What is neonatal sepsis?
Neonatal sepsis is an infection involving the bloodstream of a newborn infant, less than 28 days old.
Classification
Types of neonatal sepsis are
- Early-onset sepsis (EOS): occurring within the first 72 hours
- Late onset sepsis (LOS): occuring after 72 hours of life
What causes neonatal sepsis?
The immune system of the neonate is immature and unable to target the source of infection. Localized infection can quickly become systemic.
Risk factors for neonatal sepsis include:
- Preterm birth
- Low birth weight
- Prenatal infections
- Group beta strep (GBS)
- E. coli
- Prolonged labor
- Multiple vaginal exams during labor
- Rupture of membranes > 18 hours
- Chorioamnionitis during labor
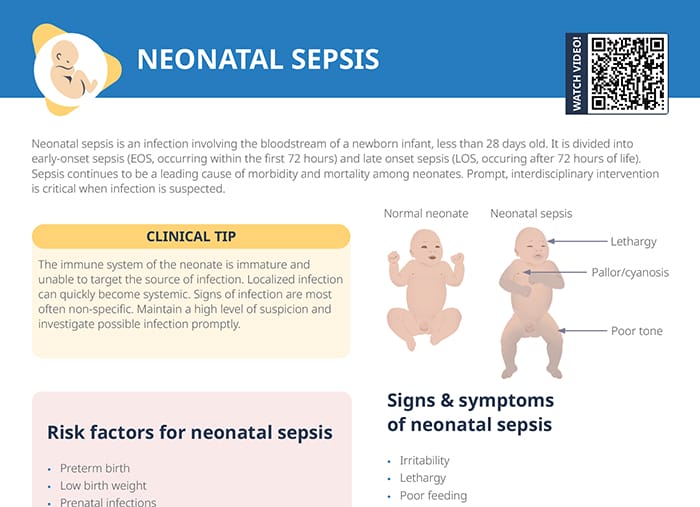
Signs of infection in newborns
Signs of infection are most often non-specific. Maintain a high level of suspicion and investigate possible infection promptly.
Symptoms of neonatal sepsis:
- Irritability
- Lethargy
- Poor feeding
- Poor tone
- Pallor or cyanosis
- Respiratory distress
- Temperature instability (fever or hypothermia)
- Tachycardia or bradycardia
- Hemodynamic instability or collapse
Prevention and assessment
Preventive measures that help lower the risk of neonatal sepsis:
- Adequate prenatal care
- Identification and treatment of GBS
- Limited vaginal exams in labor
- Adequate hand hygiene (in healthcare personnel, client, also monitor visitors for illness)
- Maintenance of sterile technique when indicated
Assess for risk factors and monitor vital signs. Assess for signs of infection every 2 hours following rupture of membranes.
Lab work:
- Blood cultures
- CBC with differential
- BMP
- C-reactive protein
Treatment and nursing interventions
- IV antibiotics
- IV fluids
- Thermoregulatory support
- Nutritional support
- Decrease of stimuli
- Educate/ reassure family members