Hypertensive Pregnancy Disorders (Clinical)
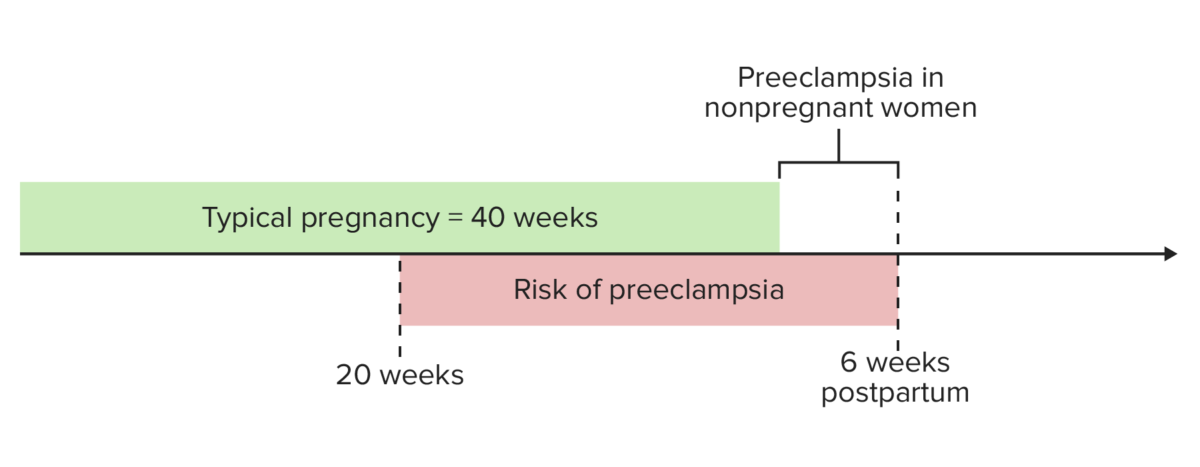
Overview Classification and definitions[1,3,4,9,11] Epidemiology[3,6,9] Risk factors[4,5,7,8] High-risk factors: Moderate risk factors: Prophylactic treatment with aspirin has been shown to reduce the risk of developing preeclampsia in individuals at high risk. Identifying these high-risk individuals is based on risk factors, though the United States and United Kingdom classify these risk factors slightly differently. Because the […]
Pelvic Organ Prolapse (Clinical)
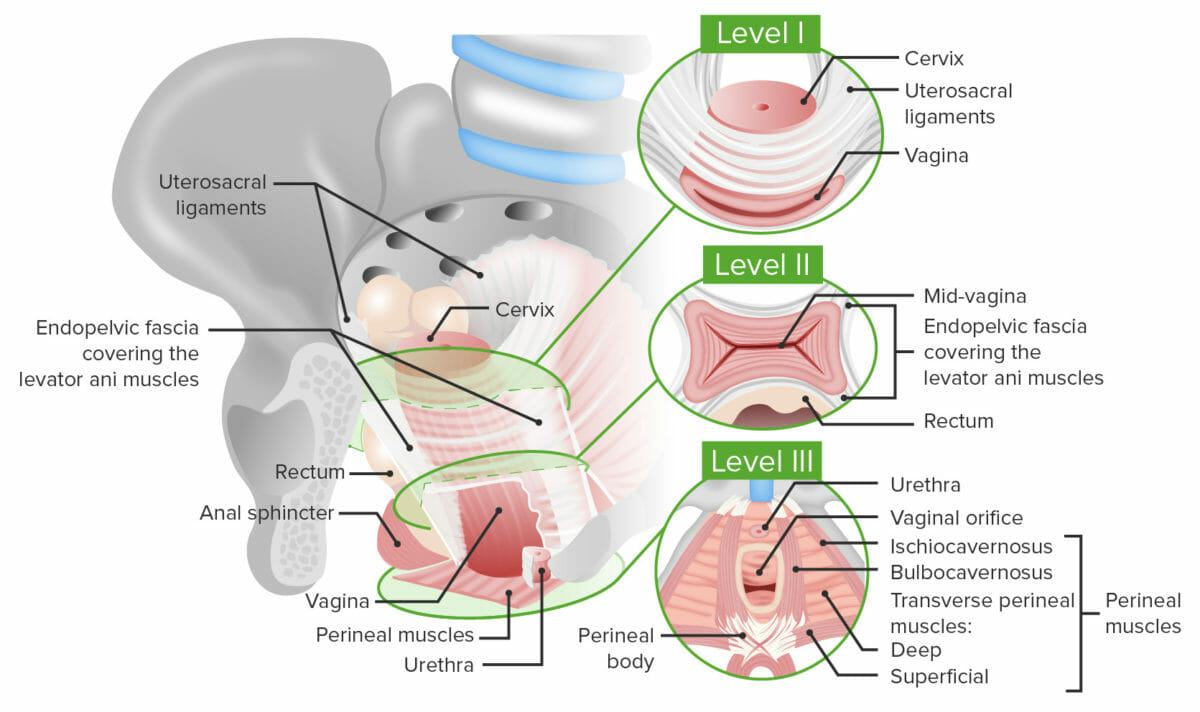
Overview Definitions[1,4] Pelvic organ prolapse (POP): a general term referring to prolapse of 1 or more of the pelvic organs (e.g., bladder, uterus, rectum) into the vaginal canal Visualizing POP Visualizing POP, especially apical POP, can be difficult. Etiology[1,4] Prolapse is due to weakness and insufficiency of the pelvic floor, which normally keeps organs in […]
Ovarian Torsion (Clinical)
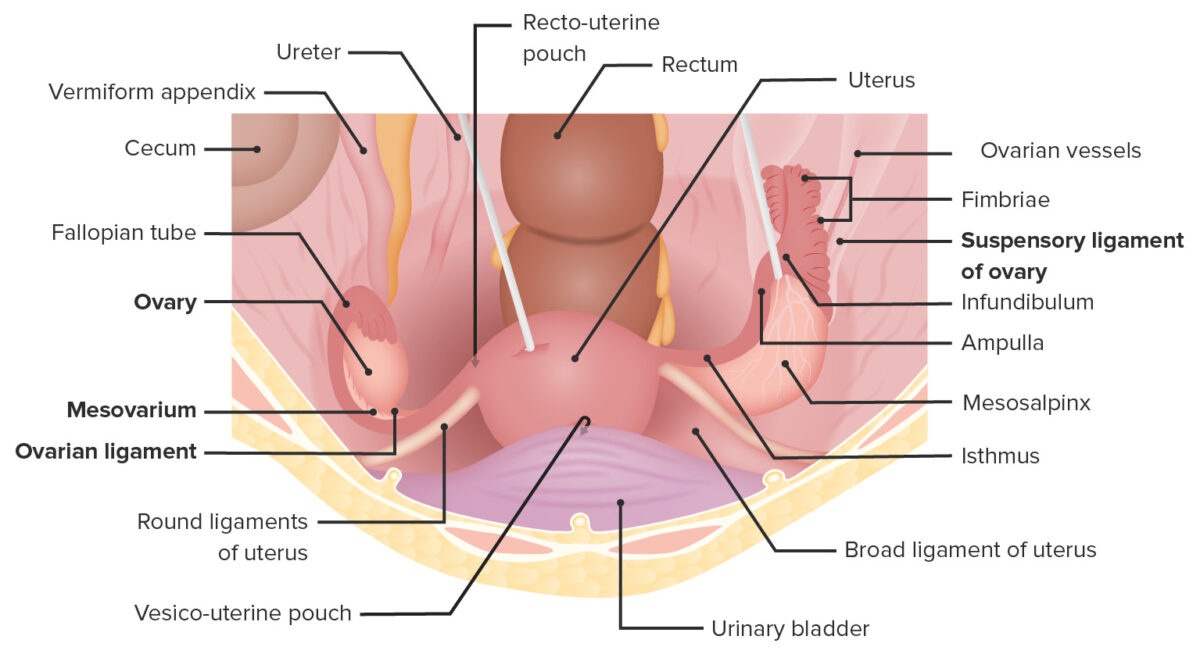
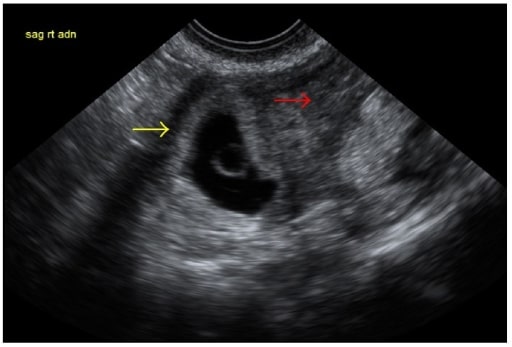
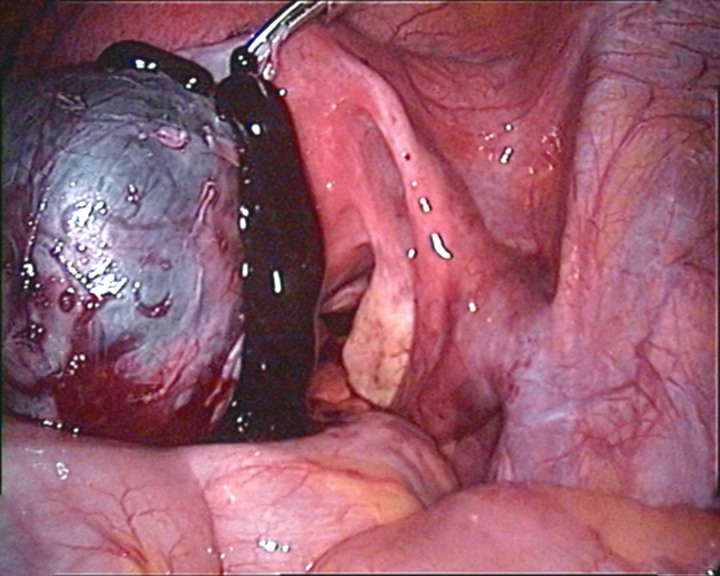
Overview Definition Ovarian torsion is the twisting of the ovaries along their axis. Ovarian torsion may or may not include the fallopian tubes and if it does, it is termed adnexal torsion. Anatomy[2] Epidemiology[1–5,7,8] Pathogenesis Ovarian or adnexal torsion involves the following sequence of events:[1–3] Clinical Presentation Diagnosis and Management Adnexal torsion is suspected based […]
Chorioamnionitis (Clinical)
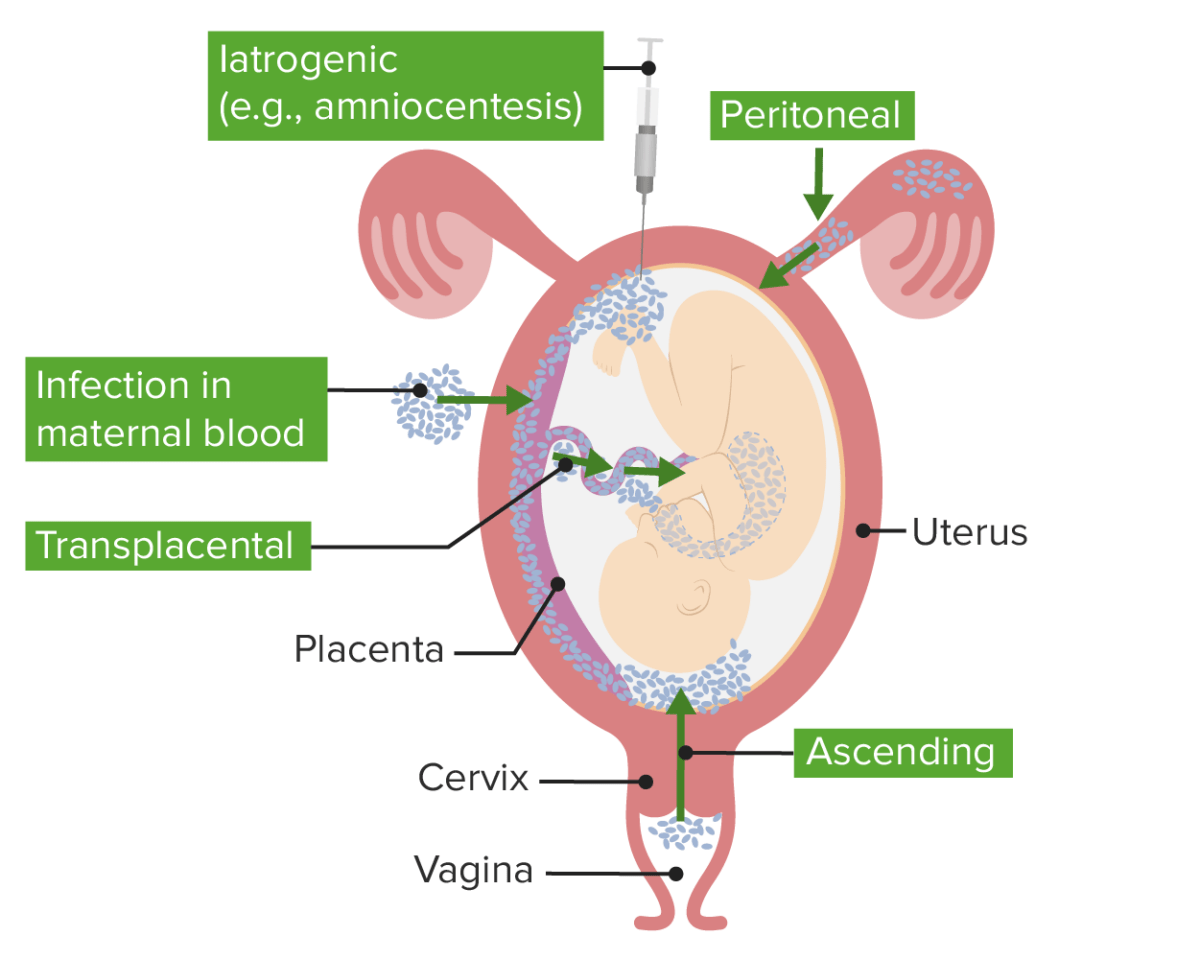
Definition and Epidemiology Definition Also known as intraamniotic infection (IAI), chorioamnionitis is an infection, and resulting inflammation, of any combination of the fetal membranes (chorion and amnion), amniotic fluid, placenta, umbilical cord (funisitis), and/or the fetus. Epidemiology[1,4–7] Chorioamnionitis is the most common cause of peripartum infection, with the following incidence rates: Etiology Intraamniotic infection and […]
Polyhydramnios (Clinical)
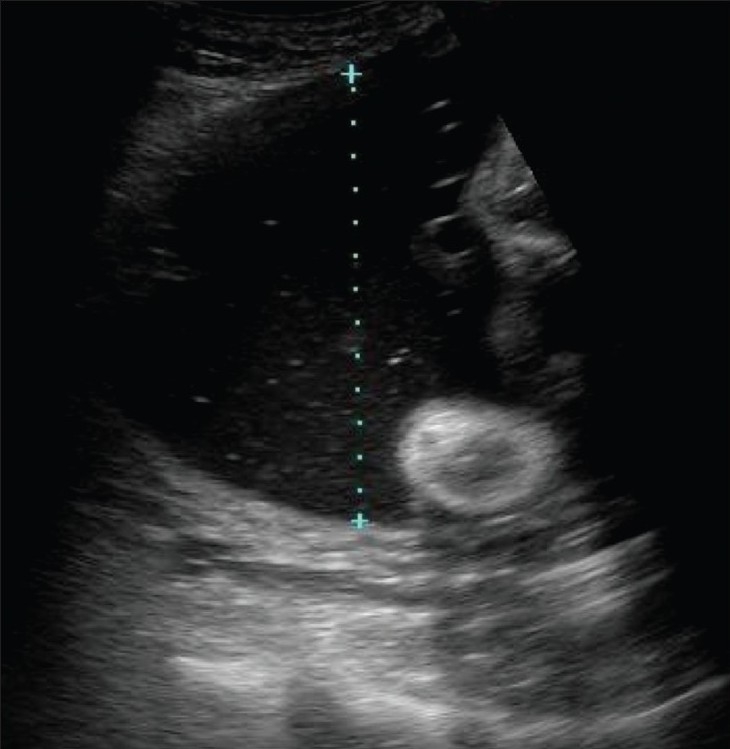
Overview Definition Polyhydramnios is an abnormally high level of amniotic fluid in the amniotic sac. Epidemiology[1,2,6] Etiology[1,2,5] Pathophysiology Two major causes of polyhydramnios: Clinical Presentation Diagnosis Diagnostic criteria can vary based on location. The following information is based on US medical society recommendations. History[1,2] Physical exam[1,2,6,9] Amniotic fluid assessment[3,4,8,9] Table: Classification of mild, moderate, and […]
Oligohydramnios (Clinical)
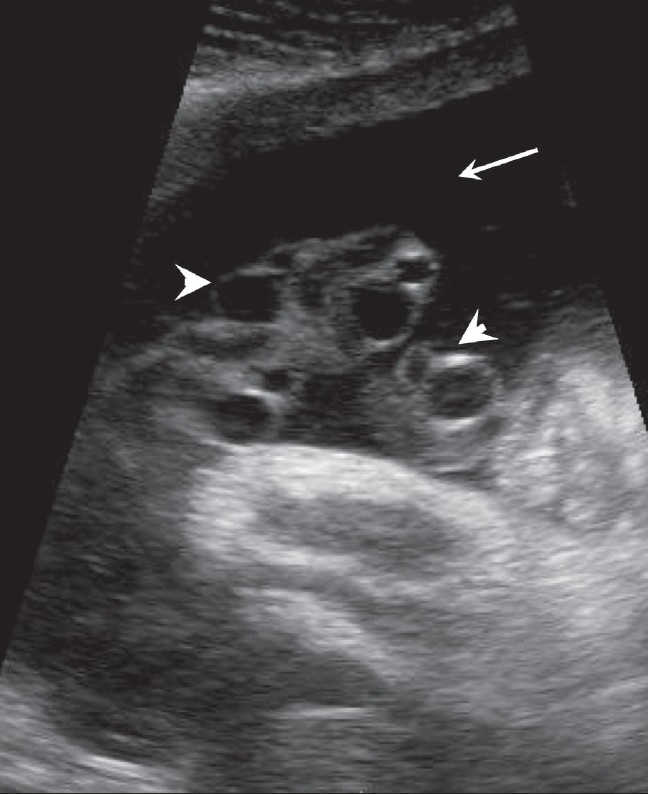
Overview Definition Decreased amniotic fluid volume for gestational age is referred to as oligohydramnios. Oligohydramnios is diagnosed based on ultrasound measurements of amniotic fluid volume and can be defined as either: Anhydramnios is an extreme case of oligohydramnios with no measurable pockets of amniotic fluid present. Epidemiology[4,5,8,9] Pathophysiology and Etiology Normal amniotic fluid production[5,7,9] Amniotic […]
Ectopic Pregnancy (Clinical)
Epidemiology and Etiology Epidemiology[5] Etiology[5,8,9,12] Ectopic pregnancy (EP) can occur when the fertilized egg does not enter the uterine cavity by way of the fallopian tube by the 5th to 6th day of gestation. Clinical Presentation Ectopic pregnancy can present before, during, or after rupture. Early on (prior to rupturing), symptoms can be relatively mild, […]
Endometriosis (Clinical)
Overview Definition[8] Endometriosis is a condition in which endometrial glands and stroma implant outside of the uterus. These implants can be highly inflammatory but are generally not malignant. Epidemiology[1–3,9] Risk factors[3,13–15] Pathophysiology Contributing factors[3,14,15] Theories about the establishment of implants[2,3,9,13–15] Sites of ectopic implantation[8,9] Histologic phenotypes[3,7] There are 3 primary phenotypes that can be identified […]
Mastitis (Clinical)
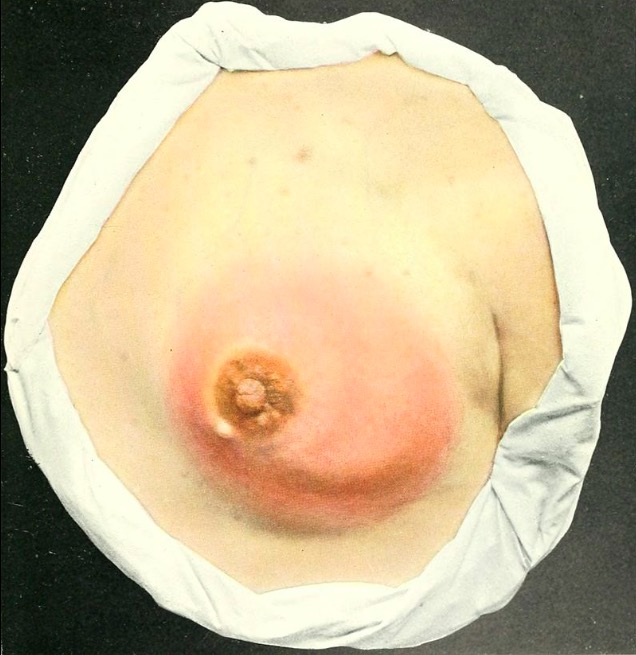
Overview Definition Mastitis refers to inflammation of the breast that may or may not be associated with infection. Classification[3–5] Epidemiology[1,2,4,5] Etiology and Pathophysiology Lactational mastitis[4,6,7] Non-lactational mastitis[1,2,5,9] Periductal mastitis: IGM: Clinical Presentation General[3–5] Lactational mastitis[4,7] Periductal mastitis[2,5,9] IGM[1,5] Diagnosis Lactating mothers[6,7] Non-lactating women[1,9] Periductal mastitis: IGM: Management Lactational mastitis Non-lactational mastitis Periductal mastitis: IGM: Differential […]
Fat Necrosis of the Breast (Clinical)
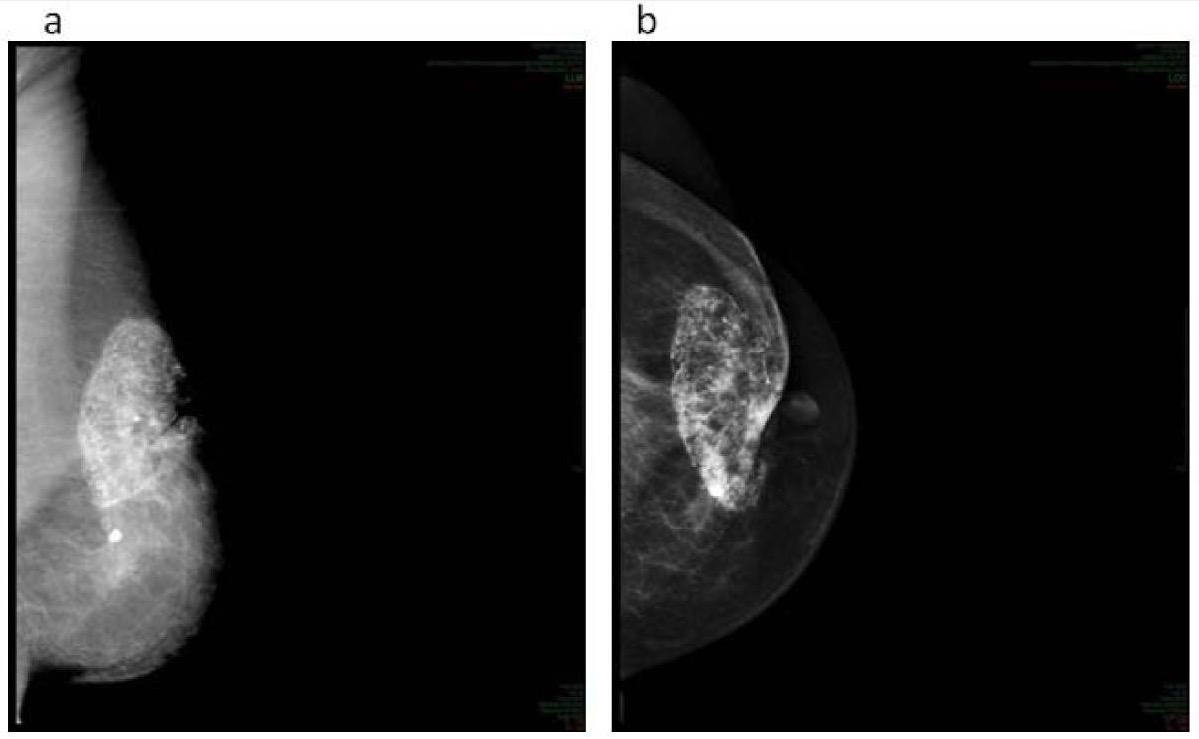
Overview Definition Fat necrosis is a benign breast lesion that results from injury to the breast tissue. Epidemiology[6] Etiology[6,7] Risk factors[6] Pathophysiology and Clinical Presentation Pathophysiology[5,6] Mechanisms of injury: Tissue response: Clinical presentation[5,6] Diagnosis History[6] Physical exam[6] Imaging[6] Image categorization system: BI-RADs Findings on breast imaging studies are classified according to the Breast Imaging Reporting […]