Los LOS Neisseria antiarrítmicos de clase 2 incluyen los LOS Neisseria betabloqueadores, que ejercen sus efectos terapéuticos bloqueando la unión de la epinefrina y la norepinefrina a los LOS Neisseria receptores beta-adrenérgicos del tejido cardíaco. El resultado es un efecto antiarrítmico, que resulta de la disminución de la actividad del nodo sinoauricular y del aumento del tiempo de conducción auriculoventricular y del período refractario. Otros efectos adicionales son la disminución de la contractilidad cardíaca, la poscarga y la presión arterial. Los LOS Neisseria antiarrítmicos de clase 2 se utilizan en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el tratamiento de fibrilación auricular, flutter auricular, taquicardia supraventricular y arritmias ventriculares. Los LOS Neisseria efectos secundarios incluyen bradicardia, hipotensión, broncoespasmo, retención de líquidos y fatiga. Los LOS Neisseria betabloqueadores no deben emplearse en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum individuos con insuficiencia cardíaca descompensada, shock Shock Shock is a life-threatening condition associated with impaired circulation that results in tissue hypoxia. The different types of shock are based on the underlying cause: distributive (↑ cardiac output (CO), ↓ systemic vascular resistance (SVR)), cardiogenic (↓ CO, ↑ SVR), hypovolemic (↓ CO, ↑ SVR), obstructive (↓ CO), and mixed. Types of Shock y bradicardia severa.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Los LOS Neisseria antiarrítmicos de clase 2 incluyen los LOS Neisseria betabloqueadores, que inhiben de forma competitiva la unión de la epinefrina y la norepinefrina a los LOS Neisseria receptores beta-adrenérgicos de las células vasculares y cardíacas.
Estructura química del propranolol
Imagen: “Chemical structure of propranolol” por catclock. Licencia: Dominio Público
El efecto de los antiarrítmicos de clase 2 (betabloqueadores) sobre el potencial de acción nodal:
La línea punteada muestra la disminución de la pendiente y el aumento de la duración de la fase 4.
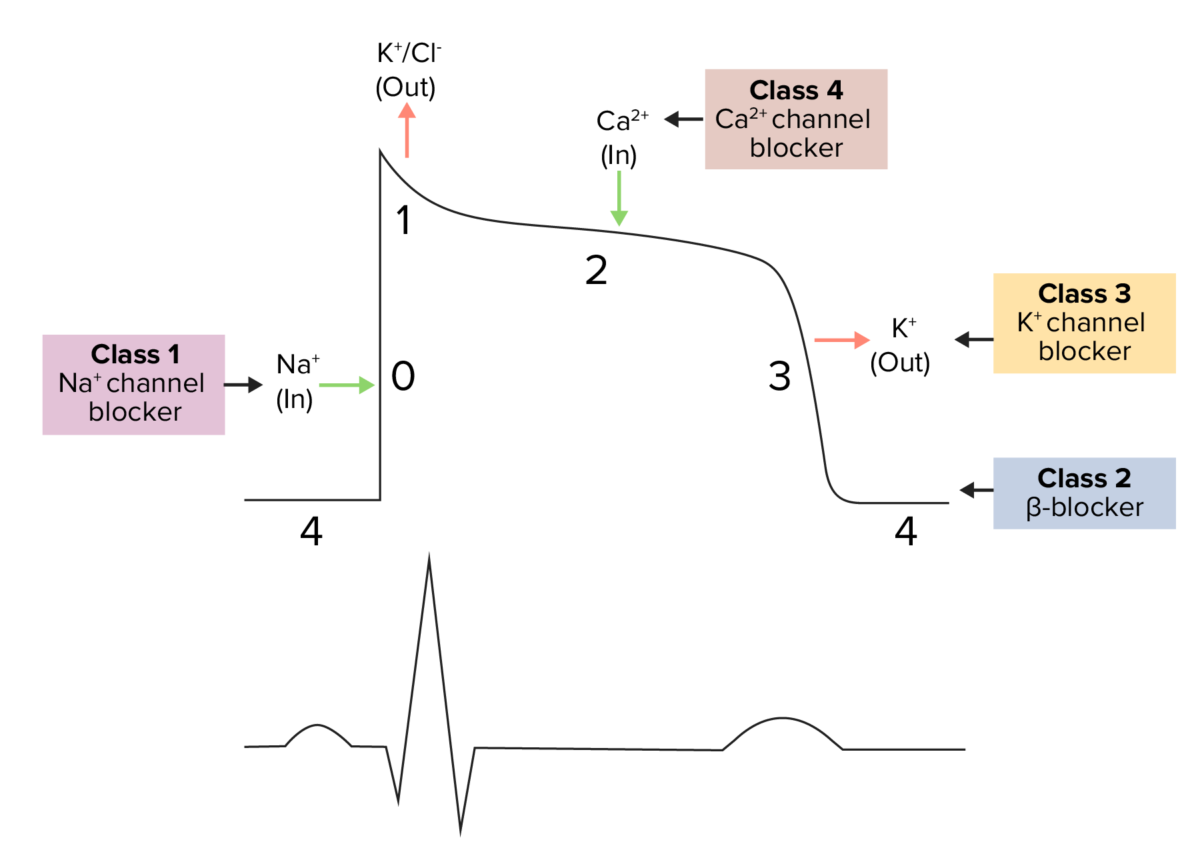
Diagrama que muestra un potencial de acción cardíaco y las fases de acción de diferentes clases de medicamentos antiarrítmicos:
El ciclo comienza con la fase 4, el potencial de reposo. La fase 0 es cuando se produce una despolarización rápida debido a la entrada de iones de sodio en la célula. A continuación, se produce la repolarización, con salida de potasio a través de los canales rápidos de potasio en la fase 1, entrada de calcio en la fase 2 que provoca una meseta (lugar de acción de los bloqueadores de los canales de calcio) y salida de potasio a través de los canales de potasio retardados en la fase 3.
| Ubicación del receptor Receptor Receptors are proteins located either on the surface of or within a cell that can bind to signaling molecules known as ligands (e.g., hormones) and cause some type of response within the cell. Receptors | Respuesta al AL Amyloidosis estímulo | Respuesta al AL Amyloidosis bloqueo | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Receptores B1 | |||
| Corazón | Nodo SA | ↑ FC Fc Crystallizable fragments composed of the carboxy-terminal halves of both immunoglobulin heavy chains linked to each other by disulfide bonds. Fc fragments contain the carboxy-terminal parts of the heavy chain constant regions that are responsible for the effector functions of an immunoglobulin (complement fixation, binding to the cell membrane via fc receptors, and placental transport). This fragment can be obtained by digestion of immunoglobulins with the proteolytic enzyme papain. Immunoglobulins: Types and Functions | ↓ FC Fc Crystallizable fragments composed of the carboxy-terminal halves of both immunoglobulin heavy chains linked to each other by disulfide bonds. Fc fragments contain the carboxy-terminal parts of the heavy chain constant regions that are responsible for the effector functions of an immunoglobulin (complement fixation, binding to the cell membrane via fc receptors, and placental transport). This fragment can be obtained by digestion of immunoglobulins with the proteolytic enzyme papain. Immunoglobulins: Types and Functions |
| Aurículas | ↑ Contractilidad y velocidad de conducción | ↓ Contractilidad y velocidad de conducción | |
| Nodo AV y fibras de His-Purkinje | ↑ Automatismo y velocidad de conducción | ↓ Automatismo y velocidad de conducción | |
| Ventrículos | ↑ Contractilidad, automatismo, velocidad de conducción | ↓ Contractilidad, automatismo, velocidad de conducción | |
| Riñón | Células YG | ↑ Liberación de renina | ↓ Liberación de renina |
| Receptores B2 | |||
| Arterias |
|
Vasodilatación | Vasoconstricción |
| Pulmones | Músculo liso bronquiolar | Broncodilatación | Broncoconstricción |
| Vejiga | Pared | Relajación | Contracción |
| Hígado | Tejido hepático | Estimula la glucogenolisis |
|
| Receptores A1 | |||
| Arterias | Periféricas | Vasoconstricción | Vasodilatación |
| Vejiga | Esfínter | Contracción | Relajación |
Algunos betabloqueadores pueden presentar las siguientes propiedades y efectos:
| Propiedad de betabloqueadores | Efecto |
|---|---|
| ISA | Estimulación parcial de los LOS Neisseria receptores B → descenso subóptimo de la FC Fc Crystallizable fragments composed of the carboxy-terminal halves of both immunoglobulin heavy chains linked to each other by disulfide bonds. Fc fragments contain the carboxy-terminal parts of the heavy chain constant regions that are responsible for the effector functions of an immunoglobulin (complement fixation, binding to the cell membrane via fc receptors, and placental transport). This fragment can be obtained by digestion of immunoglobulins with the proteolytic enzyme papain. Immunoglobulins: Types and Functions (evitar post-IM) |
| MSA MSA A syndrome complex composed of three conditions which represent clinical variants of the same disease process: striatonigral degeneration; shy-drager syndrome; and the sporadic form of olivopontocerebellar atrophies. Clinical features include autonomic, cerebellar, and basal ganglia dysfunction. Pathologic examination reveals atrophy of the basal ganglia, cerebellum, pons, and medulla, with prominent loss of autonomic neurons in the brain stem and spinal cord. Atypical Parkinsonian Syndromes | El medicamento puede ↓ la velocidad de conducción cardíaca al AL Amyloidosis bloquear los LOS Neisseria canales de Na+ de los LOS Neisseria miocitos |
| NO (Oxído nítrico) | El medicamento estimula la producción de NO → vasodilatación periférica |
Los LOS Neisseria antiarrítmicos de clase 2 pueden clasificarse en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum función de su selectividad de los LOS Neisseria receptores beta:
Los LOS Neisseria antiarrítmicos de clase 2 se utilizan en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el tratamiento de:
Los LOS Neisseria betabloqueadores, como clase medicamentosa, pueden usarse como tratamiento para las siguientes entidades aprobadas por la Food and Drug Administration (FDA, por sus siglas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum inglés):
| Medicamento | Arritmia | Angina | IAM | Insuficiencia cardíaca | Hipertensión | MSA MSA A syndrome complex composed of three conditions which represent clinical variants of the same disease process: striatonigral degeneration; shy-drager syndrome; and the sporadic form of olivopontocerebellar atrophies. Clinical features include autonomic, cerebellar, and basal ganglia dysfunction. Pathologic examination reveals atrophy of the basal ganglia, cerebellum, pons, and medulla, with prominent loss of autonomic neurons in the brain stem and spinal cord. Atypical Parkinsonian Syndromes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Atenolol Atenolol A cardioselective beta-1 adrenergic blocker possessing properties and potency similar to propranolol, but without a negative inotropic effect. Class 2 Antiarrhythmic Drugs (Beta Blockers)* |
|
X | X | X | ||
| Betaxolol Betaxolol A cardioselective beta-1-adrenergic antagonist with no partial agonist activity. Class 2 Antiarrhythmic Drugs (Beta Blockers)* | Fibrilación auricular | X | X | |||
| Bisoprolol Bisoprolol A cardioselective beta-1 adrenergic blocker. It is effective in the management of hypertension and angina pectoris. Class 2 Antiarrhythmic Drugs (Beta Blockers)* |
|
X | X | X | ||
| Metoprolol Metoprolol A selective adrenergic beta-1 blocking agent that is commonly used to treat angina pectoris; hypertension; and cardiac arrhythmias. Antiadrenergic Drugs* |
|
X | X | X | X | X |
| Esmolol Esmolol Antiadrenergic Drugs* |
|
X | ||||
| Acebutolol Acebutolol A cardioselective beta-1 adrenergic antagonist with little effect on the bronchial receptors. The drug has stabilizing and quinidine-like effects on cardiac rhythm, as well as weak inherent sympathomimetic action. Class 2 Antiarrhythmic Drugs (Beta Blockers)* | Ventricular | X | X | X | X | |
| Nadolol Nadolol A non-selective beta-adrenergic antagonist with a long half-life, used in cardiovascular disease to treat arrhythmias, angina pectoris, and hypertension. Nadolol is also used for migraine disorders and for tremor. Class 2 Antiarrhythmic Drugs (Beta Blockers) |
|
X | X | X | ||
| Propranolol Propranolol A widely used non-cardioselective beta-adrenergic antagonist. Propranolol has been used for myocardial infarction; arrhythmia; angina pectoris; hypertension; hyperthyroidism; migraine; pheochromocytoma; and anxiety but adverse effects instigate replacement by newer drugs. Antiadrenergic Drugs |
|
X | X | X | X | |
| Timolol Timolol A beta-adrenergic antagonist that is similar in action to propranolol; the levo-isomer is more active. Timolol has been proposed as an anti-hypertensive, anti-arrhythmic, anti-angina, and anti-glaucoma agent. It is also used in the treatment of migraine disorders and tremor. Class 2 Antiarrhythmic Drugs (Beta Blockers) | Fibrilación auricular | X | X | X | ||
| Carvedilol Carvedilol A carbazole and propanol derivative that acts as a non-cardioselective beta blocker and vasodilator. It has blocking activity for alpha 1 adrenergic receptors and, at higher doses, may function as a blocker of calcium channels; it also has antioxidant properties. Carvedilol is used in the treatment of hypertension; angina pectoris; and heart failure. It can also reduce the risk of death following myocardial infarction. Class 2 Antiarrhythmic Drugs (Beta Blockers) | Fibrilación/flutter auricular | X | X | X | X | X |
La siguiente tabla compara los LOS Neisseria antiarrítmicos, clases 1-4. La clase 5 no se incluye debido a sus variados mecanismos de acción y efectos.
| Clase | Mecanismo de acción | Efectos | Indicaciones para arritmia | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1A |
|
|
|
| 1B | Ventricular | |||
| 1C | Mayormente auricular | |||
| 2 |
|
|
Auricular y ventricular | |
| 3 |
|
Auricular y ventricular | ||
| 4 |
|
|
Auricular | |