Un aneurisma aórtico es la dilatación anormal de un segmento de la aorta Aorta The main trunk of the systemic arteries. Mediastinum and Great Vessels: Anatomy. El aneurisma de la aorta Aorta The main trunk of the systemic arteries. Mediastinum and Great Vessels: Anatomy abdominal es el aneurisma de aorta Aorta The main trunk of the systemic arteries. Mediastinum and Great Vessels: Anatomy más común y ocurre con frecuencia en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el área infrarrenal. Los LOS Neisseria trastornos aórticos degenerativos son la etiología prevalente, afectando a pacientes > 60 años de edad. La mayoría de los LOS Neisseria aneurismas son asintomáticos, pero pueden causar compresión de estructuras circundantes o ruptura, lo cual es una emergencia que pone en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum peligro la vida. El diagnóstico se hace HACE Altitude Sickness a menudo por ultrasonido. Dado que la ruptura del aneurisma conlleva una alta tasa de mortalidad, se recomienda la vigilancia de los LOS Neisseria casos asintomáticos para monitorear el diámetro aórtico. La cirugía electiva (la mayoría a través de reparación aórtica endovascular) es una forma efectiva de reducir las complicaciones y la muerte relacionada con el aneurisma. Esta cirugía se realiza según el tamaño de la aorta Aorta The main trunk of the systemic arteries. Mediastinum and Great Vessels: Anatomy, la afección subyacente y los LOS Neisseria síntomas asociados.
Last updated: Nov 17, 2022
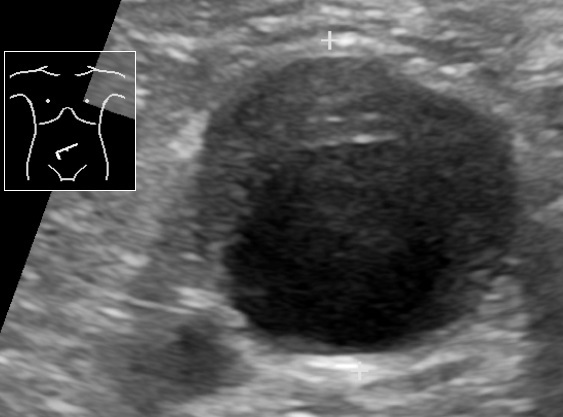
Ultrasonido que muestra un aneurisma de aorta abdominal con un trombo mural
Imagen: “Ultrasonography of abdominal aortic aneurysm with mural thrombus” por Mikael Häggström, M.D. Licencia: Dominio Público| Tratamiento de AAA AAA An aortic aneurysm is the abnormal dilation of a segment of the aorta. Abdominal aortic aneurysm is the most common aortic aneurysm, occurring frequently in the infrarenal area. Most aneurysms are asymptomatic, but can cause compression of surrounding structures or rupture, which is a life-threatening emergency. Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum pacientes asintomáticos (ultrasonido) | Tamaño de AAA AAA An aortic aneurysm is the abnormal dilation of a segment of the aorta. Abdominal aortic aneurysm is the most common aortic aneurysm, occurring frequently in the infrarenal area. Most aneurysms are asymptomatic, but can cause compression of surrounding structures or rupture, which is a life-threatening emergency. Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms |
|---|---|
| Reevaluar después de 10 años | ≥ 2,5 cm pero < 3 cm |
| Imagenología cada 3 años | 3–3,9 cm |
| Imagenología cada 12 meses | 4–4,9 cm |
| Imagenología cada 6 meses | 5–5,4 cm |
| Considerar la reparación electiva | ≥ 5,5 cm Considerar reparación si ≥5 cm en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum mujeres; expansión de < 0,5 cm/6 meses o > 1 cm/1 año; aneurisma femoral, ilíaco, poplíteo asociado o enfermedad arterial periférica que requiere revascularización |
Indicaciones para la reparación quirúrgica
Opciones quirúrgicas