Hormonal Contraceptives
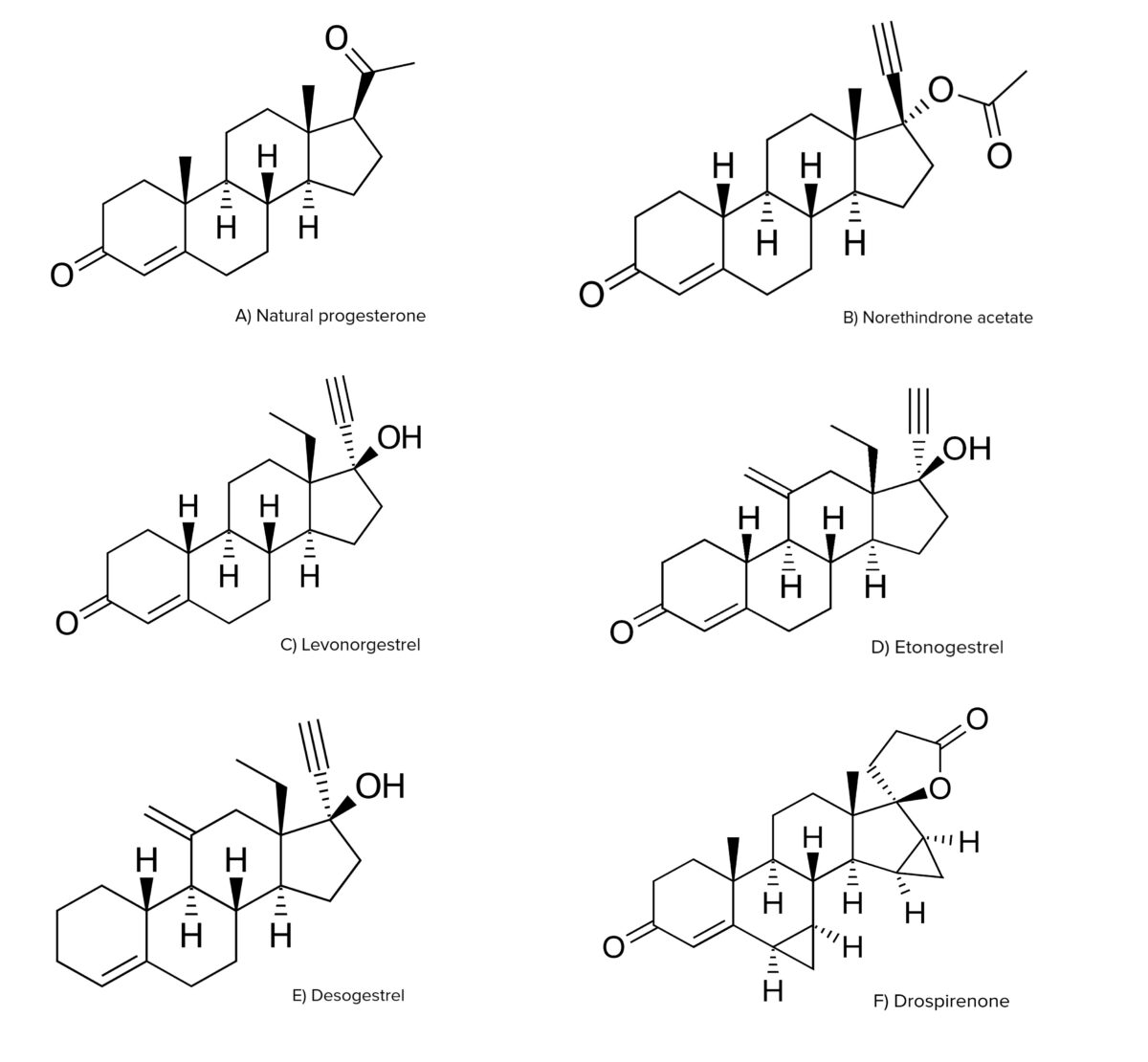
Overview Components Hormonal contraceptives (HCs) contain synthetic analogs of the reproductive hormones estrogen and progesterone. HCs may contain either: Choice of contraception The choice of contraceptive method is very individual and often is dictated by a variety of factors, including: Chemistry Both estrogens and progestins are steroid hormones, making them fat-soluble. Ethinyl estradiol (EE): Progestins: […]
Inhaled Anesthetics
Chemistry and Pharmacodynamics Table: Chemical characteristics of commonly used inhaled anesthetics Agent Characteristics Minimum alveolar concentration (MAC) Nitrous oxide (N2O) Naturally occurring nonvolatile gas Can be artificially synthesized Nonflammable 104% Halothane Hydrocarbon Nonflammable Halogenated Volatile liquid No longer commercially available in the United States 0.75% Desflurane Fluorinated ether Clear and volatile liquid 6.6% Sevoflurane Fluorinated […]
Sympathomimetic Drugs

Chemistry and Pharmacodynamics Sympathomimetic drugs, also known as adrenergic agonists, mimic the action of the stimulators of the sympathetic autonomic nervous system, specifically α, β, or dopamine receptors: Chemical structures Mechanism of action Classification Physiologic effects Pharmacokinetics and Indications The primary drugs used as IV vasopressors in the hospital are dopamine and norepinephrine. Dobutamine is […]
Stimulants
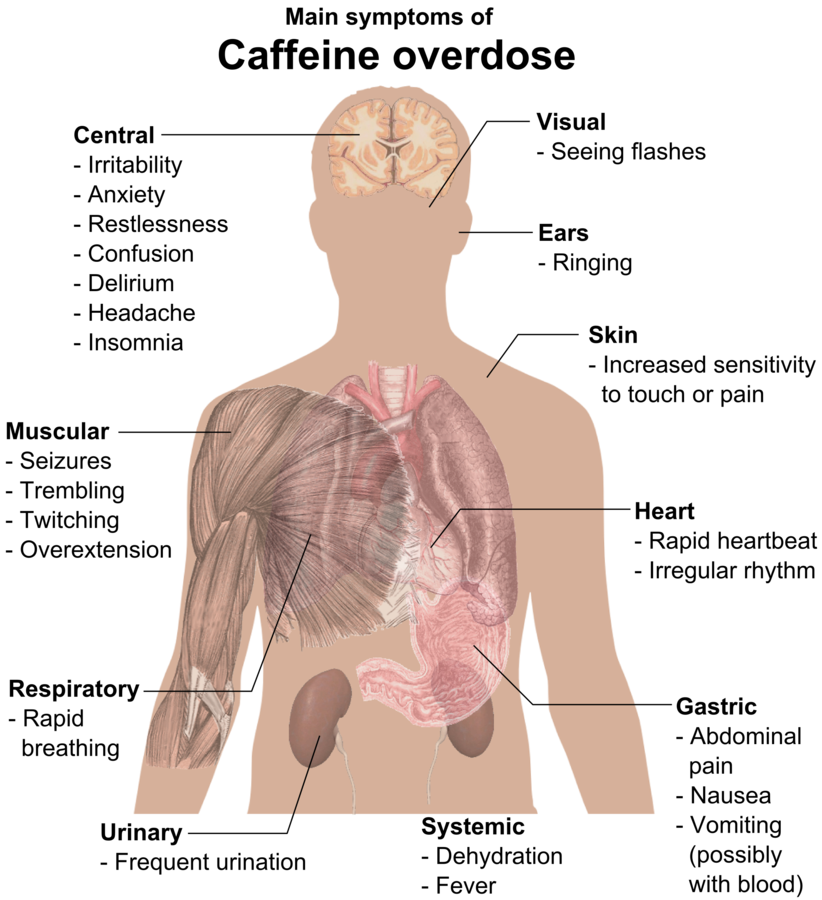
Caffeine Overview Pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics Effects Clinical uses Adverse effects and contraindications Drug-drug interactions Withdrawal syndrome Overdose and toxicity Nicotine Overview Pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics Effects Clinical uses Smoking-cessation therapy (nicotine patch, gum, nasal spray, or inhaler) Adverse effects and contraindications Drug-drug interactions Withdrawal syndrome Overdose and toxicity Amphetamines Overview Pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics Effects Clinical uses […]
Antitumor Antibiotics
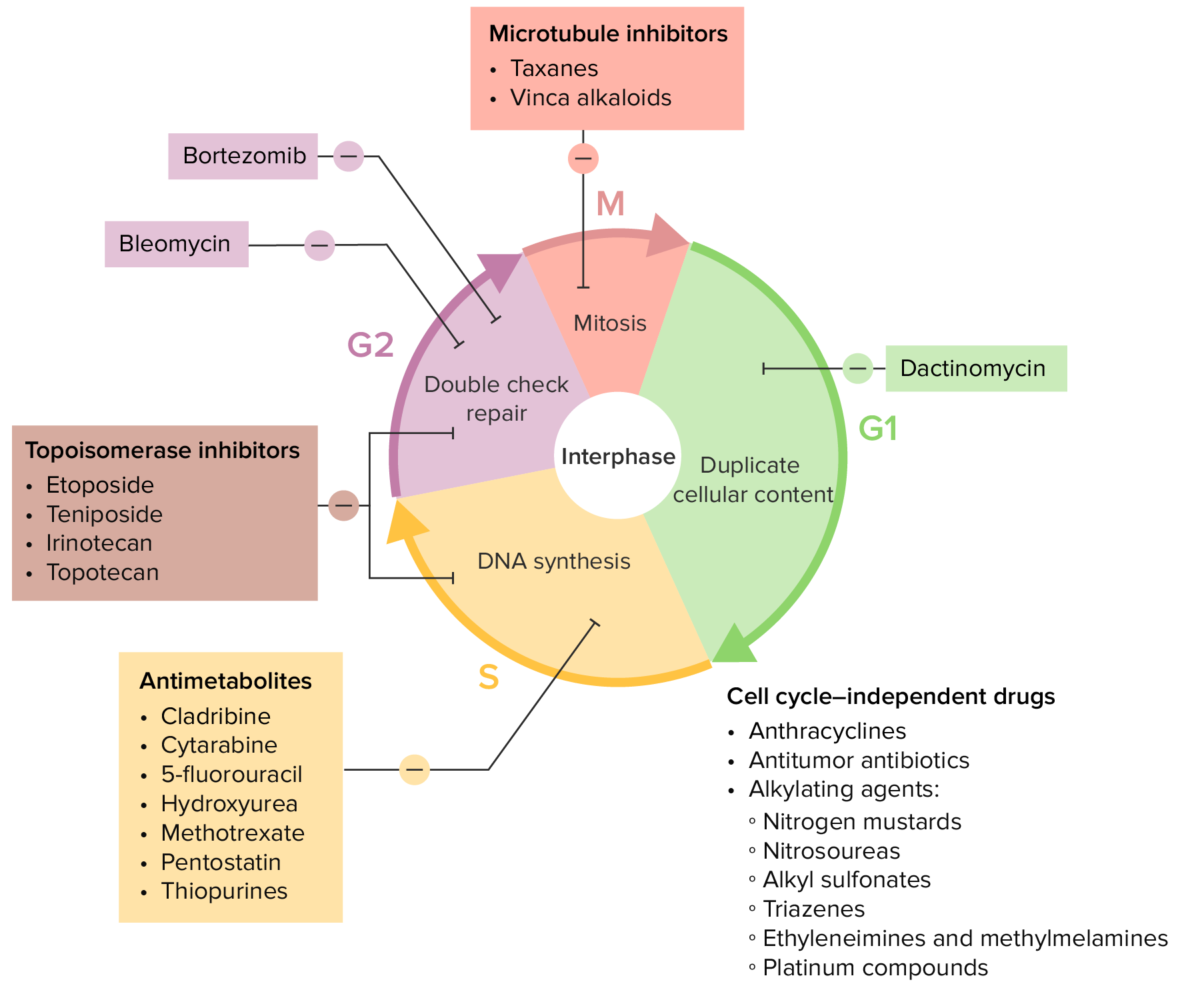
Overview Antitumor antibiotics, agents isolated from strains of Streptomyces, are used for cancer treatment owing to their ability to interfere with DNA and/or RNA synthesis, thus leading to cancer cell death. The effects of these drugs are too toxic for use in bacterial infections. Agents within this class include: Bleomycin Description Adverse effects Contraindications and […]
Microtubule and Topoisomerase Inhibitors
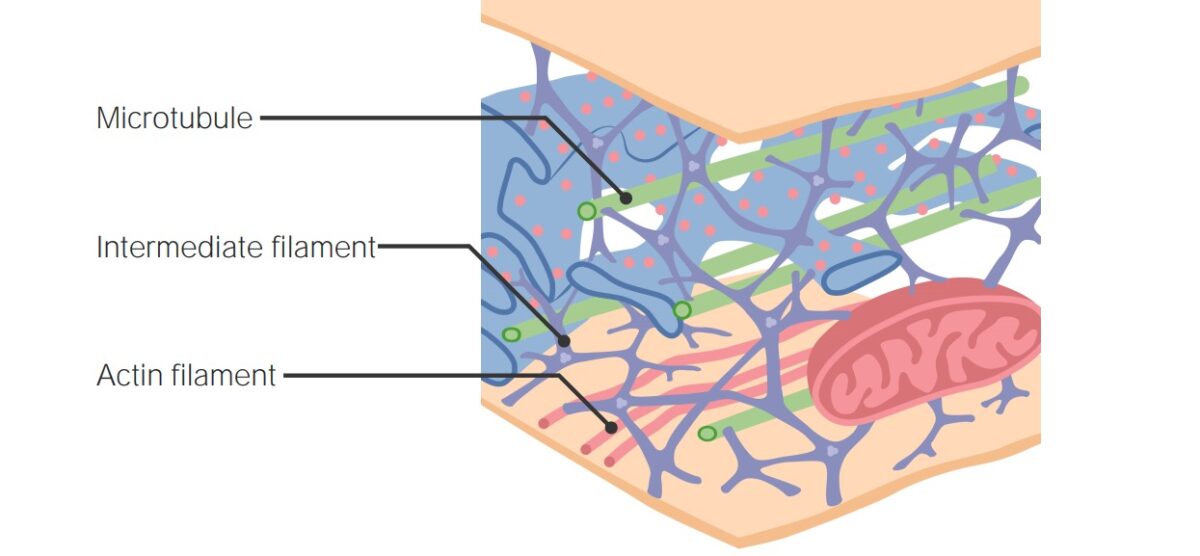
Overview Microtubule inhibitors Topoisomerase inhibitors Taxanes Description Paclitaxel Docetaxel Cabazitaxel Contraindications and drug interactions Vinca Alkaloids Description Vinblastine Vincristine Vinorelbine Contraindications and drug interactions Topoisomerase I Inhibitors Description Irinotecan Topotecan Contraindications and drug interactions Topoisomerase II Inhibitors Description Etoposide Teniposide Comparison with Other Chemotherapeutic Agents Table: Comparison of the cell cycle–independent chemotherapy drugs Drug class […]
Other Antiresorptive Drugs
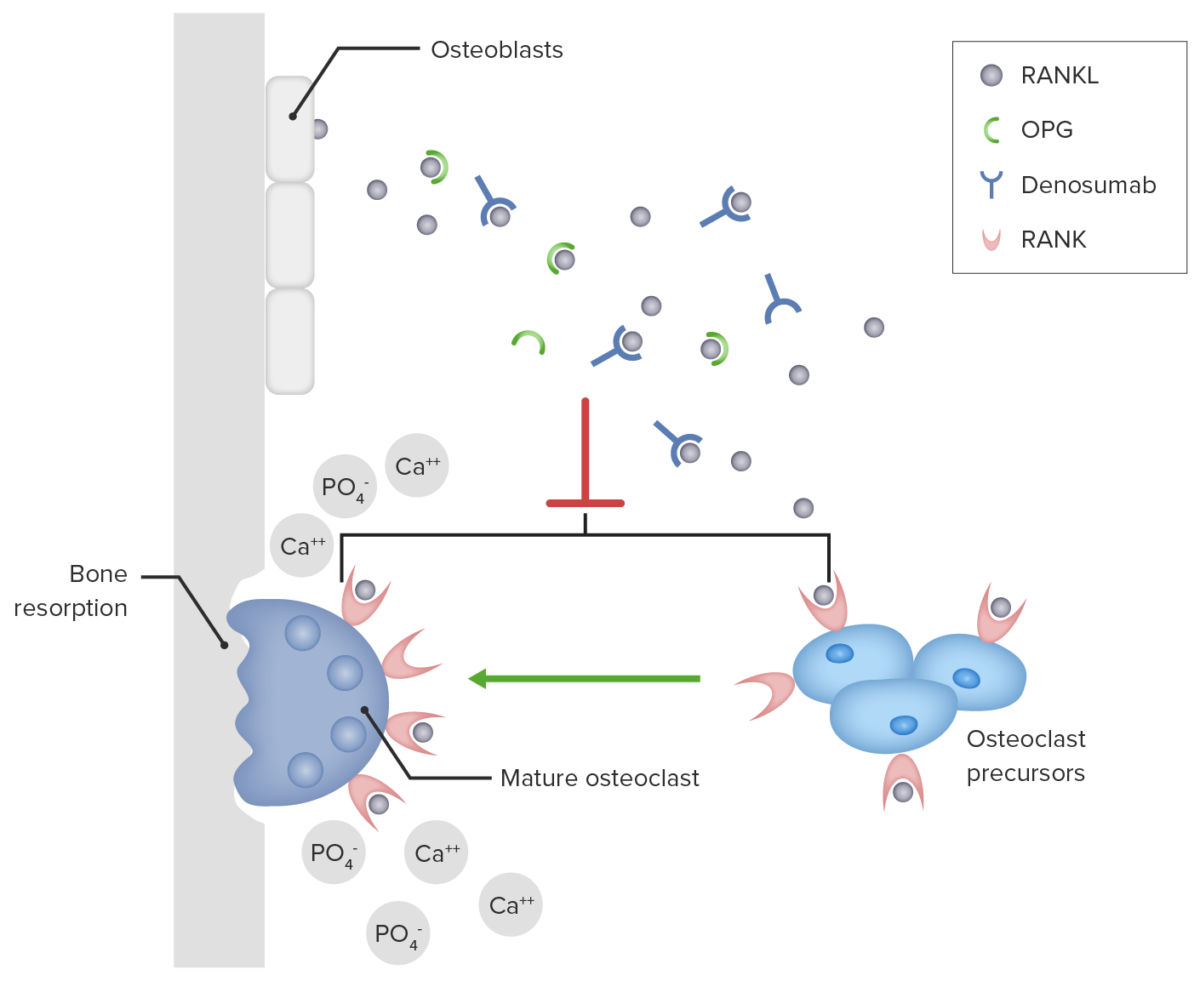
Overview Osteoporosis is a skeletal disorder caused by the deterioration of bone tissue, which leads to bone fragility. Antiresorptive medications are often used in the treatment of osteoporosis to prevent disease progression. Pathogenesis of osteoporosis Antiresorptive medications Hormones Medications in this class Pharmacodynamics Teriparatide: Abaloparatide: Calcitonin: Pharmacokinetics Teriparatide: Abaloparatide: Calcitonin: Indications Adverse effects Teriparatide and […]
Class 3 Antiarrhythmic Drugs (Potassium Channel Blockers)
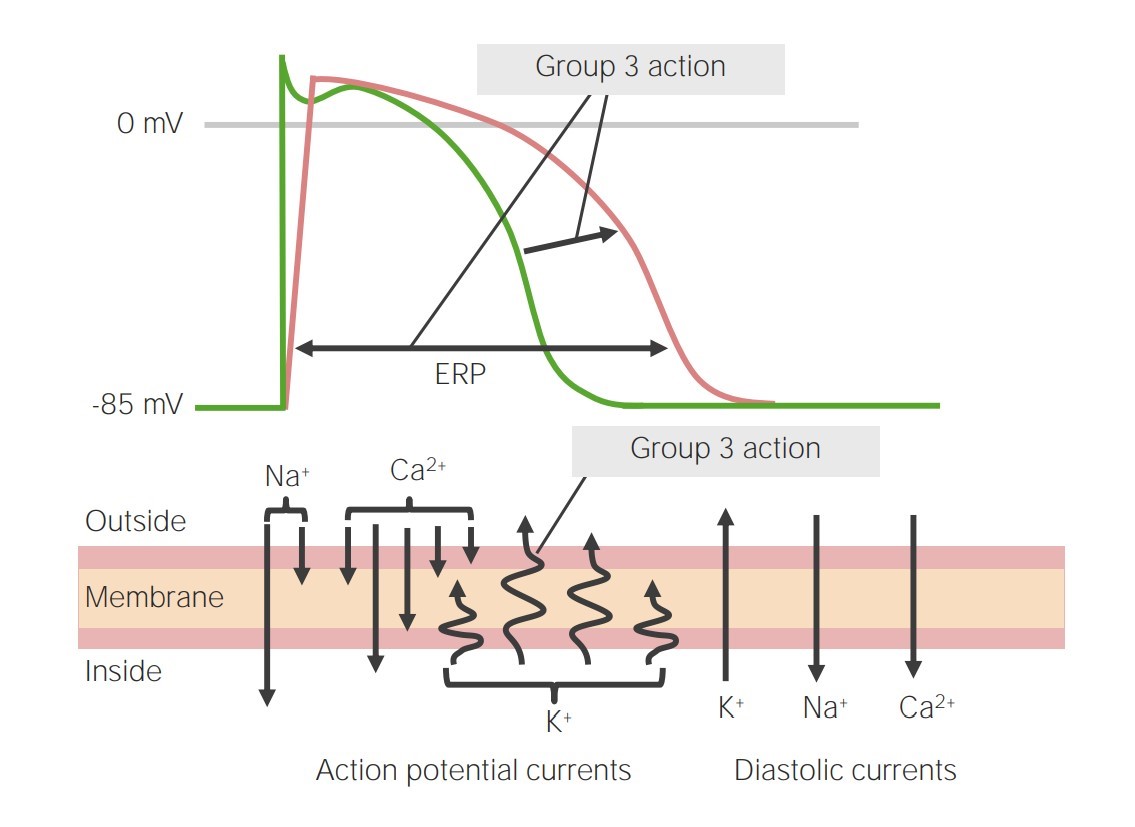
Overview Cardiac action potential Vaughan-Williams classification General mechanism of action Medications within this drug class Class 3 antiarrhythmics include a variety of medications that vary in K channel selectivity and other antiarrhythmic effects: Amiodarone Mechanism of action Pharmacokinetics Indications Adverse effects Adverse effects of amiodarone are seen mainly in long-term oral therapy (rather than short-term […]
Alkylating Agents and Platinum
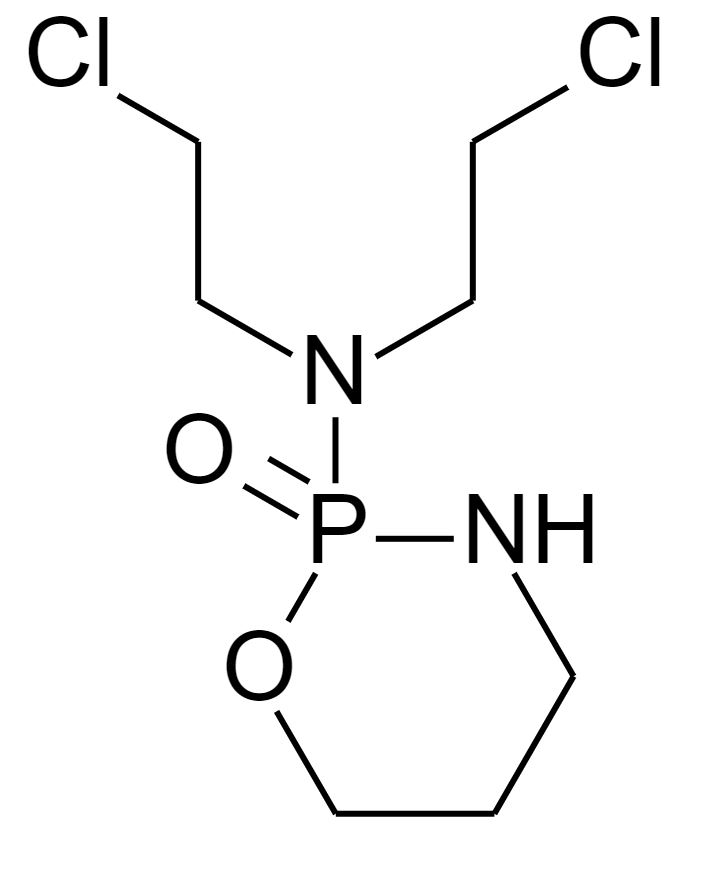
Overview Alkylating agents Alkylating agents are antineoplastic drugs that attach an alkyl group onto DNA to cause cancer (CA) cell death. Types of alkylating agents Nitrogen Mustards General description Chlorambucil Cyclophosphamide Ifosfamide Melphalan Bendamustine Contraindications and drug interactions Nitrosoureas General description Carmustine Lomustine Contraindications and drug interactions Alkyl Sulfonates General description Busulfan Triazines General description […]
Insulin
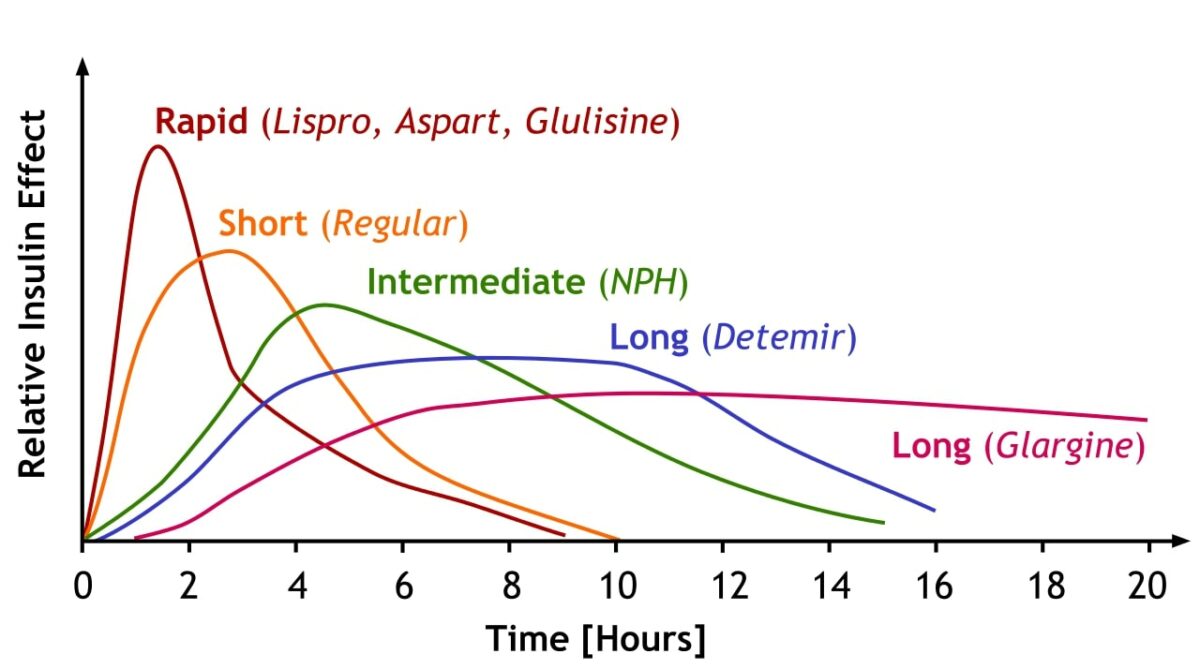
Pharmacodynamics Chemistry Insulin is a small protein normally created and released by pancreatic beta cells. Available formulations can be: Human insulin: identical to endogenously produced insulin Analog insulin: altered to create pharmacokinetic advantages Mechanism of action Insulin acts on cells to ↑ glucose uptake in all tissues, including the: Liver Skeletal muscle Adipose tissue This […]