La colecistitis es la inflamación de la vesícula biliar generalmente causada por la obstrucción del conducto cístico (colecistitis aguda). La irritación mecánica por cálculos biliares también puede producir inflamación crónica de la vesícula biliar. La colecistitis es una de las complicaciones más comunes de la colelitiasis (colecistitis calculosa), pero la inflamación sin cálculos biliares (colecistitis acalculosa) puede ocurrir en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum una minoría de pacientes. El tipo agudo generalmente se presenta con dolor Dolor Inflammation en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el cuadrante superior derecho, fiebre y leucocitosis. El diagnóstico se realiza clínicamente y se confirma mediante ultrasonido. El tratamiento definitivo es la colecistectomía, preferentemente dentro de las 72 horas. Esta condición puede presentarse como una condición leve o como una enfermedad grave (con complicaciones como gangrena de la vesícula biliar, perforación, empiema) que requieren una intervención urgente.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
La colecistitis es la inflamación de la vesícula biliar.
Tipos:
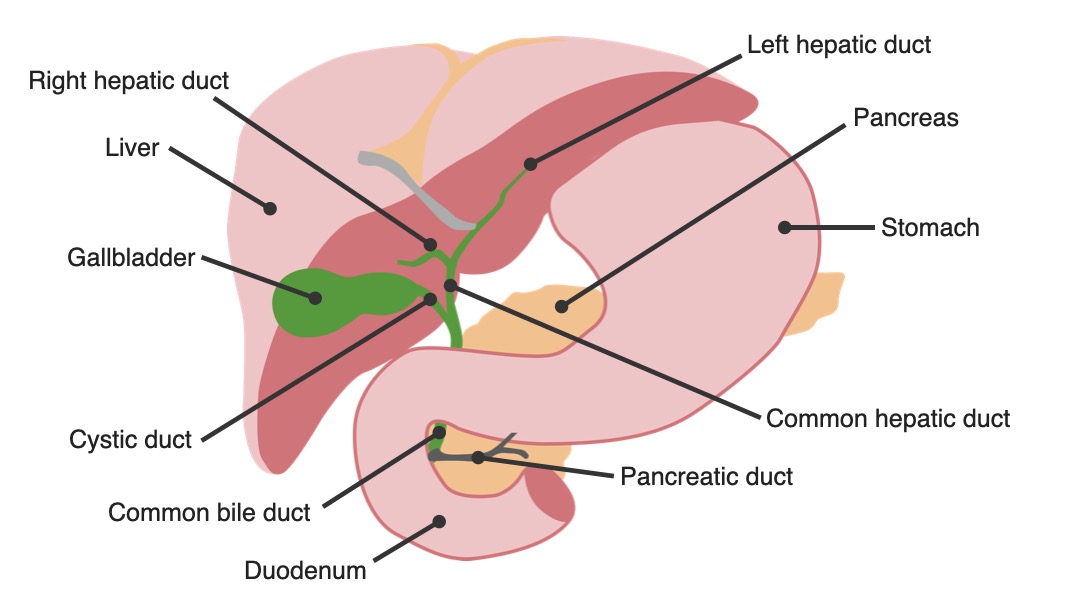
Anatomía del árbol biliar: vesícula biliar en relación con otros órganos
Imagen por Lecturio.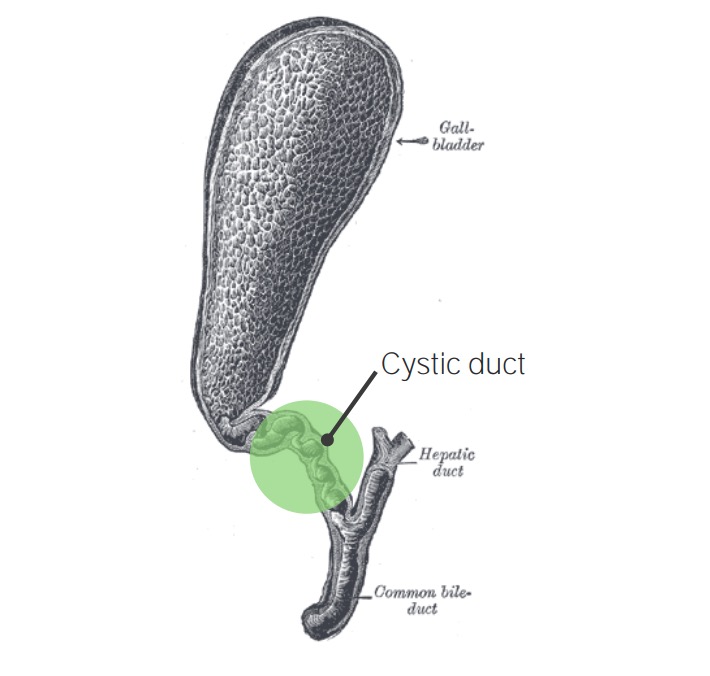
Vesícula biliar con colecistitis: obstrucción del conducto cístico
Imagen: “Gray1095-gall bladder” por Henry Vandyke Carter. Licencia: Dominio Público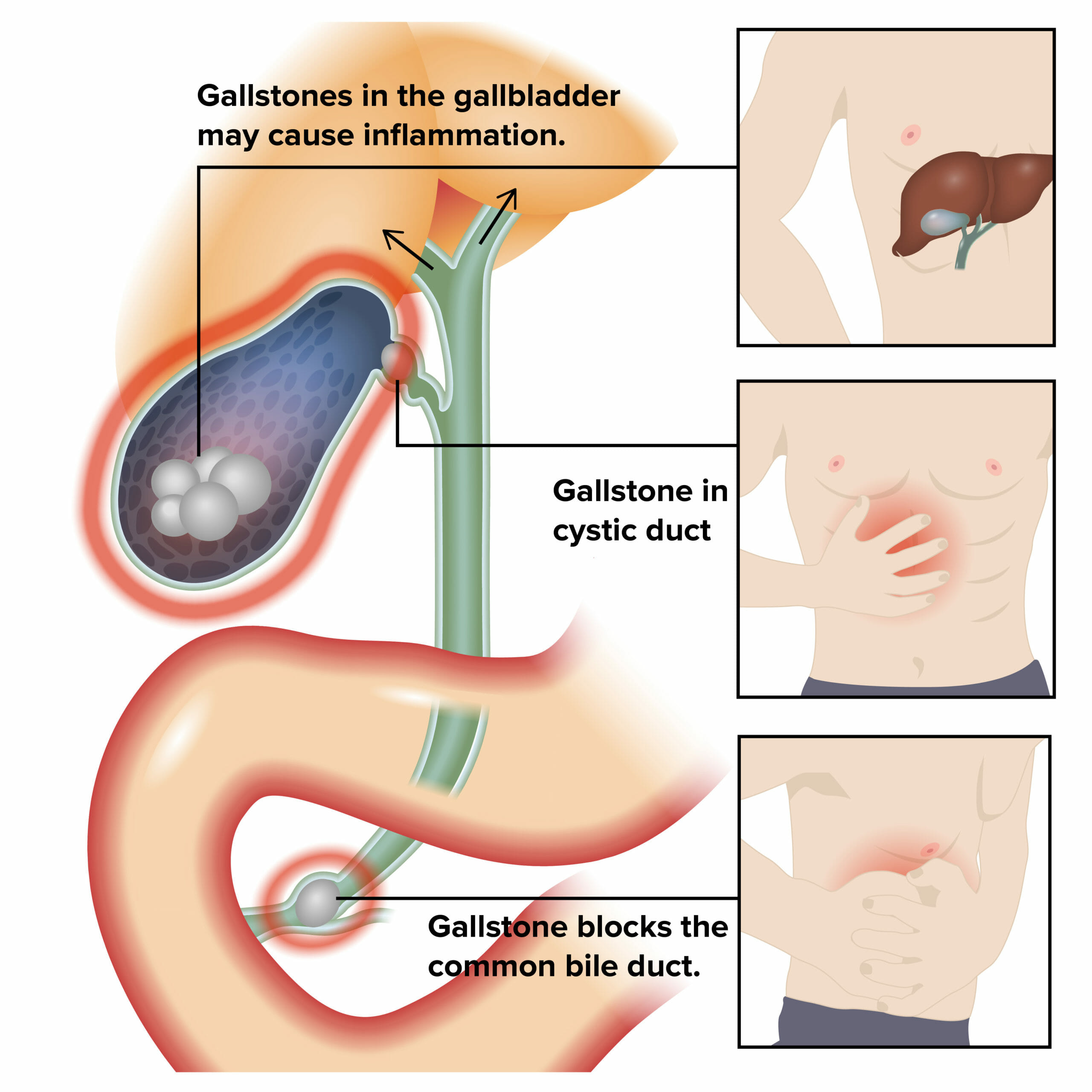
Etiología y fisiopatología de la colecistitis:
La inflamación de la vesícula biliar y la obstrucción biliar dan lugar a los síntomas.
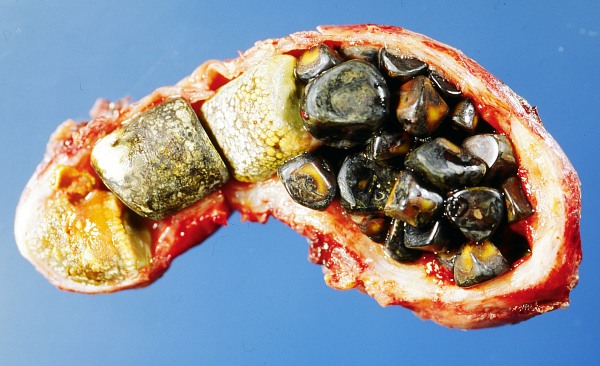
Vesícula biliar abierta con cálculos biliares
Imagen: “Opened gall bladder containing numerous gallstones” por Emmanuelm. Licencia: CC BY 3.0
El signo de Boas es hiperestesia debajo de la escápula derecha (observada en la colecistitis aguda).
Imagen por Lecturio.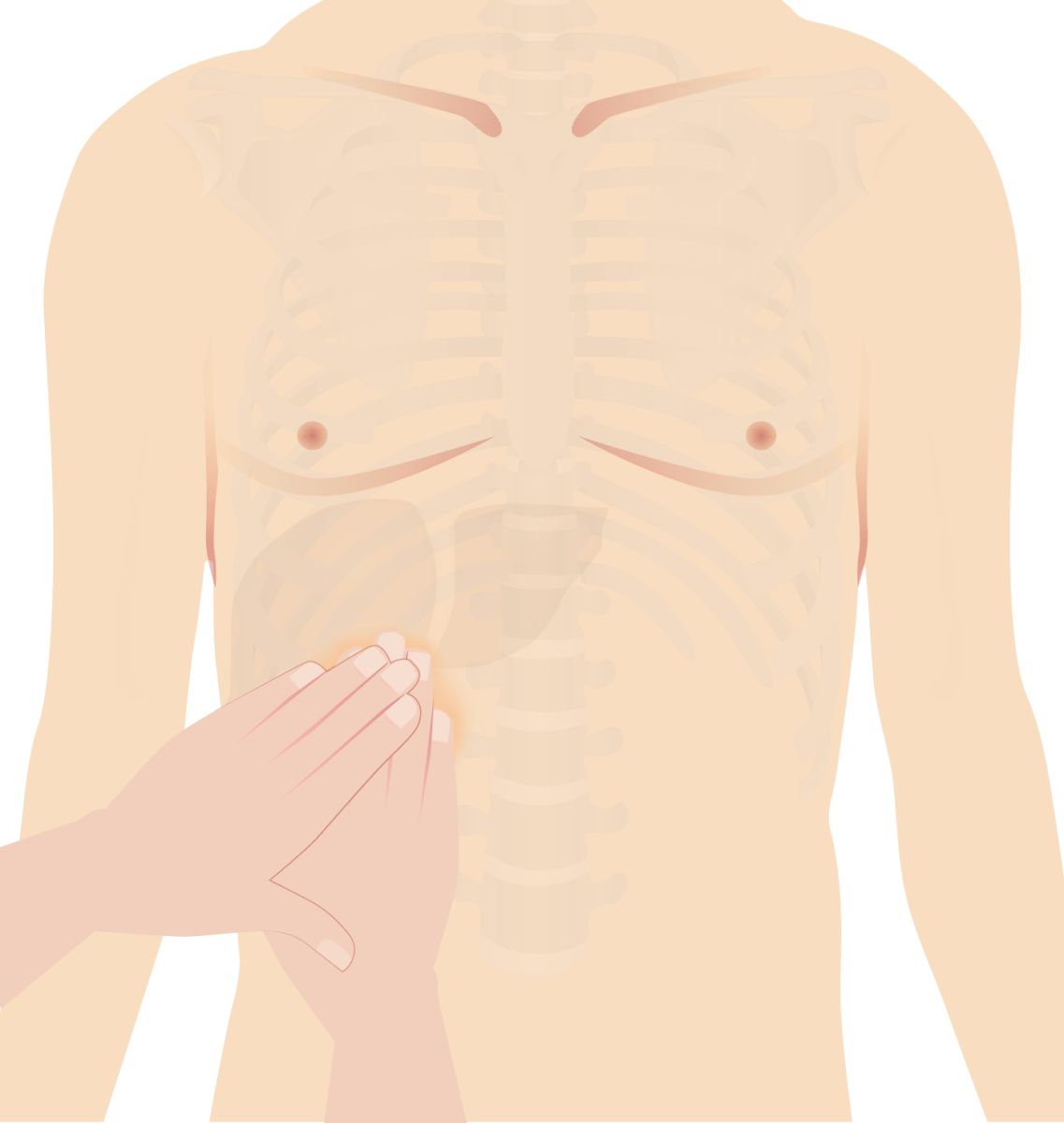
Signo de Murphy: El examinador coloca la mano en el área de la vesícula biliar (área subcostal derecha). Se le indica al paciente que respire profundamente. En la inspiración, la vesícula biliar inflamada desciende, entra en contacto con la mano del examinador y causa dolor.
Imagen por Lecturio.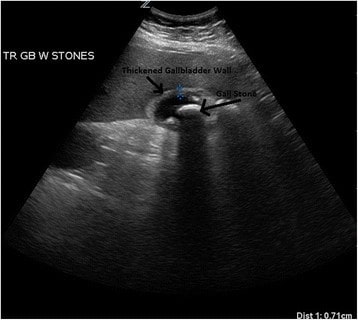
Ultrasonido de un paciente con colecistitis aguda: Se puede ver un cálculo biliar muy grande con un edema circundante significativo.
Imagen: “Ultrasound of a patient with acute cholecystitis” por Department of Emergency Medicine, University of Maryland School of Medicine, 110 South Paca Street, 6th Floor, Suite 200, Baltimore 21201, MD, USA. Licencia: CC BY 4.0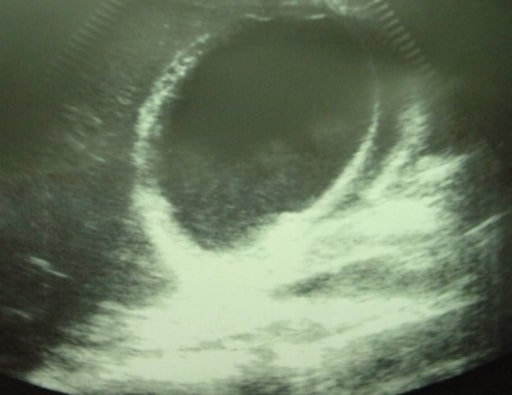
Colecistitis aguda que muestra líquido pericolecístico
Imagen: “Ultrasonographic image of the gallbladder” por Department of Surgery, University Hospital Hassan II, Morocco. Licencia: CC BY 2.0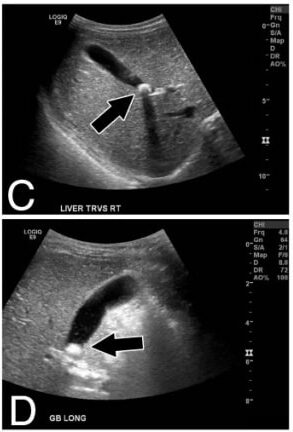
Paneles C, D: Vistas de ultrasonido transversales y longitudinales del hígado y la vesícula biliar (las flechas indican el cálculo biliar)
Imagen: “Calcified gallstone” por Division of Pediatric Surgery, Children’s Hospital Los Angeles, 4650 Sunset Blvd Mailstop 100, Los Angeles, CA 90027, USA. Licencia: CC BY 2.0