La enfermedad de Lyme es una infección transmitida por garrapatas y causada por la espiroqueta gram-negativa Borrelia burgdorferi Borrelia burgdorferi A specific species of bacteria, part of the borrelia burgdorferi group, whose common name is lyme disease spirochete. Borrelia. La enfermedad de Lyme es transmitida por la garrapata Ixodes (comúnmente conocida como garrapata del ciervo), que sólo se encuentra en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum determinadas regiones geográficas. La presentación en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria pacientes puede variar en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum función del estadio de la enfermedad y puede incluir una erupción eritematosa característica. Las manifestaciones neurológicas, cardíacas, oculares y articulares también son comunes en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum las etapas posteriores. El diagnóstico se basa en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria hallazgos clínicos y la exposición a las garrapatas, y se apoya en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum las pruebas serológicas. Se utilizan antibióticos para el tratamiento. Evitar la exposición a las garrapatas es la clave de la prevención en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum las zonas endémicas.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
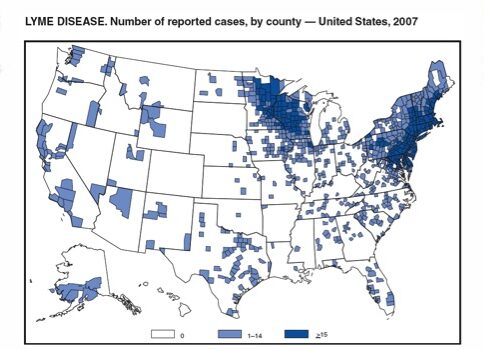
La mayoría de los casos de la enfermedad de Lyme se registran en las regiones del noreste y el medio oeste superior de Estados Unidos, según el Centro para el Control y la Prevención de Enfermedades (CDC) en 2017.
Imagen: “Reported cases of Lyme disease” por CDC. Licencia: Dominio Público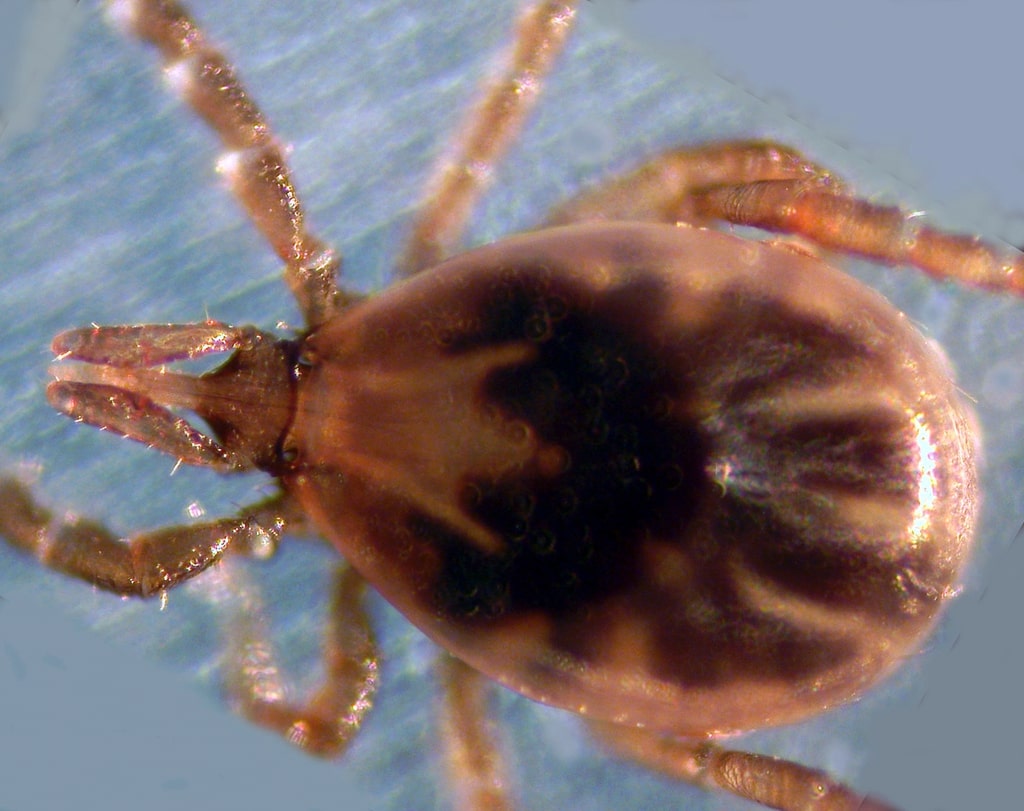
La garrapata de patas negras (Ixodes scapularis) es el principal vector de la enfermedad de Lyme.
Imagen: “The blacklegged tick” por Liza Gross. Licencia: CC BY 2.5El periodo de incubación de la enfermedad de Lyme es de 3–30 días (media de 7 días). Las manifestaciones clínicas de la enfermedad de Lyme se dividen en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum 3 etapas: enfermedad temprana localizada, enfermedad temprana diseminada y enfermedad tardía.
Los LOS Neisseria síntomas aparecen en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum 1–5 semanas y se resuelven en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum aproximadamente 30 días.
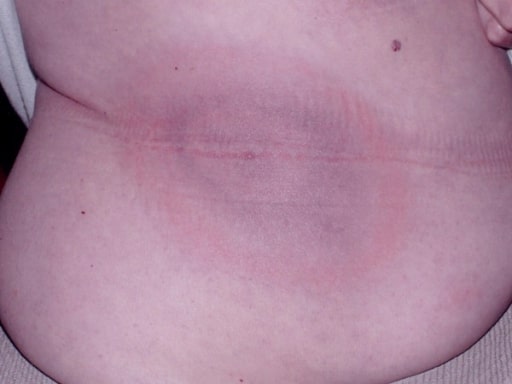
La clásica erupción en forma de “ojo de buey” (eritema migratorio) de Borrelia burgdorferi
Imagen: “Classic EM bull’s eye” por Department of Medicine, Johns Hopkins School of Medicine, Baltimore, Maryland, USA. Licencia: CC BY 2.0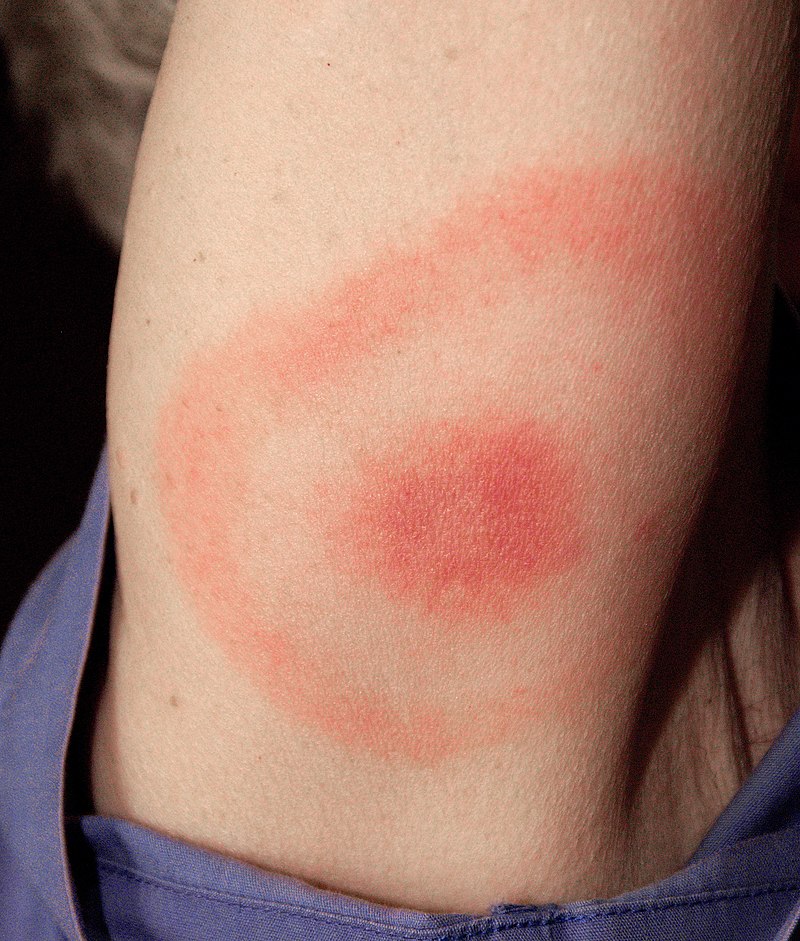
Eritema migratorio
Imagen por James Gathany. Licencia: Dominio PúblicoLos LOS Neisseria síntomas se desarrollan en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum semanas o meses en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum pacientes no tratados.
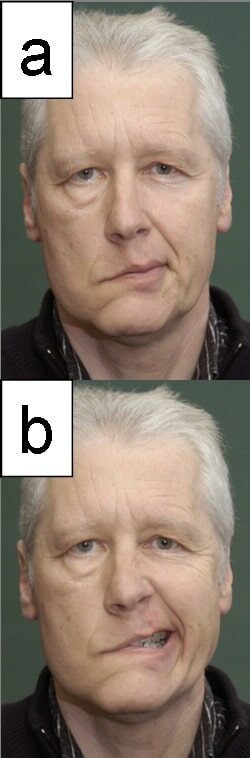
Un paciente con parálisis del nervio facial: Esta es la manifestación neurológica más común de la enfermedad de Lyme.
Imagen: “Facial paralysis” por the Department of Otolaryngology, University of Jena, Lessingstrasse 2, Jena, Germany. Licencia: CC BY 2.0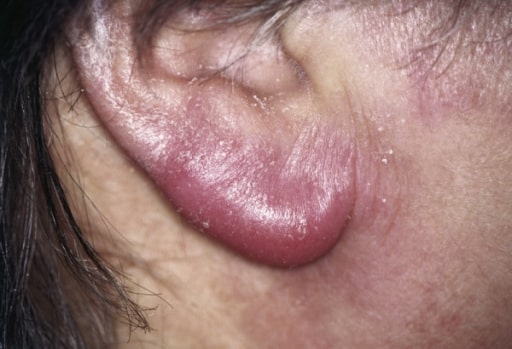
Linfadenosis cutis benigna, también conocida como linfocitoma, de la oreja de un paciente: Se trata de un hallazgo cutáneo poco frecuente en la enfermedad de Lyme temprana diseminada.
Imagen: “Lymphocytoma” por the Department of General and Visceral Surgery, Augusta Kranken Anstalt, Academic Hospital of the Ruhr University Bochum, Germany. Licencia: CC BY 2.0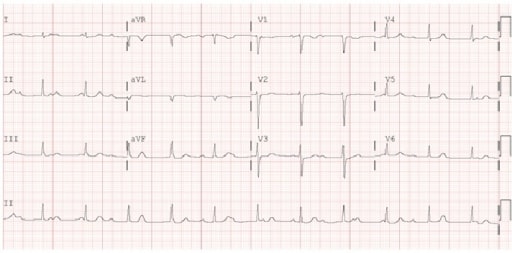
Electrocardiograma (ECG) que demuestra un bloqueo auriculoventricular de tercer grado: Esta es una de las manifestaciones cardíacas de la enfermedad de Lyme temprana diseminada.
Imagen: “Electrocardiogram” por Maxwell Eyram Afari et al. Licencia: CC BY 4.0Los LOS Neisseria síntomas se desarrollan en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum meses o años en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum pacientes no tratados.
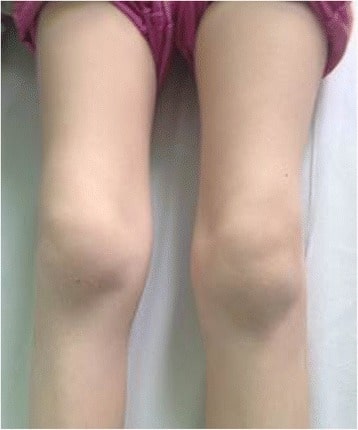
Inflamación bilateral de la rodilla y artritis en un paciente pediátrico con enfermedad de Lyme
Imagen: “Bilateral knee arthritis” por Krzysztof Orczyk et al. Licencia: CC BY 4.0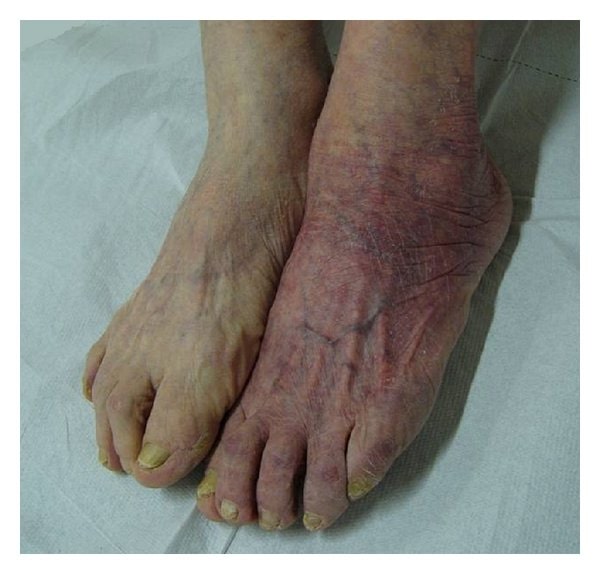
Acrodermatitis crónica atrofiante
Imagen: “Chronic atrophic acrodermatitis” por Giuseppe Stinco et al. Licencia: CC BY 3.0Los LOS Neisseria síntomas comunes de la enfermedad de Lyme pueden recordarse con la frase mnemotécnica en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum inglés “a key Lyme pie to the FACE” (un pastel de limón en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la cara).
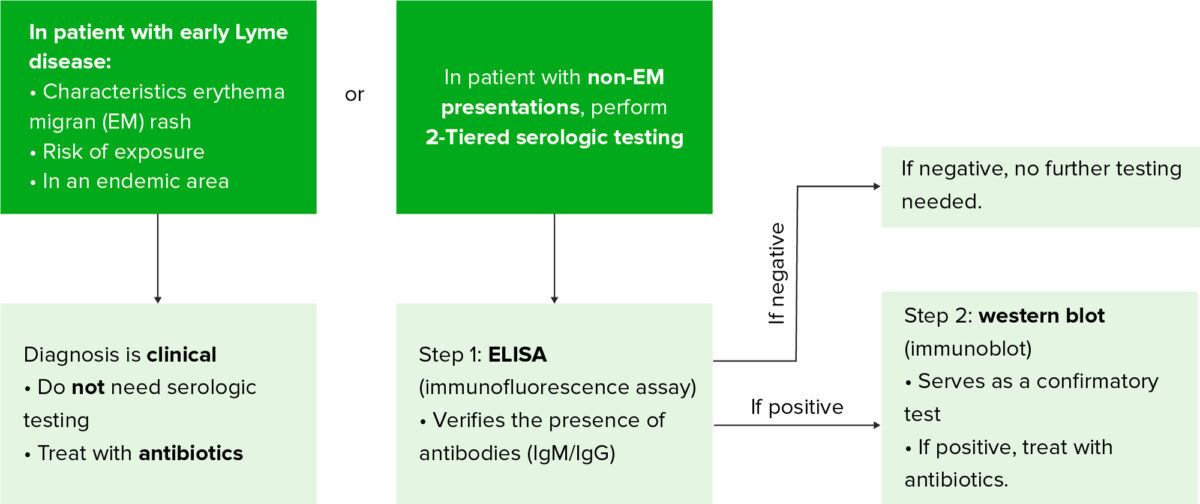
Algoritmo de diagnóstico de la enfermedad de Lyme
ELISA: ensayo inmunoenzimático
Las pruebas de laboratorio sólo son significativas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum conjunción con la historia clínica debido a una alta tasa de falsos positivos y falsos negativos.
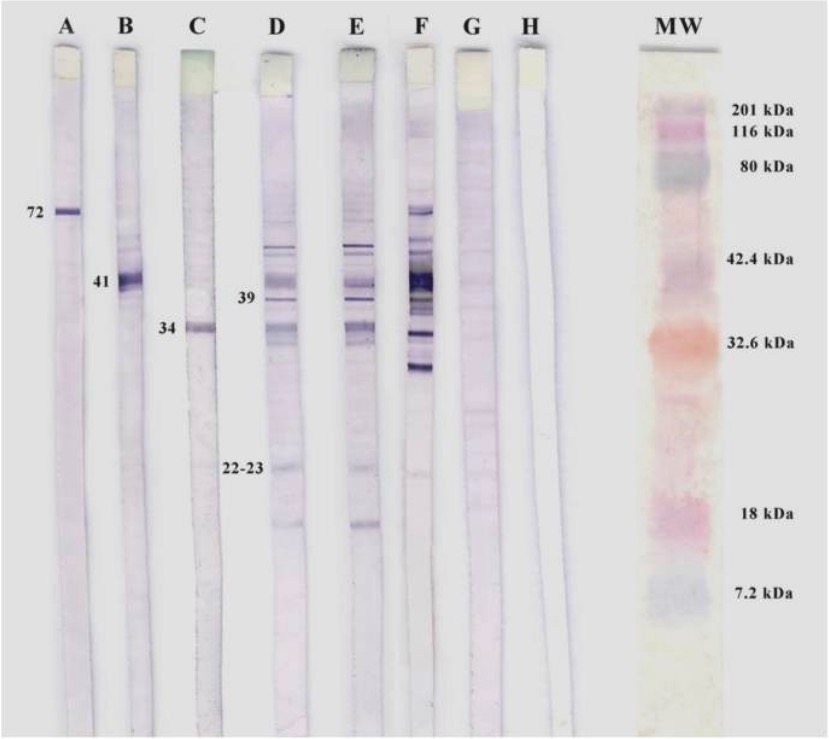
Western blotting de B. burgdorferi.
A, B y C: controles positivos para anticuerpos monoclonales específicos
D y E: pacientes seropositivos para IgM
F: control positivo
G: control negativo
H: control blanco
MW: peso molecular
Antibióticos orales:
Antibióticos intravenosos:
Consideraciones adicionales:
| Manifestaciones clínicas | Tratamiento |
|---|---|
El paciente asintomático con una picadura de garrapata no requiere tratamiento profiláctico a menos que:
|
Si cumple los LOS Neisseria criterios, debe recibir doxiciclina profiláctica en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum las 72 horas siguientes a la mordedura |
| Eritema migratorio (enfermedad localizada) |
|
Enfermedad temprana diseminada:
|
|
|
|
| Manifestaciones cardíacas y neurológicas | Ceftriaxona intravenosa |
Enfermedad tardía:
|
|
| Reinfección | El mismo antibiótico que se recomienda para una infección primaria |
La profilaxis con doxiciclina está indicada si se cumplen todos los LOS Neisseria criterios siguientes: