Bunyaviridae Bunyaviridae A family of viruses, mainly arboviruses, consisting of a single strand of RNA. Virions are enveloped particles 90-120 nm diameter. The complete family contains over 300 members arranged in five genera: orthobunyavirus; hantavirus; nairovirus; phlebovirus; and tospovirus. Bunyavirales é uma família de vírus de RNA RNA A polynucleotide consisting essentially of chains with a repeating backbone of phosphate and ribose units to which nitrogenous bases are attached. RNA is unique among biological macromolecules in that it can encode genetic information, serve as an abundant structural component of cells, and also possesses catalytic activity. RNA Types and Structure classificada em 5 géneros: Orthobunyavirus Orthobunyavirus A genus of the family bunyaviridae containing over 150 viruses, most of which are transmitted by mosquitoes or flies. They are arranged in groups defined by serological criteria, each now named for the original reference species (previously called serogroups). Many species have multiple serotypes or strains. Bunyavirales (vírus La Crosse), Hantavirus Hantavirus A genus of the family bunyaviridae causing hantavirus infections, first identified during the korean war. Infection is found primarily in rodents and humans. Transmission does not appear to involve arthropods. Hantaan virus is the type species. Bunyavirales, Nairovirus Nairovirus A genus of the family bunyaviridae named after nairobi sheep disease, an acute, hemorrhagic, tick-borne, gastroenteritis affecting sheep and goats. The type species is dugbe virus. Some viruses in this genus are capable of causing severe and fatal disease in humans. Bunyavirales (vírus da febre hemorrágica da Crimeia-Congo), Phlebovirus Phlebovirus A genus of the family bunyaviridae comprising many viruses, most of which are transmitted by phlebotomus flies and cause phlebotomus fever. The type species is rift valley fever virus. Bunyavirales (vírus da febre do Vale do Rift) e Tospovirus Tospovirus A genus of plant viruses in the family bunyaviridae. Tomato spotted wilt virus is the type species. Transmission occurs by at least nine species of thrips. Bunyavirales. As características comuns desta família de vírus incluem uma estrutura esférica com invólucro contendo um genoma de RNA RNA A polynucleotide consisting essentially of chains with a repeating backbone of phosphate and ribose units to which nitrogenous bases are attached. RNA is unique among biological macromolecules in that it can encode genetic information, serve as an abundant structural component of cells, and also possesses catalytic activity. RNA Types and Structure de cadeia simples e sentido negativo, com 3 segmentos. As infeções são geralmente transmitidas por artrópodes ou por roedores. Existem várias manifestações clínicas, mas, em geral, apresentam-se como febres hemorrágicas e/ou encefalites. Os exames de diagnóstico incluem a serologia e o RT-PCR RT-PCR A variation of the pcr technique in which cDNA is made from RNA via reverse transcription. The resultant cDNA is then amplified using standard pcr protocols. Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR). O tratamento é de suporte.
Last updated: Feb 23, 2025

Identificação do vírus RNA:
Os vírus podem ser classificados de várias maneiras. A maioria dos vírus, no entanto, terá um genoma formado por DNA ou RNA. Os vírus de genoma de RNA podem ser ainda caracterizados com base na presença de RNA de fita simples ou dupla. Os vírus “envelopados” são cobertos por uma fina camada de membrana celular (geralmente retirada da célula hospedeira). Se a pelagem estiver ausente, os vírus são chamados de vírus “nus”. Vírus com genomas de fita simples são chamados de vírus de “sentido positivo” se o genoma for usado diretamente como RNA mensageiro (mRNA), que é traduzido em proteínas. Os vírus de “sentido negativo” de fita simples usam RNA polimerase dependente de RNA, uma enzima viral, para transcrever seu genoma em RNA mensageiro.
Imagem de uma partícula do vírus Sin Nombre a sair de uma célula Vero:
O vírus Sin Nombre causa a síndrome pulmonar por hantavírus na América do Norte.
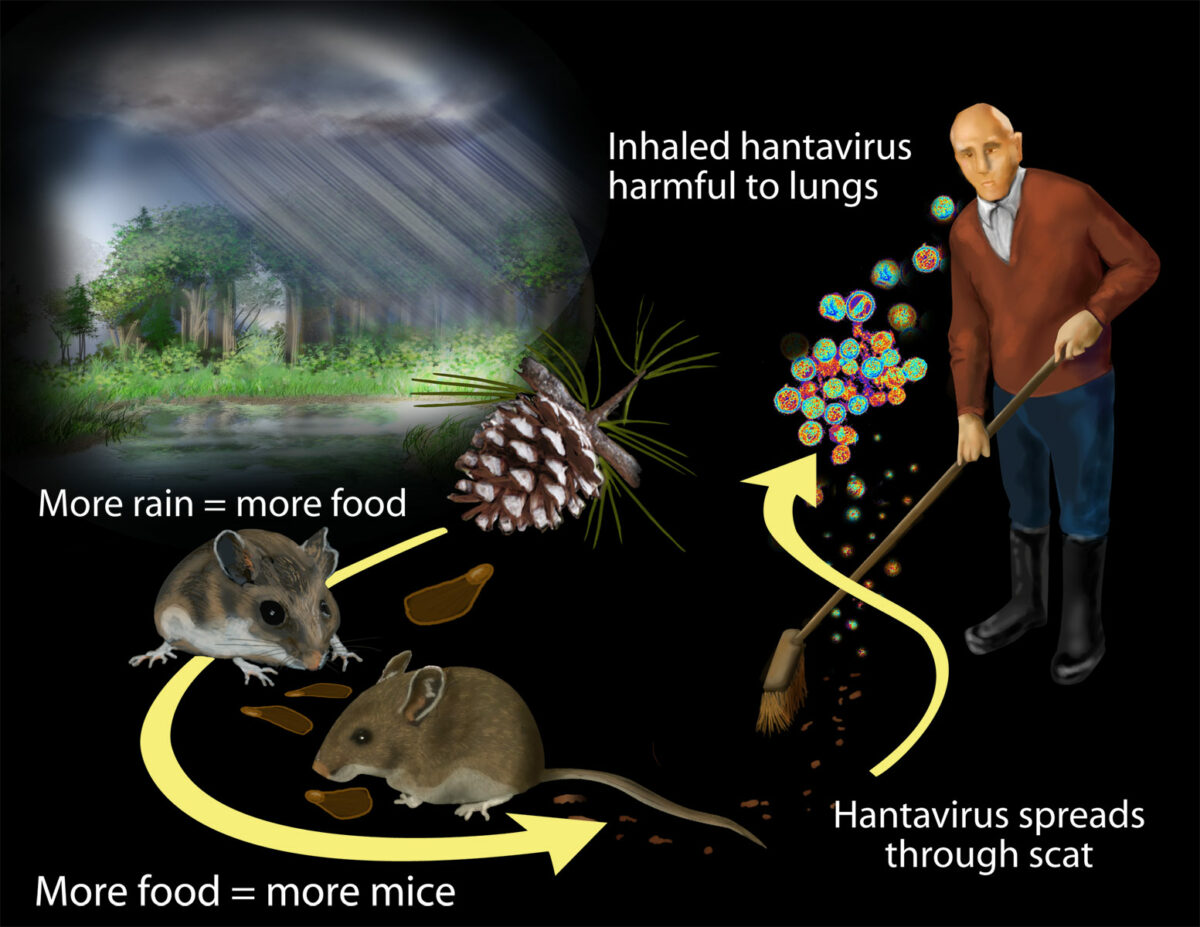
Transmissão do hantavírus:
Os investigadores descobriram que o contacto com roedores e respetivos resíduos coloca os humanos em risco de exposição ao hantavírus. As chuvas maciças associadas ao El Niño de 1991–1992 aumentaram a produtividade das plantas.
A população de roedores cresceu devido à abundância de matéria vegetal. O aumento do contacto com os roedores e os seus resíduos coloca mais humanos em risco de exposição ao hantavírus.
| Síndrome pulmonar por hantavírus | Febre hemorrágica por hantavírus | |
|---|---|---|
| Incubação | 1-3 semanas | 1-3 semanas (até 6 semanas) |
| Diagnóstico |
|
|
| Manifestações clínicas | Pródromo: sintomas gripais, início súbito de dispneia com edema Edema Edema is a condition in which excess serous fluid accumulates in the body cavity or interstitial space of connective tissues. Edema is a symptom observed in several medical conditions. It can be categorized into 2 types, namely, peripheral (in the extremities) and internal (in an organ or body cavity). Edema pulmonar de evolução rápida | Febre, hipotensão/choque, LRA |
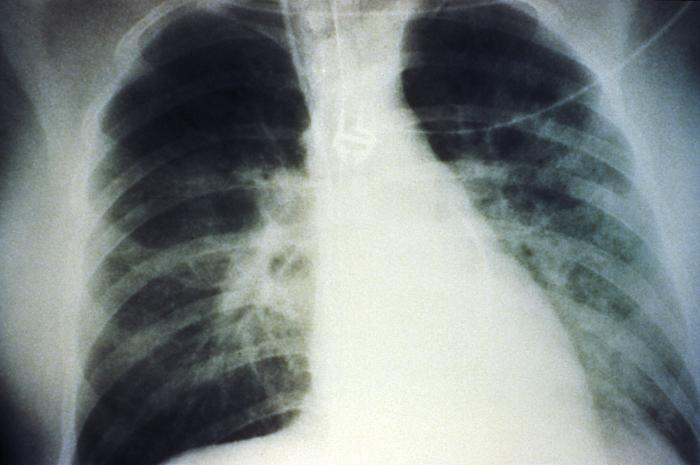
Radiografia de tórax anteroposterior que mostra um derrame pulmonar bilateral em fase intermédia devido à síndrome pulmonar por hantavírus (HPS):
A evolução radiológica da HPS inicia-se com alterações mínimas correspondentes a edema pulmonar intersticial, que progride para edema alveolar com atingimento bilateral grave. Os derrames pleurais são comuns e muitas vezes grandes o suficiente para serem evidentes radiograficamente.
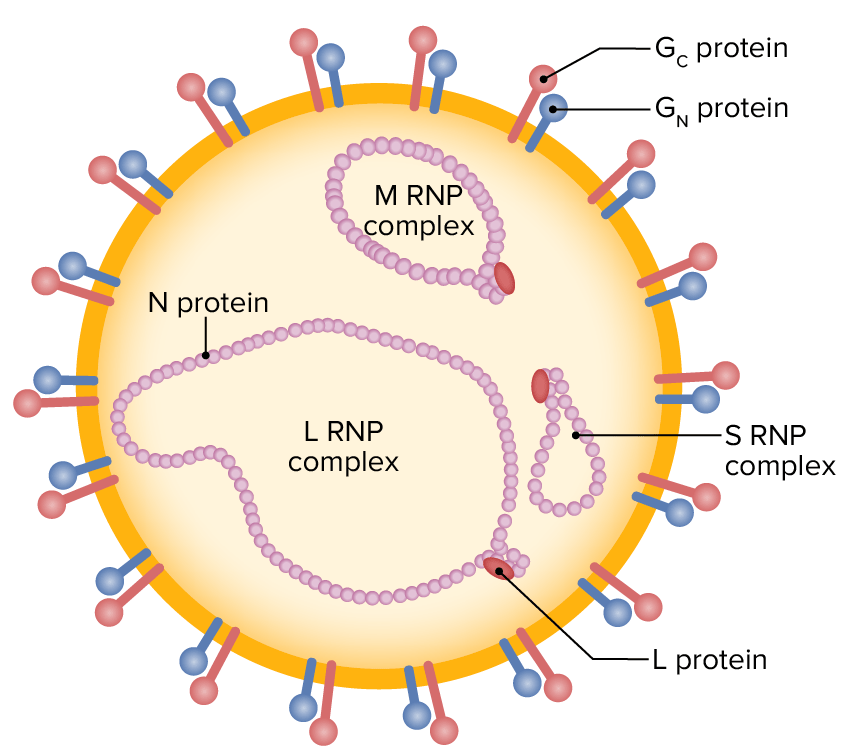
Ilustração esquemática de uma partícula de nairovírus (RNA de cadeia única envelopado, contendo segmentos L, M, e S, rodeado por glicoproteínas externas)
RNP: ribonucleoproteína
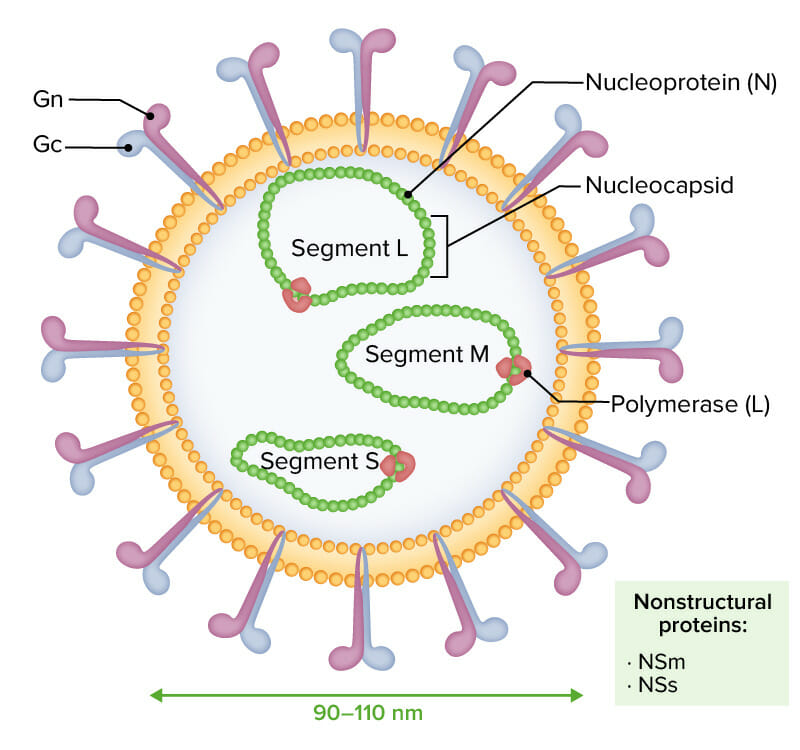
Os viriões envelopados do vírus da febre do Vale do Rifte caracterizam-se por um genoma RNA negativo ou ambisenso composto por 3 segmentos de cadeia simples (designados L, M, e S):
As 3 moléculas de RNA são encapsuladas por nucleoproteína (N), moldando a nucleocápside e interagindo com a polimerase viral (L). As glicoproteínas Gn e Gc são notadas externamente. As proteínas não-estruturais NSm e NSs são expressas durante a infeção.
Imagem que mostra a morfologia ultraestrutural de numerosas partículas do vírus La Crosse (LCV)
Imagem: Image showing the ultrastructural morphology exhibited by numerous La Crosse virus (LCV) particles” de Dr. Erskine Palmer, USCDCP. Licença: Domínio Público| Organismo | Hantavírus | Vírus da febre hemorrágica da Crimeia-Congo | Vírus da febre do Vale do Rift | Vírus La Crosse | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Características | Vírus de RNA RNA A polynucleotide consisting essentially of chains with a repeating backbone of phosphate and ribose units to which nitrogenous bases are attached. RNA is unique among biological macromolecules in that it can encode genetic information, serve as an abundant structural component of cells, and also possesses catalytic activity. RNA Types and Structure de cadeia simples e sentido negativo, com invólucro | ||||
| Género | Hantavirus Hantavirus A genus of the family bunyaviridae causing hantavirus infections, first identified during the korean war. Infection is found primarily in rodents and humans. Transmission does not appear to involve arthropods. Hantaan virus is the type species. Bunyavirales ou Ortohantavirus | Nairovirus Nairovirus A genus of the family bunyaviridae named after nairobi sheep disease, an acute, hemorrhagic, tick-borne, gastroenteritis affecting sheep and goats. The type species is dugbe virus. Some viruses in this genus are capable of causing severe and fatal disease in humans. Bunyavirales | Phlebovirus Phlebovirus A genus of the family bunyaviridae comprising many viruses, most of which are transmitted by phlebotomus flies and cause phlebotomus fever. The type species is rift valley fever virus. Bunyavirales | Orthobunyvirus | |
| Transmissão | Inalação e contacto direto com a urina e fezes de roedores infetados | Contacto com carraças infetadas (especialmente Hyalomma spp.) |
|
Picadas de mosquito | |
| Apresentação clínica |
|
Febre hemorrágica |
|
Encefalite | |
| Diagnóstico |
|
|
|
|
|
| Tratamento | Suporte |
|
Suporte | Suporte | |