La coriorretinitis es la inflamación del segmento posterior del ojo, que incluye la coroides y la retina. La enfermedad suele ser causada por infecciones, siendo la más común la toxoplasmosis. Algunas de estas infecciones pueden afectar al feto en el útero y presentarse como anomalías congénitas. Las enfermedades sistémicas, como la sarcoidosis, también se asocian a esta afección. Las características clínicas típicas son la visión borrosa indolora, las miodesopsias o "cuerpos flotantes" y los LOS Neisseria escotomas. Con los LOS Neisseria trastornos sistémicos y congénitos, se observan manifestaciones extraoculares. El diagnóstico se realiza mediante la fundoscopia, el examen con lámpara de hendidura, el uso de pruebas de laboratorio y la imagenología, siendo orientado por los LOS Neisseria factores de riesgo, los LOS Neisseria antecedentes clínicos y el monitoreo del tratamiento. El tratamiento se dirige a eliminar la infección con antibióticos o antivirales y a reducir la inflamación con glucocorticoides o inmunosupresores.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
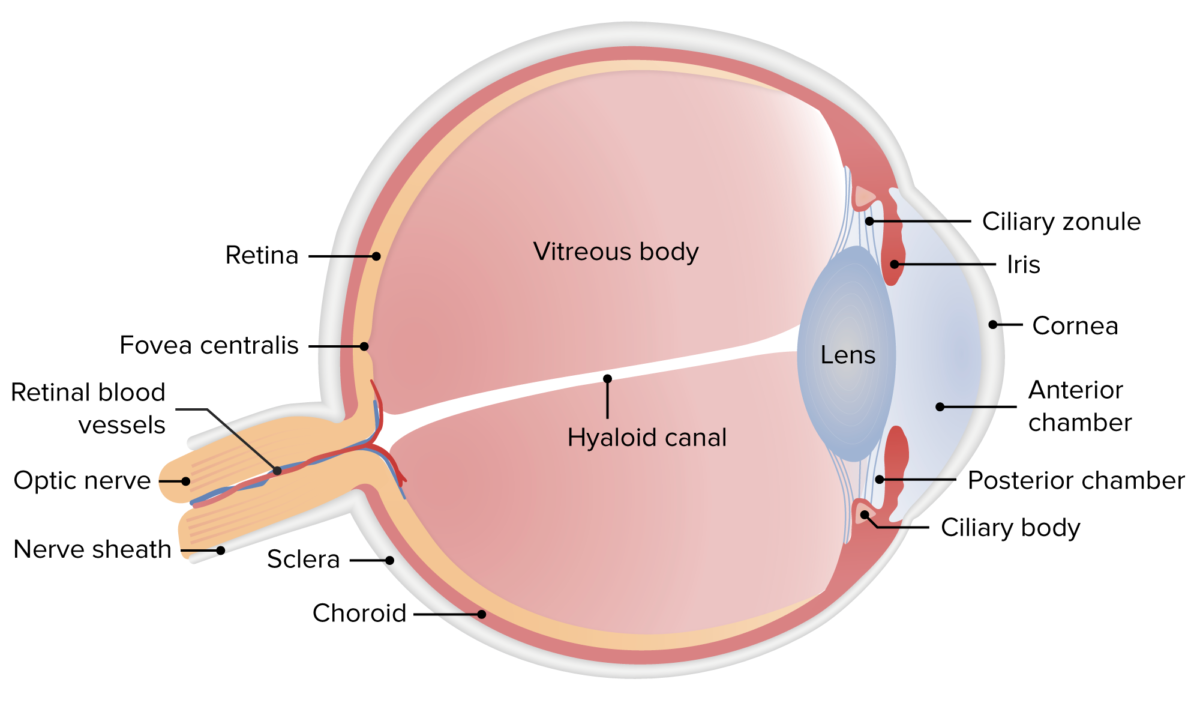
Anatomía del ojo humano
Imagen por Lecturio.Infección activa
Infección reactivada
Guiadas por:
| Infecciones | Hallazgos oftalmológicos |
|---|---|
| Toxoplasmosis Toxoplasmosis Toxoplasmosis is an infectious disease caused by Toxoplasma gondii, an obligate intracellular protozoan parasite. Felines are the definitive host, but transmission to humans can occur through contact with cat feces or the consumption of contaminated foods. The clinical presentation and complications depend on the host’s immune status. Toxoplasma/Toxoplasmosis |
|
| Toxoplasmosis Toxoplasmosis Toxoplasmosis is an infectious disease caused by Toxoplasma gondii, an obligate intracellular protozoan parasite. Felines are the definitive host, but transmission to humans can occur through contact with cat feces or the consumption of contaminated foods. The clinical presentation and complications depend on the host’s immune status. Toxoplasma/Toxoplasmosis congénita | Lesión macular perforada o excavada |
| Retinitis por CMV |
|
| Tuberculosis Tuberculosis Tuberculosis (TB) is an infectious disease caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex bacteria. The bacteria usually attack the lungs but can also damage other parts of the body. Approximately 30% of people around the world are infected with this pathogen, with the majority harboring a latent infection. Tuberculosis spreads through the air when a person with active pulmonary infection coughs or sneezes. Tuberculosis |
|
| Toxocariasis Toxocariasis Toxocariasis is caused by the nematodes Toxocara canis and T. cati. These species frequently infect dogs and cats and are most commonly transmitted to humans via accidental ingestion of eggs through the fecal-oral route. Toxocara are not able to complete their life cycle in humans, but they do migrate to organs (including the liver, lungs, heart, brain, and eyes), where they cause inflammation and tissue damage. Toxocariasis | Granuloma blanquecino en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la periferia o en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el polo posterior (de localización larvaria) |
| Sífilis | Gran imitador: se presenta como coriorretinitis, papiledema, neuritis óptica, lesiones placoides |
| Síndrome de histoplasmosis Histoplasmosis Histoplasmosis is an infection caused by Histoplasma capsulatum, a dimorphic fungus. Transmission is through inhalation, and exposure to soils containing bird or bat droppings increases the risk of infection. Most infections are asymptomatic; however, immunocompromised individuals generally develop acute pulmonary infection, chronic infection, or even disseminated disease. Histoplasma/Histoplasmosis ocular | Lesiones coriorretinianas discretas, ovaladas-redondas (manchas de histoplasmosis “perforadas”) |
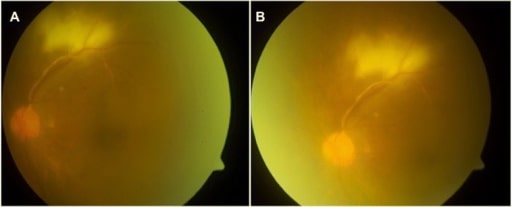
Fotografías del fondo del ojo izquierdo que muestran vitritis tuberculosa, vasculitis y coriorretinitis superior a la mácula
Imagen: “Left eye showing vitritis, vasculitis and chorioretinitis” por Department of Ophthalmology, Tan Tock Seng Hospital, Singapore, 308433 Singapore. Licencia: CC BY 4.0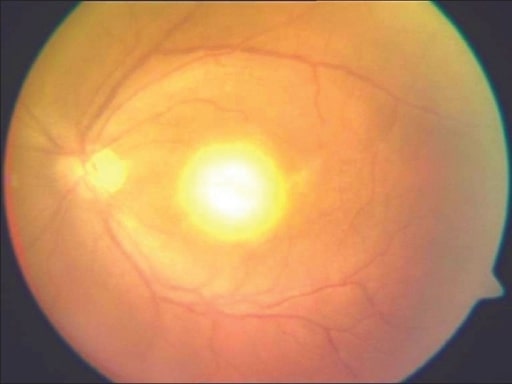
Típica “apariencia de faro en la niebla” en un paciente con toxoplasmosis adquirida
Imagen: “Headlight in the fog appearance” por Medical Research Foundation, Chennai, India. Licencia: CC BY 2.0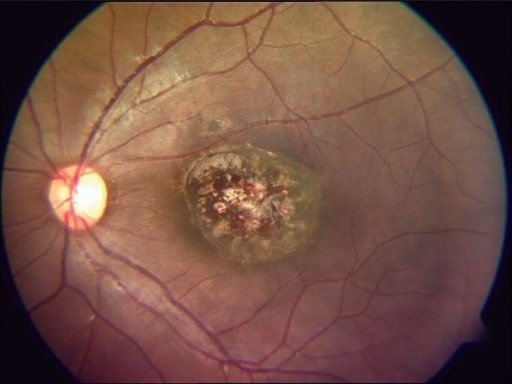
Imagen de fondo de ojo que muestra una cicatriz macular perforada típica de una toxoplasmosis congénita curada
Imagen: “healed congenital toxoplasmosis” por Medical Research Foundation, Chennai, India. Licencia: CC BY 2.0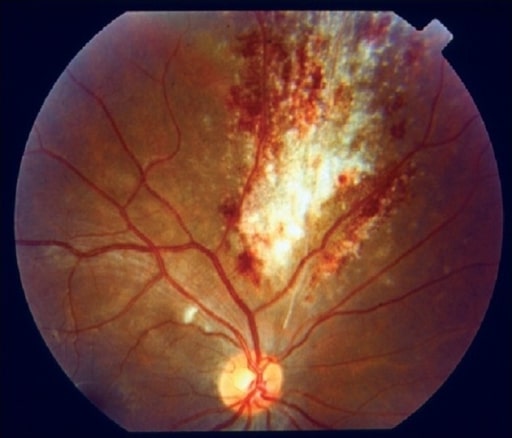
Imagen del fondo de ojo que muestra el típico “aspecto de tarta de pizza” en un paciente con retinitis por citomegalovirus
Image: “pizza pie appearance” por Medical Research Foundation, Chennai, India. Licencia: CC BY 2.0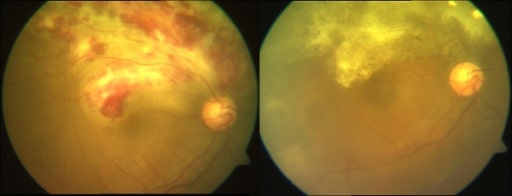
Fotografías compuestas de fondo de ojo en color que muestran un caso de retinitis por CMV activa y curada. Antes (izquierda) y después del tratamiento (derecha) con ganciclovir.
Imagen: “active and healed CMV retinitis” por Medical Research Foundation, 18, College Road, Sankara Nethralaya, Chennai, 600006, India. Licencia: CC BY 2.0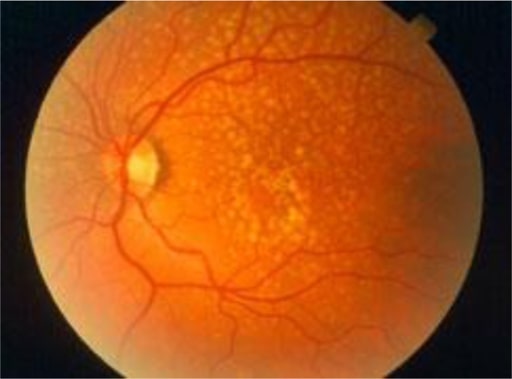
Las drusas son depósitos amarillos bajo la retina, el tejido sensible a la luz situado en la parte posterior del ojo. Las drusas están formadas por lípidos y proteínas grasas.
Imagen: “Oxidative stress, innate immunity, and age-related macular degeneration” por Department of Ophthalmology y Shiley Eye Institute, University of California San Diego, San Diego, CA, USA. Licencia: CC BY 4.0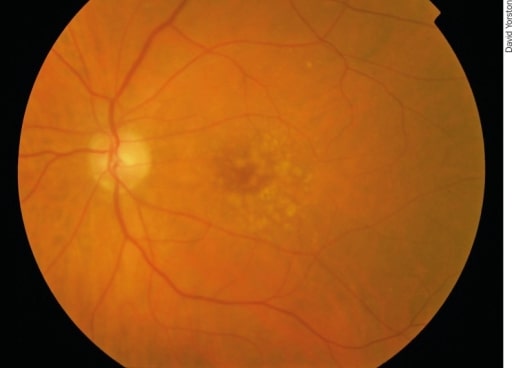
Degeneración macular asociada a la edad en una etapa temprana: Hay puntos pálidos irregulares en la mácula, que se llaman drusas. Se producen por la acumulación de productos de desecho del metabolismo de los fotorreceptores. Aunque las drusas están asociadas a la degeneración macular, la mayoría de los pacientes con drusas no desarrollarán una enfermedad grave.
Image: “Early AMD” por Africa Regional Medical Advisor: Fred Hollows Foundation, Kigali, Rwanda. Licencia: CC BY 2.0| Enfermedad/condición | Hallazgos oftalmológicos |
|---|---|
| Sarcoidosis Sarcoidosis Sarcoidosis is a multisystem inflammatory disease that causes noncaseating granulomas. The exact etiology is unknown. Sarcoidosis usually affects the lungs and thoracic lymph nodes, but it can also affect almost every system in the body, including the skin, heart, and eyes, most commonly. Sarcoidosis |
|
| Enfermedad de Behcet |
|
| Retinocoroidopatía en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum perdigonada | Lesiones en forma de “perdigones”: lesiones coroideas de color crema que irradian desde el disco óptico |
| Síndrome de puntos blancos |
|
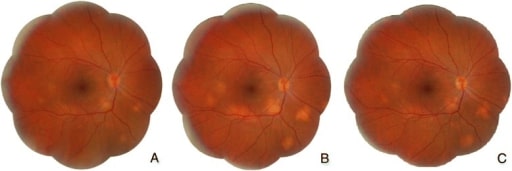
Sarcoidosis:
A. Visita inicial: hiperemia y edema del disco óptico y lesiones subretinianas amarillentas localizadas en el polo posterior y en la periferia media inferior
B. Tras 6 meses de tratamiento con prednisona: disminución de la hiperemia y el edema del disco óptico, pero aumento de los granulomas coroideos
C. Tras 18 meses de tratamiento con prednisona y metotrexato: disminución de los granulomas coroideos
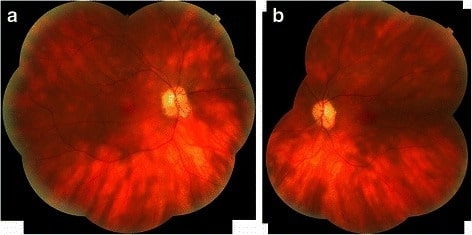
Fotomontaje de los ojos derecho (a) e izquierdo (b) de un paciente con retinocoroidopatía en perdigonada que revela las clásicas lesiones ovoides cremosas y las estrías lineales que emanan del disco óptico.
Imagen: “Birdshot chorioretinopathy” por Department of Ophthalmology, Queen Elizabeth Hospital Birmingham, University Hospitals Birmingham NHS Foundation Trust, Birmingham, UK. Licencia: CC BY 4.0La coriorretinitis no infecciosa se trata con corticoides e inmunosupresores.
En EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum caso de coriorretinitis no resolutiva, descartar las neoplasias (síndromes de enmascaramiento).
El diagnóstico diferencial de la coriorretinitis incluye las siguientes condiciones: