El virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology de la hepatitis B Hepatitis B Hepatitis B virus (HBV) is a partially double-stranded DNA virus, which belongs to the Orthohepadnavirus genus and the Hepadnaviridae family. Most individuals with acute HBV infection are asymptomatic or have mild, self-limiting symptoms. Chronic infection can be asymptomatic or create hepatic inflammation, leading to liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Hepatitis B Virus ( HBV HBV Hepatitis B virus (HBV) is a partially double-stranded DNA virus, which belongs to the Orthohepadnavirus genus and the Hepadnaviridae family. Hepatitis B virus is transmitted by exposure to infectious blood or body fluids. Examples of types of exposure include sexual intercourse, IV drug use, and childbirth. Hepatitis B Virus, por sus siglas en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum inglés) es un virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology de ADN parcialmente bicatenario, que pertenece al AL Amyloidosis género Orthohepadnavirus Orthohepadnavirus A genus of hepadnaviridae causing hepatitis in humans, woodchucks (hepatitis B virus, woodchuck) and ground squirrels. Hepatitis B virus is the type species. Hepatitis B Virus y a la familia Hepadnaviridae Hepadnaviridae A family of hepatotropic DNA viruses which contains double-stranded DNA genomes and causes hepatitis in humans and animals. There are two genera: avihepadnavirus and orthohepadnavirus. Hepadnaviruses include hepatitis B virus, duck hepatitis B virus, heron hepatitis B virus, ground squirrel hepatitis virus, and woodchuck hepatitis B virus. Hepatitis B Virus. El virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology de la hepatitis B Hepatitis B Hepatitis B virus (HBV) is a partially double-stranded DNA virus, which belongs to the Orthohepadnavirus genus and the Hepadnaviridae family. Most individuals with acute HBV infection are asymptomatic or have mild, self-limiting symptoms. Chronic infection can be asymptomatic or create hepatic inflammation, leading to liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Hepatitis B Virus se transmite por exposición a sangre o fluidos corporales infecciosos. Algunos ejemplos de tipos de exposición son las relaciones sexuales, el uso de drogas intravenosas y el parto. El virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology puede causar una enfermedad hepática potencialmente mortal. La mayoría de los LOS Neisseria individuos con infección aguda por el HBV HBV Hepatitis B virus (HBV) is a partially double-stranded DNA virus, which belongs to the Orthohepadnavirus genus and the Hepadnaviridae family. Hepatitis B virus is transmitted by exposure to infectious blood or body fluids. Examples of types of exposure include sexual intercourse, IV drug use, and childbirth. Hepatitis B Virus son asintomáticos o presentan síntomas leves y autolimitantes. La infección crónica puede ser asintomática o crear una inflamación hepática, lo que conduce a la cirrosis hepática y al AL Amyloidosis carcinoma hepatocelular. El tratamiento de la hepatitis aguda suele ser de soporte. La administración de antivirales o el trasplante de hígado pueden ser necesarios en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria casos fulminantes y crónicos.
Last updated: Jan 17, 2024
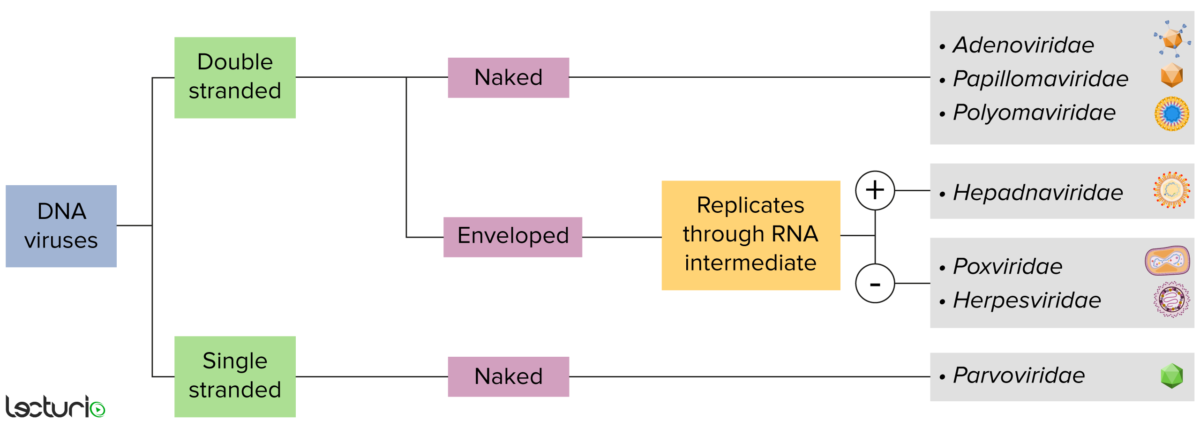
Identificación de virus de ADN:
Los virus pueden clasificarse de muchas maneras. Sin embargo, la mayoría de los virus tienen un genoma formado por ADN o ARN. Los virus con un genoma de ADN pueden caracterizarse además como monocatenario o bicatenario. Los virus “envueltos” están cubiertos por una fina capa de membrana celular, que generalmente es tomado de la célula huésped. Sin embargo, si la capa está ausente, los virus se denominan “desnudos”. Algunos virus con envoltura traducen el ADN en ARN antes de incorporarse al genoma de la célula huésped.
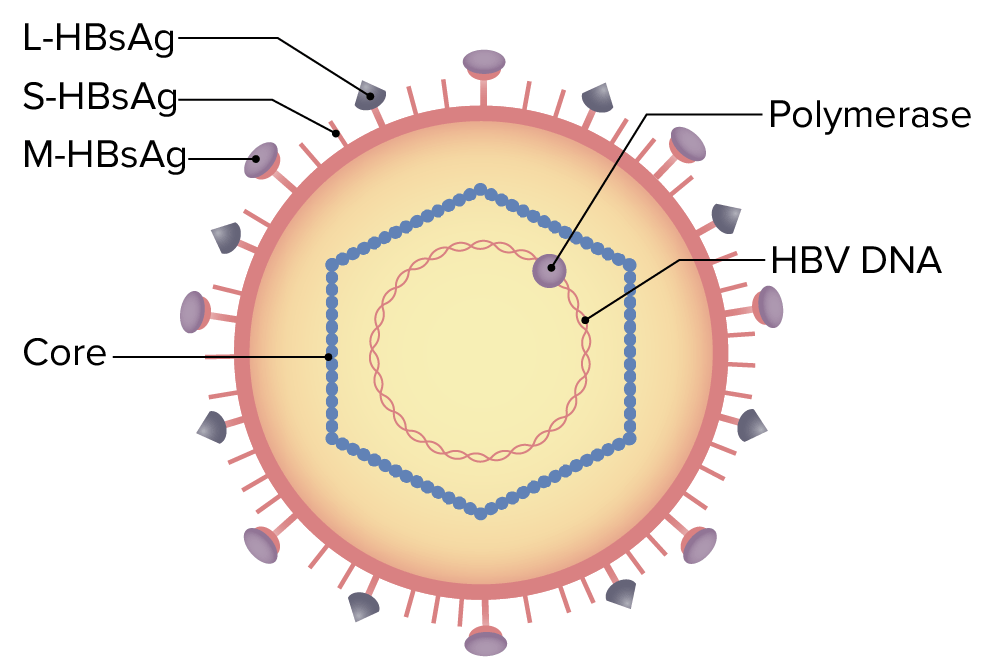
Estructura del virus de la hepatitis B (VHB):
La partícula del virus (virión) está formada por una envoltura lipídica externa. La nucleocápside (núcleo) encierra el ADN viral y una ADN polimerasa que tiene actividad de transcriptasa inversa. La envoltura externa contiene proteínas que ayudan al virus a unirse y entrar en las células objetivo.
Micrografía electrónica del virus de la hepatitis B (HBV, por sus siglas en inglés)
Imagen: “Hepatitis-B virions” por CDC. Licencia: Dominio Público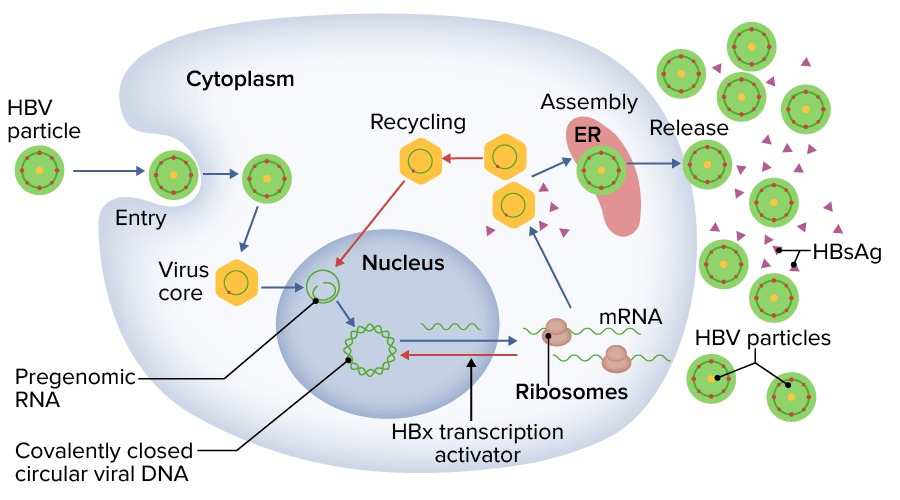
Replicación del virus de la hepatitis B (VHB):
El VHB es fagocitado para replicarse utilizando la maquinaria de replicación de la célula huésped.
HBsAg: antígeno de superficie de la hepatitis B
Monitoreo de la infección por el HBV HBV Hepatitis B virus (HBV) is a partially double-stranded DNA virus, which belongs to the Orthohepadnavirus genus and the Hepadnaviridae family. Hepatitis B virus is transmitted by exposure to infectious blood or body fluids. Examples of types of exposure include sexual intercourse, IV drug use, and childbirth. Hepatitis B Virus:
Hepatitis B Hepatitis B Hepatitis B virus (HBV) is a partially double-stranded DNA virus, which belongs to the Orthohepadnavirus genus and the Hepadnaviridae family. Most individuals with acute HBV infection are asymptomatic or have mild, self-limiting symptoms. Chronic infection can be asymptomatic or create hepatic inflammation, leading to liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Hepatitis B Virus aguda:
Personas vacunadas contra el HBV HBV Hepatitis B virus (HBV) is a partially double-stranded DNA virus, which belongs to the Orthohepadnavirus genus and the Hepadnaviridae family. Hepatitis B virus is transmitted by exposure to infectious blood or body fluids. Examples of types of exposure include sexual intercourse, IV drug use, and childbirth. Hepatitis B Virus:
Hepatitis B Hepatitis B Hepatitis B virus (HBV) is a partially double-stranded DNA virus, which belongs to the Orthohepadnavirus genus and the Hepadnaviridae family. Most individuals with acute HBV infection are asymptomatic or have mild, self-limiting symptoms. Chronic infection can be asymptomatic or create hepatic inflammation, leading to liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Hepatitis B Virus crónica:
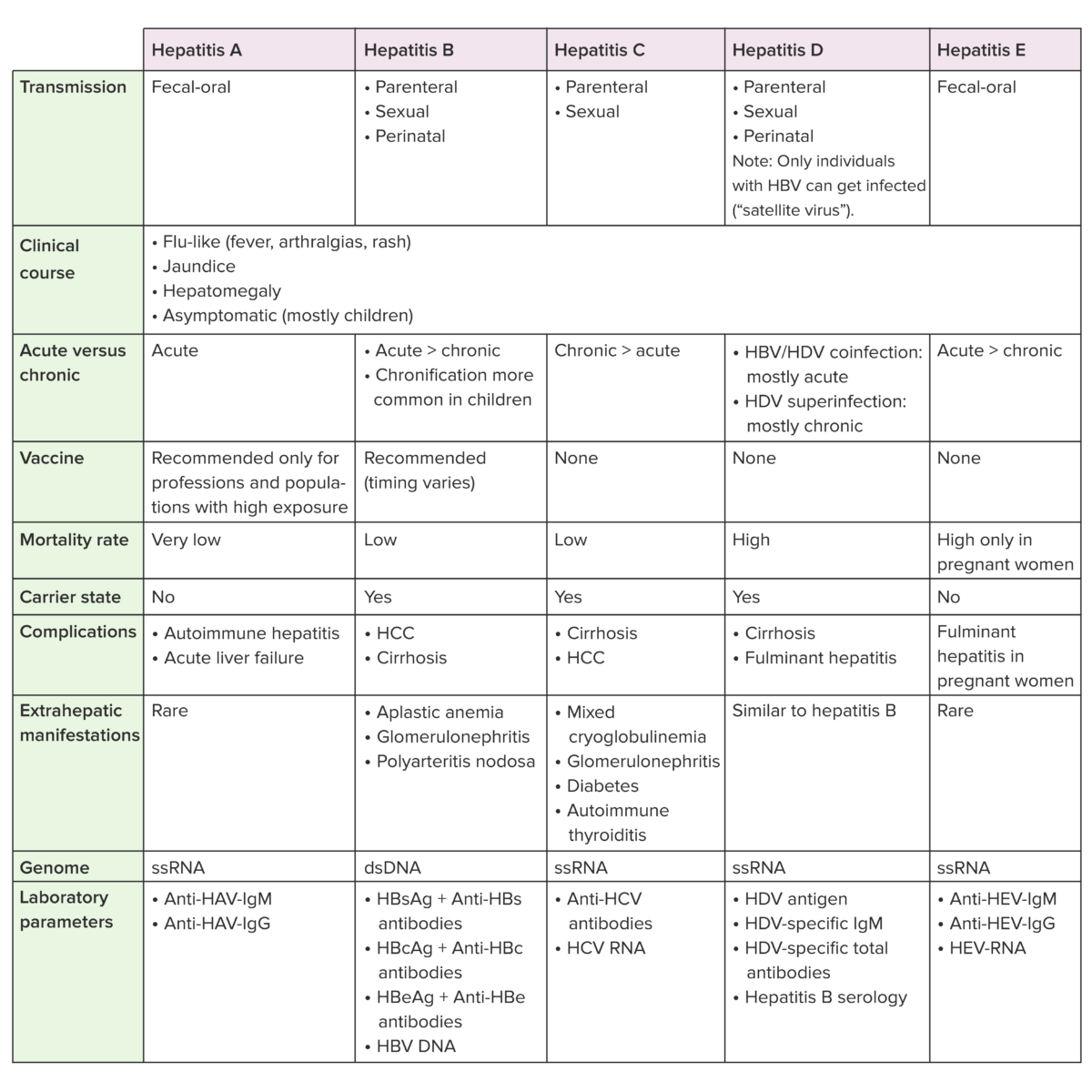
| HBsAg | Anti-HBc-IgM | Anti-HBc-IgG | Anti-HBs anti-HBs Hepatitis B Virus | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Susceptible | Negativo | Negativo | Negativo | Negativo |
| Infección aguda | Positivo | Positivo | Negativo | Negativo |
| Infección previa (inactiva) | Negativo | Negativo | Positivo | Positivo |
| Vacunación contra VHB | Negativo | Negativo | Negativo | Positivo |
| Infección crónica | Positivo | Negativo | Positivo | Negativo |
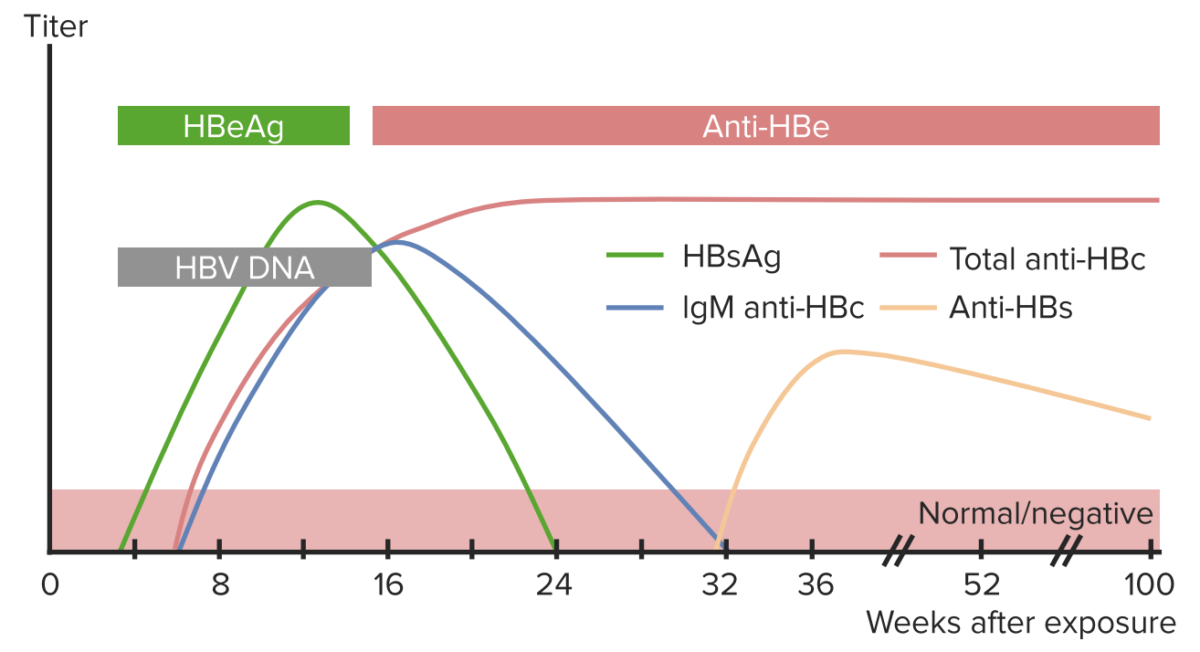
Parámetros de laboratorio de la infección por el virus de la hepatitis B (HBV, por sus siglas en inglés):
El gráfico muestra la evolución típica de los marcadores importantes en el diagnóstico de la infección por el HBV tras la exposición viral.
Hepatitis B Hepatitis B Hepatitis B virus (HBV) is a partially double-stranded DNA virus, which belongs to the Orthohepadnavirus genus and the Hepadnaviridae family. Most individuals with acute HBV infection are asymptomatic or have mild, self-limiting symptoms. Chronic infection can be asymptomatic or create hepatic inflammation, leading to liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Hepatitis B Virus aguda:
Hepatitis B Hepatitis B Hepatitis B virus (HBV) is a partially double-stranded DNA virus, which belongs to the Orthohepadnavirus genus and the Hepadnaviridae family. Most individuals with acute HBV infection are asymptomatic or have mild, self-limiting symptoms. Chronic infection can be asymptomatic or create hepatic inflammation, leading to liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Hepatitis B Virus crónica:
Tamizaje:
Vacunación:
Profilaxis postexposición:
Las opciones dependen del estado de inmunización: