Antivirals for Herpes Virus
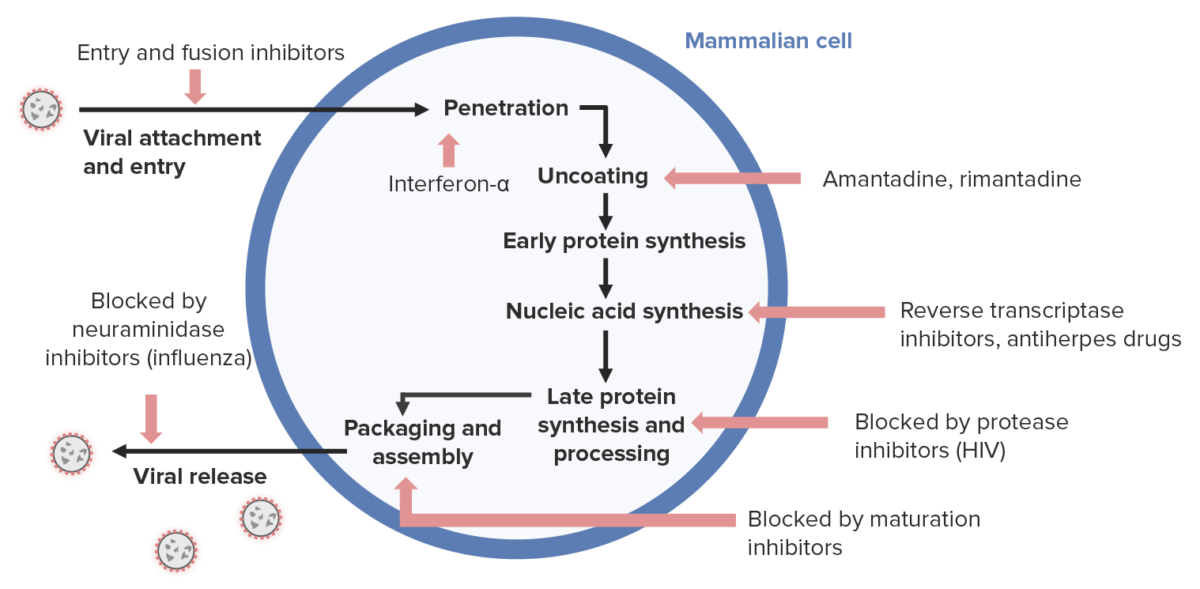
Overview Human herpesviruses (HHVs) Antiherpes agents Nucleoside Analogs Chemical structure Pharmacodynamics Acyclovir: Pharmacokinetics Indications Acyclovir (and other related agents): Adverse events and contraindications Acyclovir: Comparison of nucleoside analogs Table: Comparison of nucleoside analogs against herpesviruses Agent Characteristics and mechanism of action Pharmacokinetics Approved indication Adverse drug effects Acyclovir Nucleoside analog Polymerase inhibitor Poor oral bioavailability […]
Antivirals for Influenza

Overview Influenza Mechanism of invasion Classes of antiinfluenza agents Neuraminidase Inhibitors Chemistry and pharmacodynamics Pharmacokinetics Table: Pharmacokinetics of neuraminidase inhibitors Category Oseltamivir Peramivir Zanamivir Absorption Oral Absorbed rapidly Bioavailability not decreased by food IV Single 600-mg dose Inhalation Distribution Low plasma protein binding Half-life: 6–10 hours 30% protein-bound Half-life: 20 hours On inhalation, drug reaches […]
Class 5 Antiarrhythmic Drugs
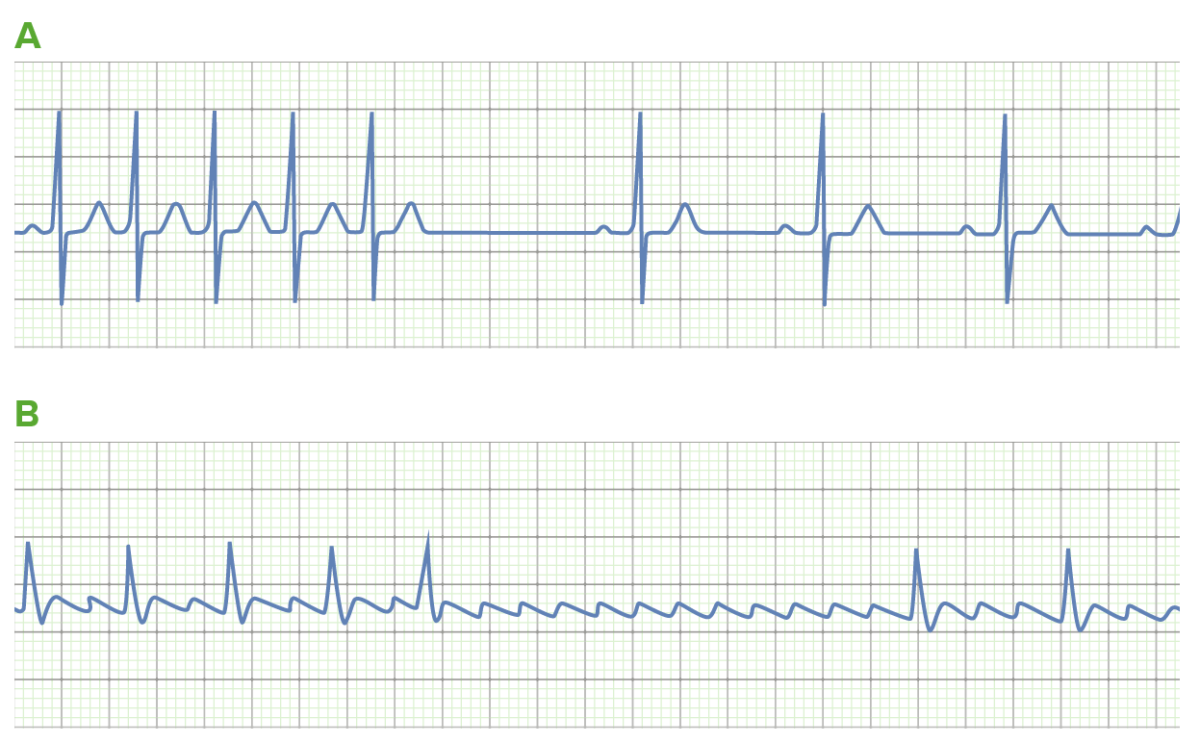
Overview Vaughan-Williams classification This is the most commonly used classifications for antiarrhythmic drugs. There are 5 classes based on the drug class’s general effect (mechanism of action): Digoxin Mechanism of action Pharmacokinetics Indications Adverse effects Contraindications Drug interactions Adenosine Chemistry Adenosine is a naturally occurring purine nucleoside base. Mechanism of action Cardiac nodal cells: Vascular […]
Class 1 Antiarrhythmic Drugs (Sodium Channel Blockers)
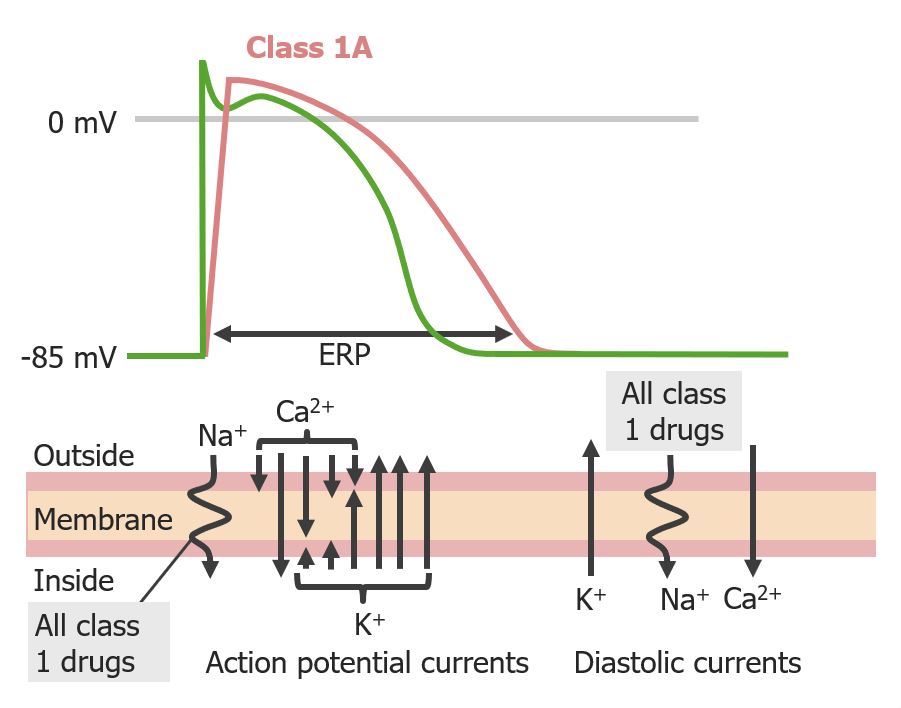
Overview Cardiac action potential Vaughan–Williams classification Mechanism of action of Na channel blockers Class 1 antiarrhythmics bind to and block the fast Na channels in non-nodal tissue (e.g., myocytes of the atria and ventricles, His-Purkinje system): Differences among the class 1 subgroups Electrophysiologic effects of class 1 antiarrhythmic drugs Table: Electrophysiologic effects of the class […]
Hypertension Drugs
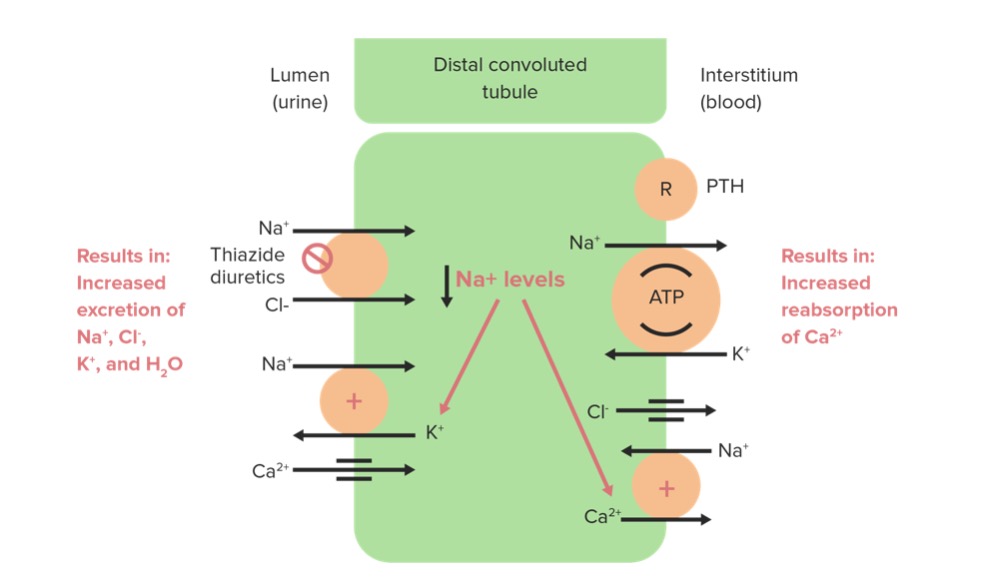
Overview Etiology Pathophysiology Classes of antihypertensive medications Current guidelines American Heart Association and American College of Cardiology guidelines (2017, 2021): Eighth Joint National Committee (JNC 8, 2014) guidelines: Selection of antihypertensive agent should be based on: Classification of hypertension Table: Classification of hypertension (2017 JNC 8 guidelines) BP category Systolic BP (mm Hg) Diastolic BP […]
Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors and Similar Antidepressants
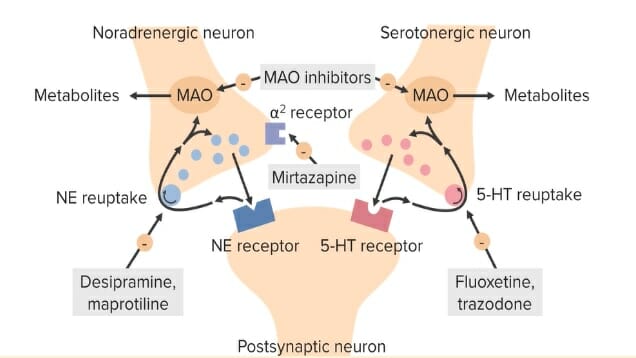
Chemistry and Pharmacodynamics Mechanisms of action Pharmacodynamics Pharmacokinetics Secondary serotonin reuptake inhibitors Serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors Serotonin antagonist and reuptake inhibitor = trazodone (nefazodone is not currently available in the US) Serotonin modulator and stimulator = vortioxetine 5-Hydroxytryptamine1A receptor partial agonist = vilazodone Classification and Indications Antidepressant medications that affect serotonin levels in the brain to […]
Nonhormonal Contraception
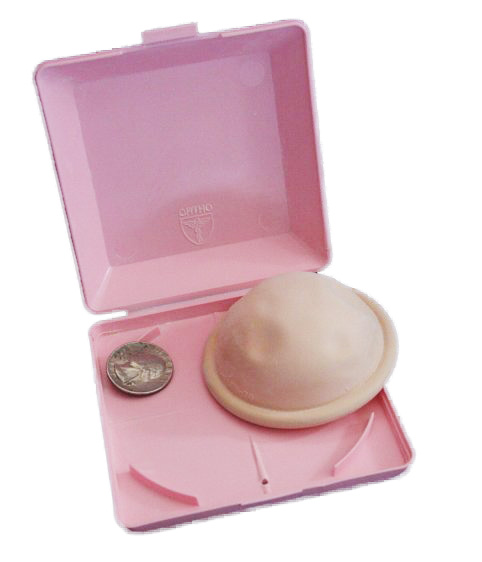

Overview Classification Nonhormonal contraception can be classified into: Choice of contraception Physiologic Methods Withdrawal/coitus interruptus Fertility awareness methods Rhythm method (calendar method) Basal body temperature method Cervical mucus method Lactational amenorrhea Barrier Methods Condoms Mechanism: Male condom: Female condom: Advantages: Disadvantages: Spermicides Diaphragm Contraceptive sponge Vaginal pH regulator gel Copper Intrauterine Device The copper IUD […]
First-Generation Antipsychotics

Chemistry and Pharmacodynamics Neurotransmitters that may be modulated by antipsychotics for a therapeutic effect include dopamine, serotonin (also called 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT)), and norepinephrine (NE). Mechanism of action Physiologic effects Pharmacokinetics and Classification Pharmacokinetics There are numerous medications with unique pharmacokinetics. Classification The FGAs can be classified based on their potency: Indications Adverse Effects The adverse […]
Antimycobacterial Drugs
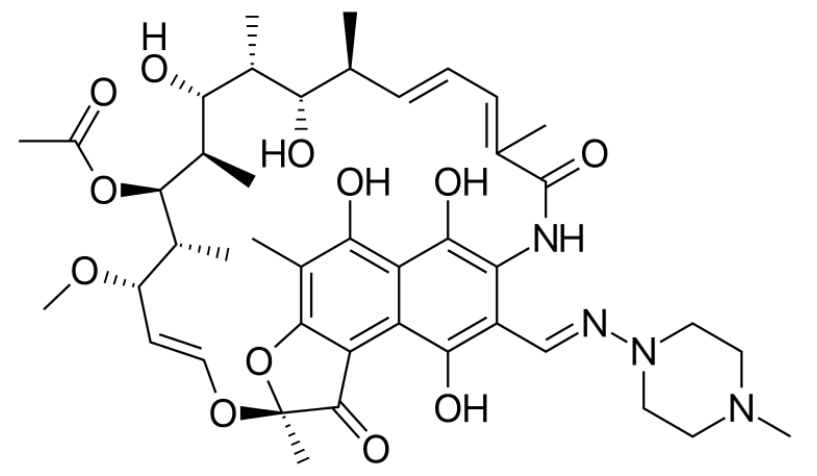
Overview Definition Antimycobacterial agents represent a diverse group of compounds used against mycobacterial infections (e.g., TB, leprosy, Mycobacterium avium complex). Antimycobacterial agents Table: Treatment regimens for mycobacterial infections Bacteria Treatment regimen* Prophylaxis Mycobacterium tuberculosis RIPE: Rifampin (RIF), Isoniazid (isoniazid (isonicotinic acid hydrazine (INH)), Pyrazinamide (PZA), Ethambutol (EMB) 3- to 4-drug regimen (to reduce resistance) Isoniazid […]
Parkinson’s Disease Drugs
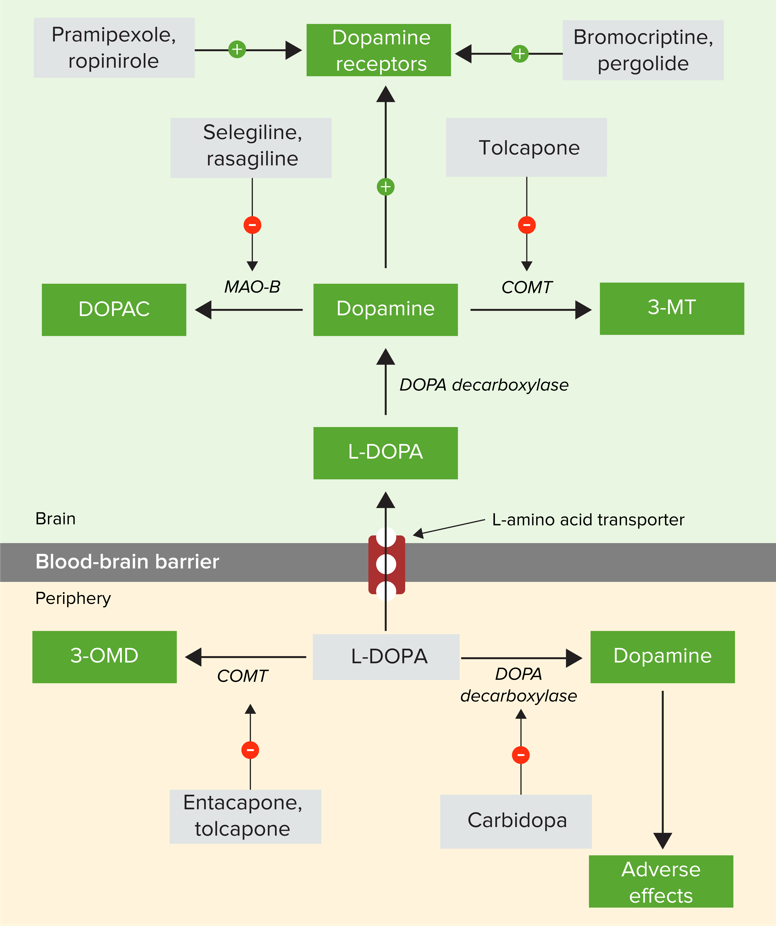
Overview Definition Parkinson’s disease (PD) is a degenerative disease of the basal ganglia characterized by a clinical syndrome manifesting with diminished facial expression, bradykinesia, festinating gait (progressively shortened and accelerated steps), cogwheel rigidity, and a “pill-rolling” tremor at rest. Pathophysiology Pharmacotherapy for Parkinson’s disease Levodopa Chemistry and pharmacodynamics Pharmacokinetics Indications Recommended as 1st-line therapy for […]