La artritis séptica es una infección de la articulación debida a la inoculación directa, la extensión contigua o la propagación hematógena de organismos infecciosos en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el espacio articular. Este proceso provoca una artritis aguda, inflamatoria y monoarticular. Se han implicado diversos microorganismos, el más común es Staphylococcus aureus Staphylococcus aureus Potentially pathogenic bacteria found in nasal membranes, skin, hair follicles, and perineum of warm-blooded animals. They may cause a wide range of infections and intoxications. Brain Abscess. Las articulaciones previamente afectadas (e.g., por artritis reumatoide) son las que presentan un mayor riesgo de infección. Los LOS Neisseria pacientes presentan una articulación inflamada, caliente y sensible, que suele afectar a la rodilla. Los LOS Neisseria cultivos positivos de la artrocentesis son diagnósticos, con una terapia antibiótica específica para el microorganismo evidenciado. En EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum algunos casos se requiere la aspiración articular seriada o el drenaje quirúrgico. Si el espacio articular está infectado con una prótesis en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum posición, también puede ser necesario desbridar y retirar la prótesis.
Last updated: Feb 3, 2026
La mayoría de las infecciones en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la artritis séptica son monomicrobianas. Los LOS Neisseria microorganismos más comunes son:
| Factores de riesgo | Agentes infecciosos |
|---|---|
| Ningún factor de riesgo específico | S. aureus S. aureus Potentially pathogenic bacteria found in nasal membranes, skin, hair follicles, and perineum of warm-blooded animals. They may cause a wide range of infections and intoxications. Staphylococcus |
| Colocación de prótesis articulares |
|
| Enfermedad crónica, trastorno autoinmune, infección de la piel, traumatismo, adultos mayores | S. pyogenes (estreptococo beta-hemolítico del grupo A) |
| Joven, sexualmente activo | N. gonorrhoeae N. gonorrhoeae A species of gram-negative, aerobic bacteria primarily found in purulent venereal discharges. It is the causative agent of gonorrhea. Neisseria |
| Trauma | S. epidermidis S. epidermidis A species of staphylococcus that is a spherical, non-motile, gram-positive, chemoorganotrophic, facultative anaerobe. Mainly found on the skin and mucous membrane of warm-blooded animals, it can be primary pathogen or secondary invader. Staphylococcus |
| Anemia Anemia Anemia is a condition in which individuals have low Hb levels, which can arise from various causes. Anemia is accompanied by a reduced number of RBCs and may manifest with fatigue, shortness of breath, pallor, and weakness. Subtypes are classified by the size of RBCs, chronicity, and etiology. Anemia: Overview and Types falciforme |
|
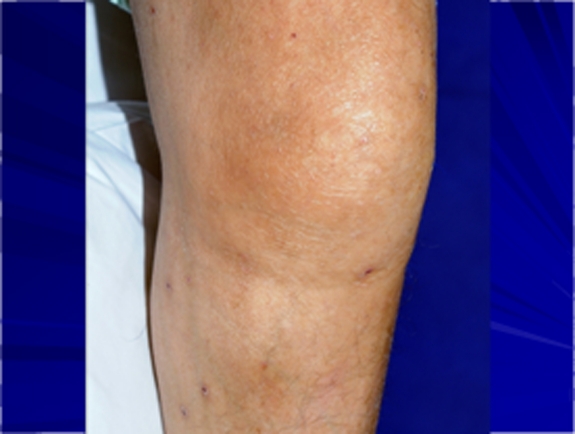
Hinchazón de la rodilla y eritema leve en un paciente con artritis séptica
Imagen: “Troublesome Tuberculosis: A Case Report on Multi-focal Tuberculous Osteomyelitisin An Immunocompetent Patient” por Lynn MM, Kukanesen JR, Khan AW. Licencia: CC BY 2.0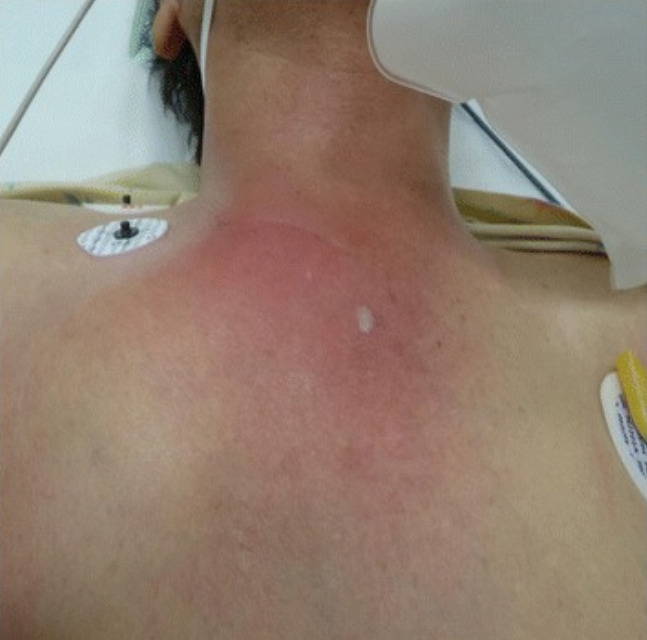
Eritema significativo e hinchazón sobre la articulación esternoclavicular derecha, lo que hace sospechar de una artritis séptica
Imagen: “Sternoclavicular joint septic arthritis with chest wall abscess in a healthy adult: a case report” por Tanaka Y, Kato H, Shirai K, Nakajima Y, Yamada N, Okada H, Yoshida T, Toyoda I, Ogura S. Licencia: CC BY 4.0El diagnóstico de la artritis séptica se realiza con el análisis del líquido sinovial.
Estudios de laboratorio que apoyan el diagnóstico:

Radiografía que muestra la inflamación de los tejidos blandos del tobillo derecho, en un paciente de 8 meses con artritis séptica
Imagen: “Polyarticular Septic Arthritis Caused by Haemophilus influenzae Serotype f in an 8-Month-Old Immunocompetent Infant: A Case Report and Review of the Literature” por Ali RA, Kaplan SL, Rosenfeld SB. Licencia: CC BY 3.0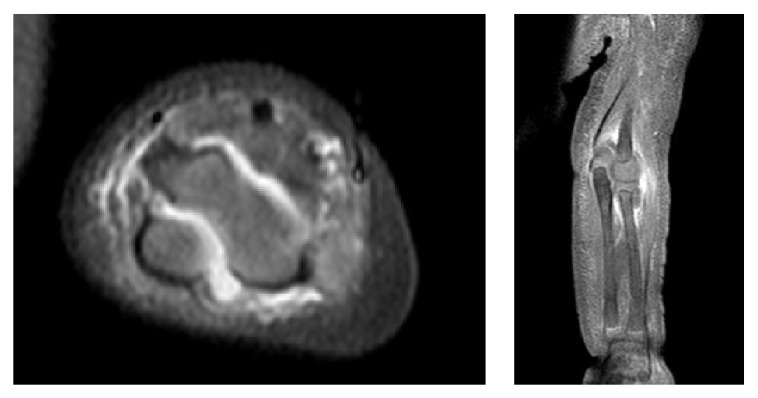
RM que muestra una gran efusión entre el húmero y la apófisis del olécranon en un paciente pediátrico con artritis séptica
Imagen: “Polyarticular Septic Arthritis Caused by Haemophilus influenzae Serotype f in an 8-Month-Old Immunocompetent Infant: A Case Report and Review of the Literature” por Ali RA, Kaplan SL, Rosenfeld SB. Licencia: CC BY 3.0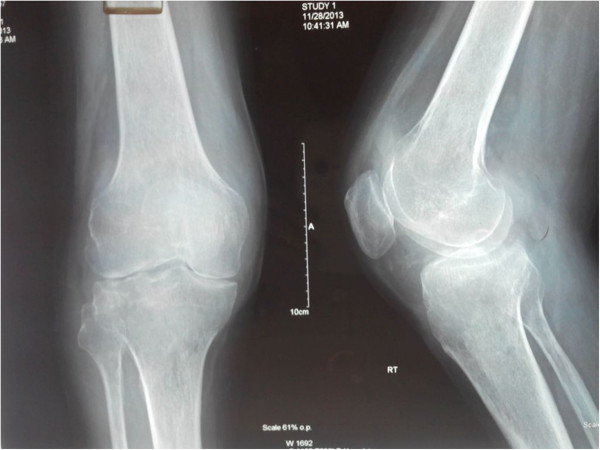
Radiografía de la rodilla que demuestra una leve osteopenia periarticular y una importante disminución del espacio articular en un paciente con artritis séptica
Imagen: “Disseminated Aspergillus flavus following septic arthritis in an immunocompetent patient: a case report” por Tiwari V, Khatri K, Khan SA, Nath D. Licencia: CC BY 4.0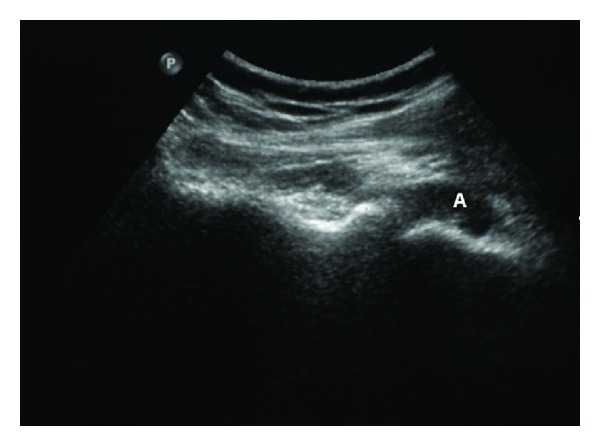
Ultrasonido de la articulación glenohumeral del hombro derecho que muestra la cara posterior de la cápsula articular distendida por líquido (A) en un paciente con artritis séptica
Imagen: “Streptococcus agalactiae Septic Arthritis of the Shoulder and the Sacroiliac Joints: A Case Report” por Imam YZ, Sarakbi HA, Abdelwahab N, Mattar I. Licencia: CC BY 3.0La selección de antibióticos está basada en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la tinción de Gram inicial y se modifica en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum función de los LOS Neisseria datos del cultivo.
La duración del tratamiento depende de factores adicionales:
Drenaje de la articulación:
Desbridamiento quirúrgico en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum pacientes con prótesis: