La endometritis Endometritis Endometritis is an inflammation of the endometrium, the inner layer of the uterus. The most common subtype is postpartum endometritis, resulting from the ascension of normal vaginal flora to the previously aseptic uterus. Postpartum Endometritis posparto es una inflamación infecciosa del endometrio (la capa interna del útero) que se produce en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el entorno posparto, y que suele aparecer en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria primeros días después del parto. Estas infecciones son el resultado del ascenso de la flora vaginal normal al AL Amyloidosis útero previamente aséptico a través del cuello uterino dilatado. Las mujeres que han tenido un parto por cesárea tienen entre 10 y 30 veces más probabilidades de desarrollar una endometritis Endometritis Endometritis is an inflammation of the endometrium, the inner layer of the uterus. The most common subtype is postpartum endometritis, resulting from the ascension of normal vaginal flora to the previously aseptic uterus. Postpartum Endometritis postparto que las que han tenido un parto vaginal espontáneo. Las pacientes presentan fiebre y una sensibilidad uterina exquisita a la palpación; también puede haber un drenaje anormal/purulento. El diagnóstico es casi siempre clínico, y el diagnóstico por imagen solo es necesario para excluir otras causas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria casos que no responden al AL Amyloidosis tratamiento empírico inicial. El manejo es con terapia antibiótica intravenosa.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
La endometritis Endometritis Endometritis is an inflammation of the endometrium, the inner layer of the uterus. The most common subtype is postpartum endometritis, resulting from the ascension of normal vaginal flora to the previously aseptic uterus. Postpartum Endometritis es una inflamación del revestimiento interno del útero, el endometrio.
Endometritis Endometritis Endometritis is an inflammation of the endometrium, the inner layer of the uterus. The most common subtype is postpartum endometritis, resulting from the ascension of normal vaginal flora to the previously aseptic uterus. Postpartum Endometritis postparto:
La endometritis Endometritis Endometritis is an inflammation of the endometrium, the inner layer of the uterus. The most common subtype is postpartum endometritis, resulting from the ascension of normal vaginal flora to the previously aseptic uterus. Postpartum Endometritis postparto está causada por el movimiento de la flora vaginal normal hacia el útero → colonización del revestimiento uterino dañado → infección e inflamación.
La
endometritis
Endometritis
Endometritis is an inflammation of the endometrium, the inner layer of the uterus. The most common subtype is postpartum endometritis, resulting from the ascension of normal vaginal flora to the previously aseptic uterus.
Postpartum Endometritis postparto es una infección polimicrobiana
en
EN
Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins.
Erythema Nodosum la que intervienen tanto organismos aerobios como anaerobios. La mayoría de las pacientes tienen un promedio de 2-3 organismos.
Organismos aeróbicos:
Organismos anaerobios:
Las pacientes se presentarán dentro de los LOS Neisseria primeros 10 días postparto (y generalmente dentro de los LOS Neisseria primeros 2-3 días), con los LOS Neisseria siguientes signos/síntomas:
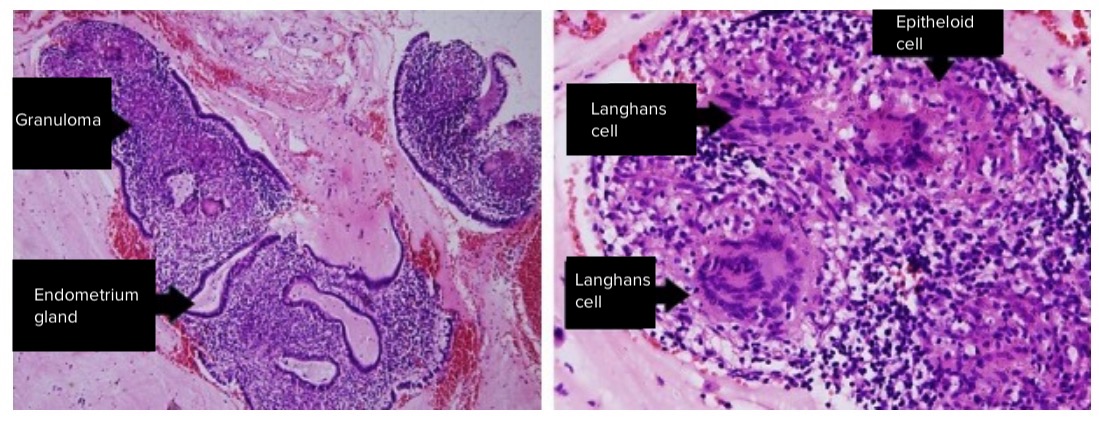
Endometritis tuberculosa:
Izquierda: Tejido endometrial con granuloma y linfocitos
Derecha: Histiocitos y células epitelioides y gigantes multinucleadas de Langhans
El tratamiento es con antibióticos intravenosos.