Existen 47 sistemas de grupo sanguíneo, entre los LOS Neisseria cuales el grupo ABO es el más importante. Los LOS Neisseria grupos sanguíneos se determinan por medio de antígenos que son marcadores de superficie en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria eritrocitos y consisten en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum proteínas y carbohidratos. Los LOS Neisseria antígenos también se encuentran en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum plaquetas, leucocitos y células tisulares, y también existen en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum forma soluble en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum secreciones corporales como leche materna, líquido seminal, saliva Saliva The clear, viscous fluid secreted by the salivary glands and mucous glands of the mouth. It contains mucins, water, organic salts, and ptyalin. Salivary Glands: Anatomy, sudor, secreciones gástricas, orina y líquido amniótico. Los LOS Neisseria individuos desarrollarán naturalmente anticuerpos contra los LOS Neisseria antígenos ABO que no tienen. Por esta razón, es importante determinar el grupo sanguíneo de un individuo antes de cualquier transfusión de hemoderivados y antes de donar o recibir un trasplante de órganos. Si no se produce el emparejamiento adecuado, se producirá una activación masiva del sistema inmunológico y de la cascada de coagulación, lo que provocará shock Shock Shock is a life-threatening condition associated with impaired circulation that results in tissue hypoxia. The different types of shock are based on the underlying cause: distributive (↑ cardiac output (CO), ↓ systemic vascular resistance (SVR)), cardiogenic (↓ CO, ↑ SVR), hypovolemic (↓ CO, ↑ SVR), obstructive (↓ CO), and mixed. Types of Shock, fallo orgánico e incluso la muerte.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Hay 4 grupos sanguíneos comunes en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el sistema ABO: A, B, AB y O.
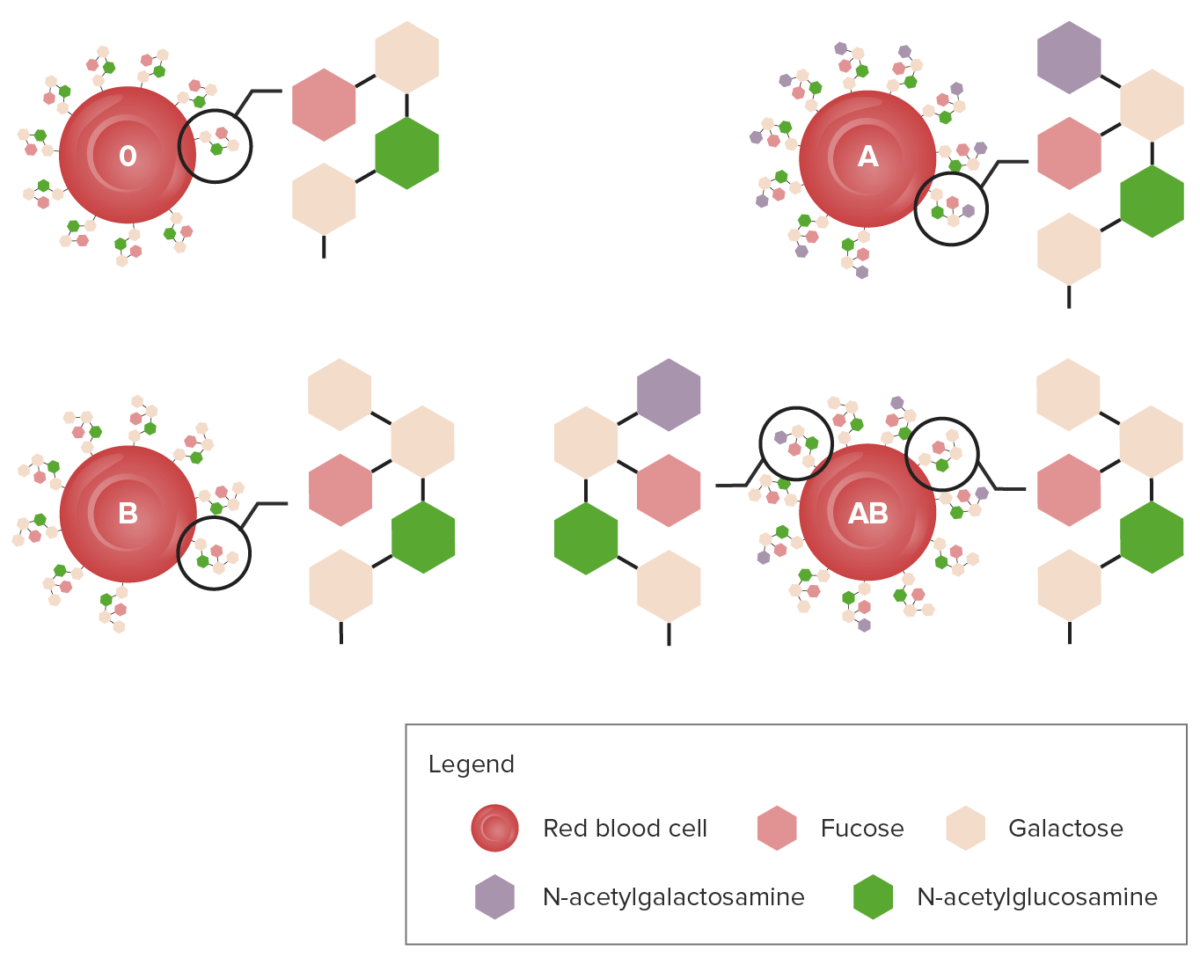
Diagrama que muestra las cadenas de carbohidratos que determinan el grupo sanguíneo ABO
Imagen por Lecturio.Las frecuencias del tipo de sangre varían en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria diferentes grupos raciales/étnicos. El grupo sanguíneo ABO se hereda de forma autosómica codominante:
| Madre A | Madre B | Madre O | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Padre A | AA AA Amyloidosis | AB | AO |
| Padre B | BA | BB | BO |
| Padre O | OA OA Osteoarthritis (OA) is the most common form of arthritis, and is due to cartilage destruction and changes of the subchondral bone. The risk of developing this disorder increases with age, obesity, and repetitive joint use or trauma. Patients develop gradual joint pain, stiffness lasting < 30 minutes, and decreased range of motion. Osteoarthritis | OB | OO |
| Alelos | Tipo de sangre |
|---|---|
| A + A | A |
| A + O | A |
| A + B | AB |
| B + B | B |
| B + O | B |
| O + O | O |
Los LOS Neisseria individuos desarrollarán naturalmente anticuerpos contra los LOS Neisseria antígenos ABO que no tienen:
Estos anticuerpos pueden provocar una respuesta hemolítica al AL Amyloidosis encontrarse con su respectivo antígeno:
Los LOS Neisseria grupos sanguíneos se asocian con un riesgo diferencial a ciertas enfermedades. El grupo sanguíneo O puede tener ↓ riesgo de:
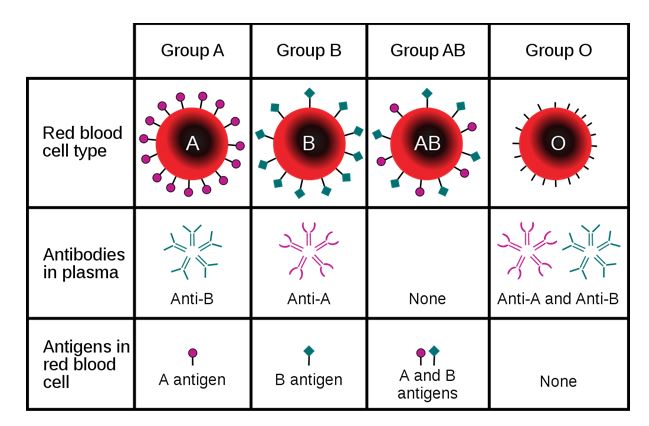
Diagrama que muestra que una persona puede expresar A, B, AB o ningún antígeno:
El diagrama también describe el tipo de anticuerpo producido por el portador.
El factor Rh (factor Rhesus) es un antígeno de superficie eritrocitario.
Los LOS Neisseria anticuerpos Anti-Rh se producen cuando:
Si el feto es Rh+ y la madre Rh-, es necesario realizar un control seriado durante el embarazo, que se lleva a cabo mediante:
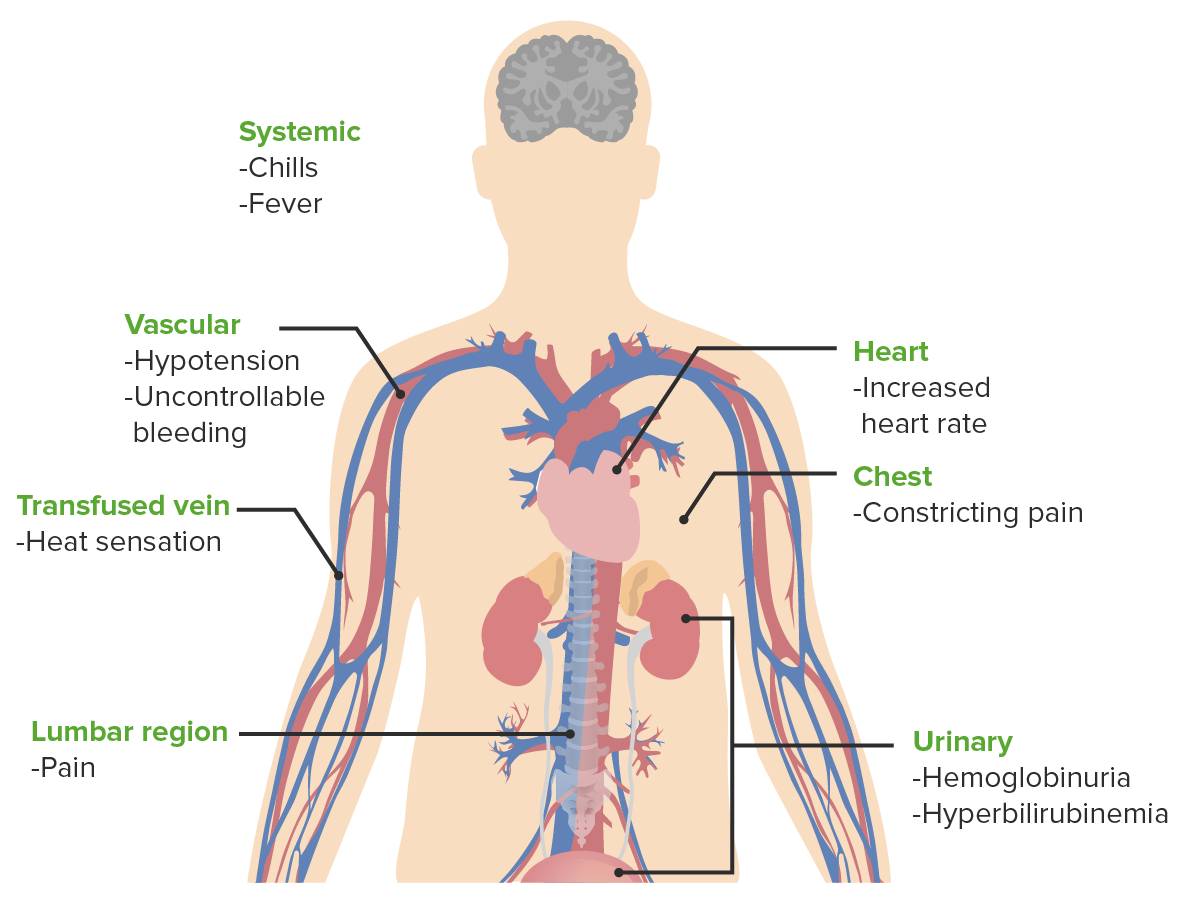
Signos y síntomas de las reacciones transfusionales hemolíticas agudas
Imagen por Lecturio.Las complicaciones de la transfusión de sangre pueden ser agudas (minutos a horas) o retardadas (días a meses).
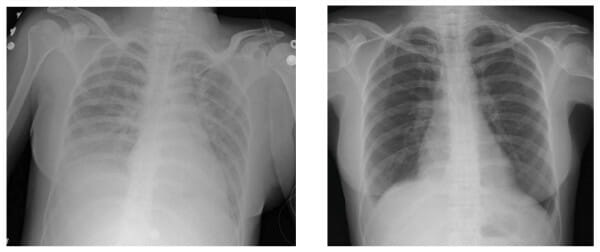
Lesión pulmonar aguda relacionada con la transfusión:
Izquierda: hallazgo en la radiografía de tórax durante los síntomas agudos
Derecha: Radiografía de tórax después de desconectar al individuo del ventilador