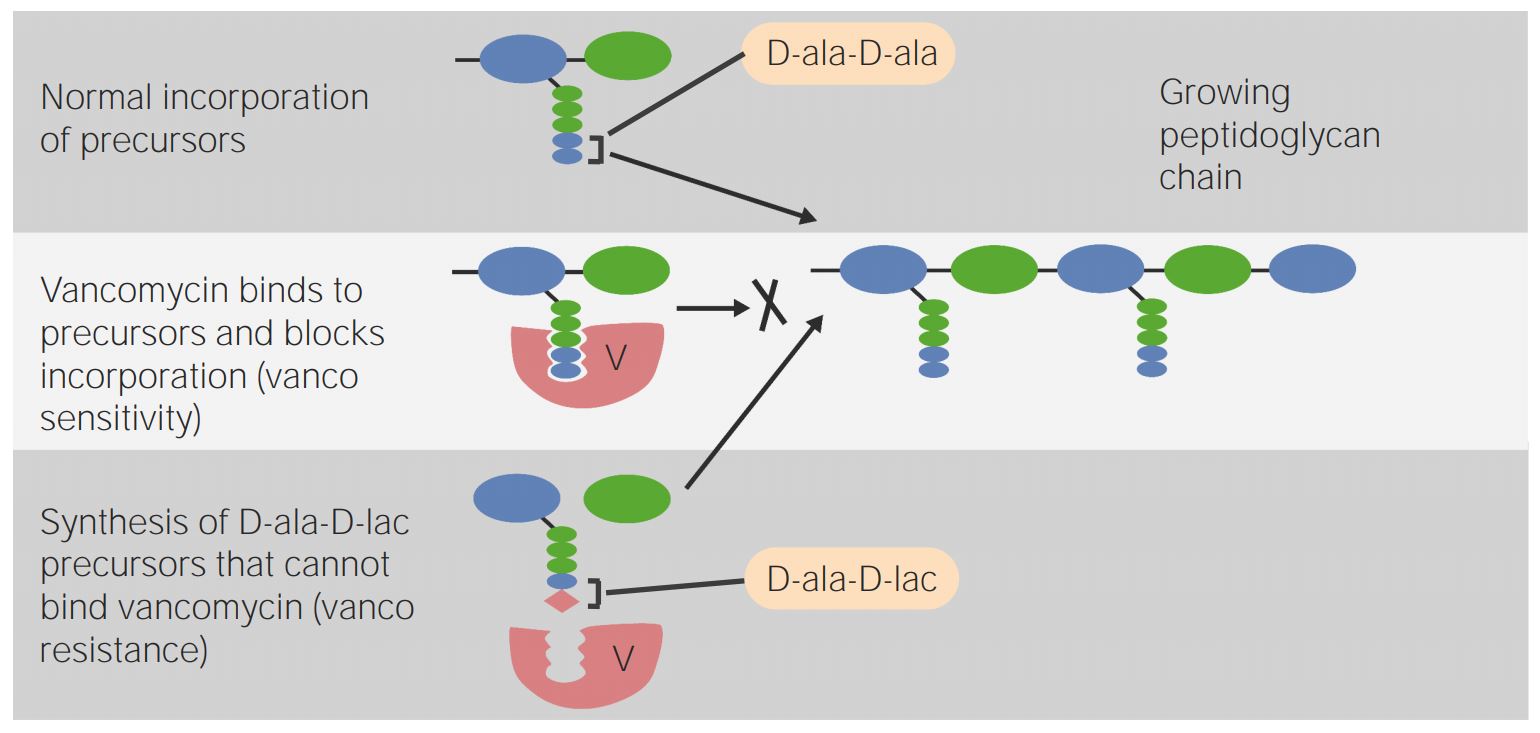
Mecanismo de acción:
La vancomicina interfiere en la incorporación normal de los precursores del peptidoglicano.
La fila inferior muestra la resistencia a la vancomicina:
La síntesis de precursores de D-alanil-D-lactato en la pared celular bacteriana provoca una mala unión con la vancomicina, lo que reduce la eficacia del antibiótico.
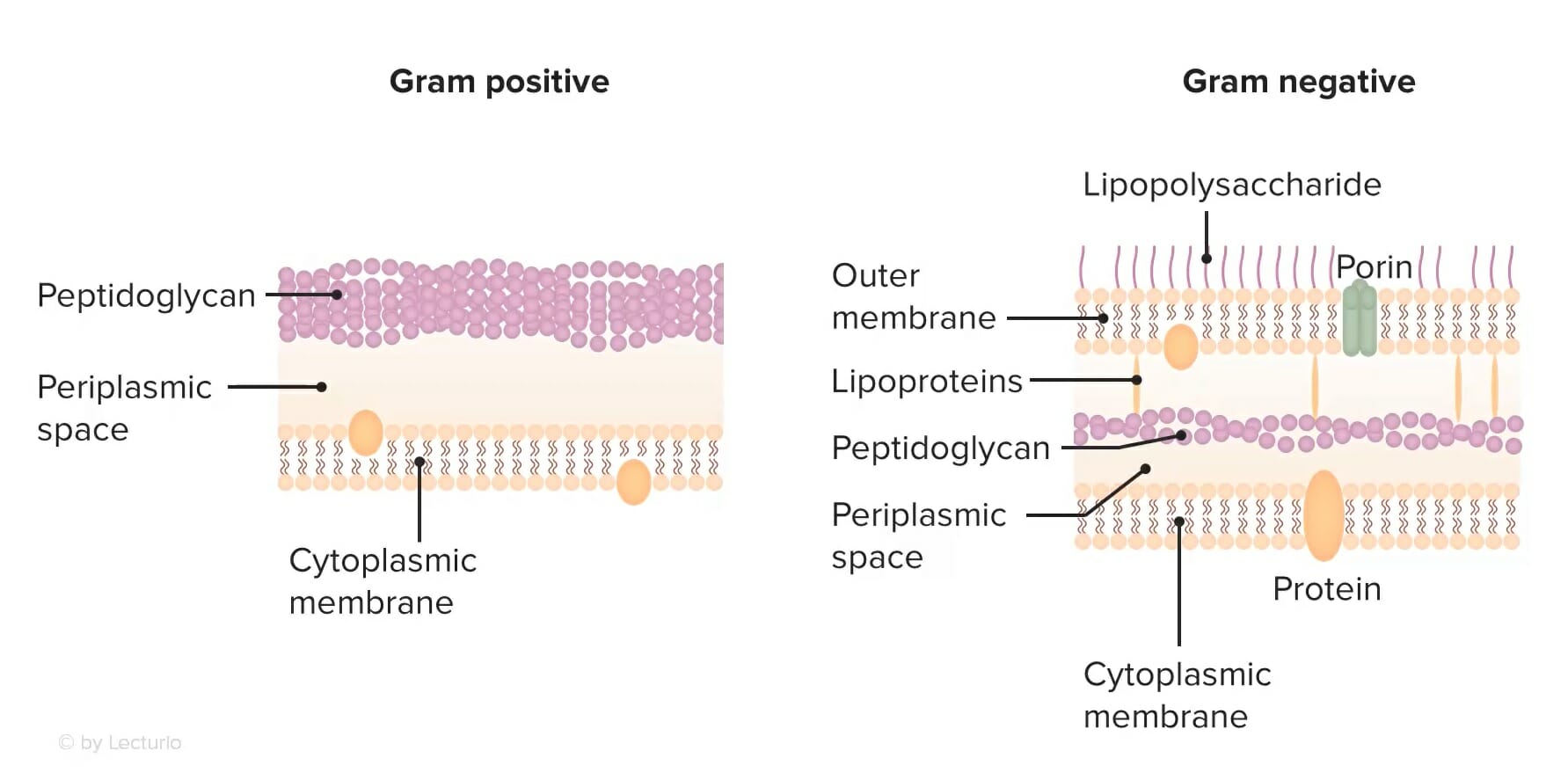
La estructura de la pared celular de las bacterias grampositivas frente a las gramnegativas: Obsérvese que la capa de peptidoglicano de la pared celular está situada en la superficie, lo que permite un acceso más fácil a los antibióticos glicopéptidos para que ejerzan un efecto bactericida. Por el contrario, las bacterias gramnegativas tienen una membrana de lipopolisacáridos que es impermeable a las moléculas grandes (como los glucopéptidos).
Los LOS Neisseria antibióticos glucopéptidos tienen una amplia actividad contra las infecciones bacterianas Gram-positivas y suelen utilizarse como tratamiento de último recurso para las afecciones graves.
| Medicamento | Indicaciones | Datos clínicos |
|---|---|---|
| Vancomicina |
|
|
| Teicoplanina | Espectro de actividad similar al AL Amyloidosis de la vancomicina |
|
Los LOS Neisseria siguientes antibióticos son agentes con actividad contra las bacterias Gram-positivas. Todos actúan sobre la pared celular bacteriana a través de distintos mecanismos.
| Clase de antibióticos | Mecanismo de acción | Medicamentos |
|---|---|---|
| Lipopéptidos | Alteración de la membrana celular bacteriana generando un canal conductor de iones, despolarizando la membrana y provocando la muerte celular | Daptomicina |
| Glucopéptidos | Inhibición de la síntesis de la pared celular mediante la unión al AL Amyloidosis extremo D-alanil-D-alanina de los LOS Neisseria precursores del peptidoglicano (PG) de la pared celular |
|
| Lipoglucopéptidos | Doble acción, inhibición de la síntesis de la pared celular y despolarización de la membrana celular |
|
Diferentes antibióticos tienen distintos grados de actividad contra diferentes bacterias. En EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la tabla siguiente se describen los LOS Neisseria antibióticos con actividad contra 3 clases importantes de bacterias: cocos Gram-positivos, bacilos Gram-negativos y anaerobios.
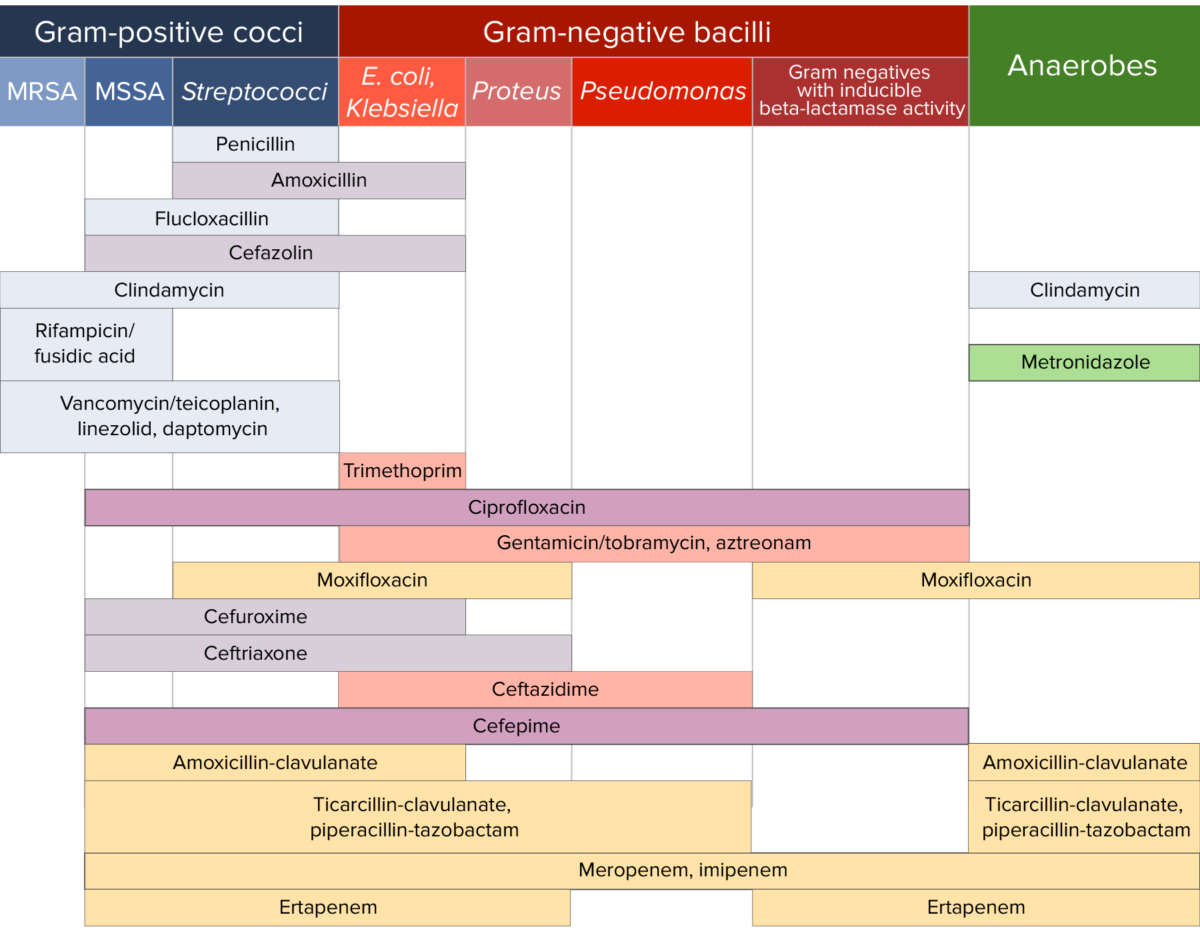
Sensibilidad a los antibióticos:
Gráfico que compara la cobertura microbiana de diferentes antibióticos para cocos Gram-positivos, bacilos Gram-negativos y anaerobios.