El síndrome de Budd-Chiari es una afección que resulta de la interrupción del drenaje normal de la sangre hepática. El tipo primario surge de un proceso venoso (que afecta a las venas hepáticas o a la vena cava inferior) como la trombosis, pero también puede deberse a una lesión que comprima o invada las venas (tipo secundario). El paciente típicamente se presenta con hepatomegalia, ascitis y molestias abdominales. El inicio suele ser subagudo o crónico. El diagnóstico se confirma mediante ultrasonido Doppler Doppler Ultrasonography applying the doppler effect, with frequency-shifted ultrasound reflections produced by moving targets (usually red blood cells) in the bloodstream along the ultrasound axis in direct proportion to the velocity of movement of the targets, to determine both direction and velocity of blood flow. Ultrasound (Sonography). El tratamiento consiste en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum abordar la afección subyacente que causó la oclusión venosa. El tratamiento posterior implica la prevención de nuevos coágulos (anticoagulación), la restauración del flujo sanguíneo y la descompresión del hígado. Se considera el trasplante hepático si el tratamiento inicial falla y/o el paciente tiene cirrosis hepática descompensada.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
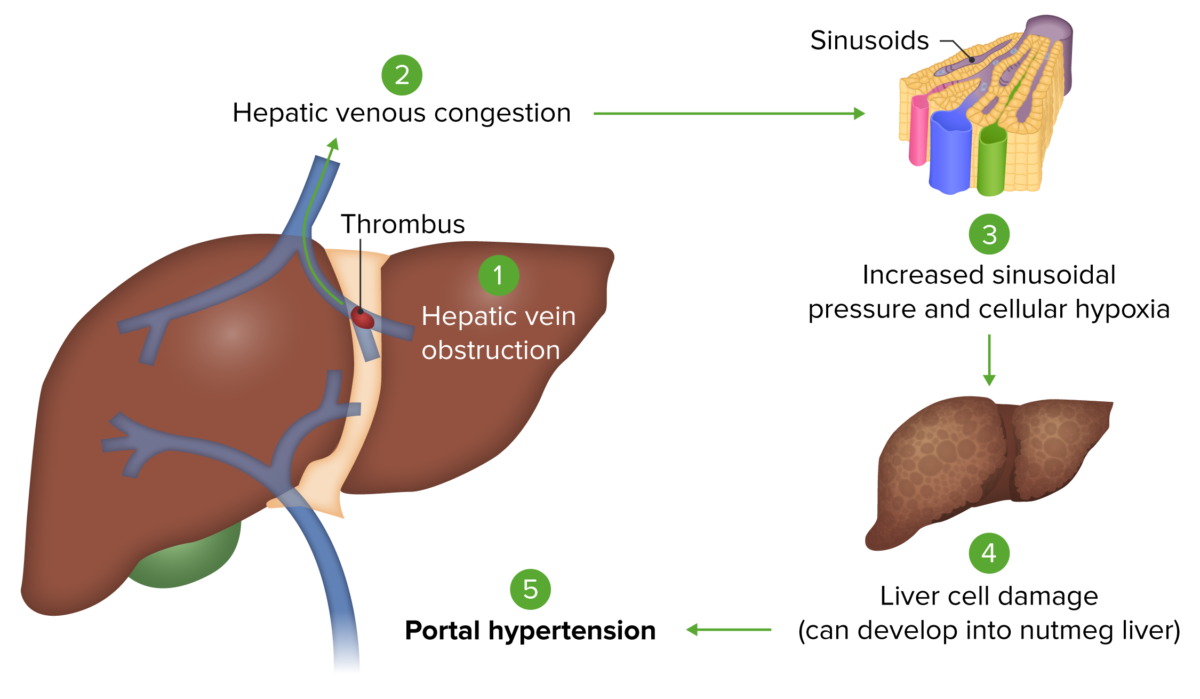
Síndrome de Budd-Chiari: la oclusión de las venas hepáticas provoca congestión venosa hepática. Esta congestión aumenta la presión sinusoidal dentro del hígado, lo que reduce el flujo sanguíneo hepático. Esto eventualmente produce lesión hepatocelular por hipoxia. El daño hepático resulta entonces en hipertensión portal.
Imagen por Lecturio.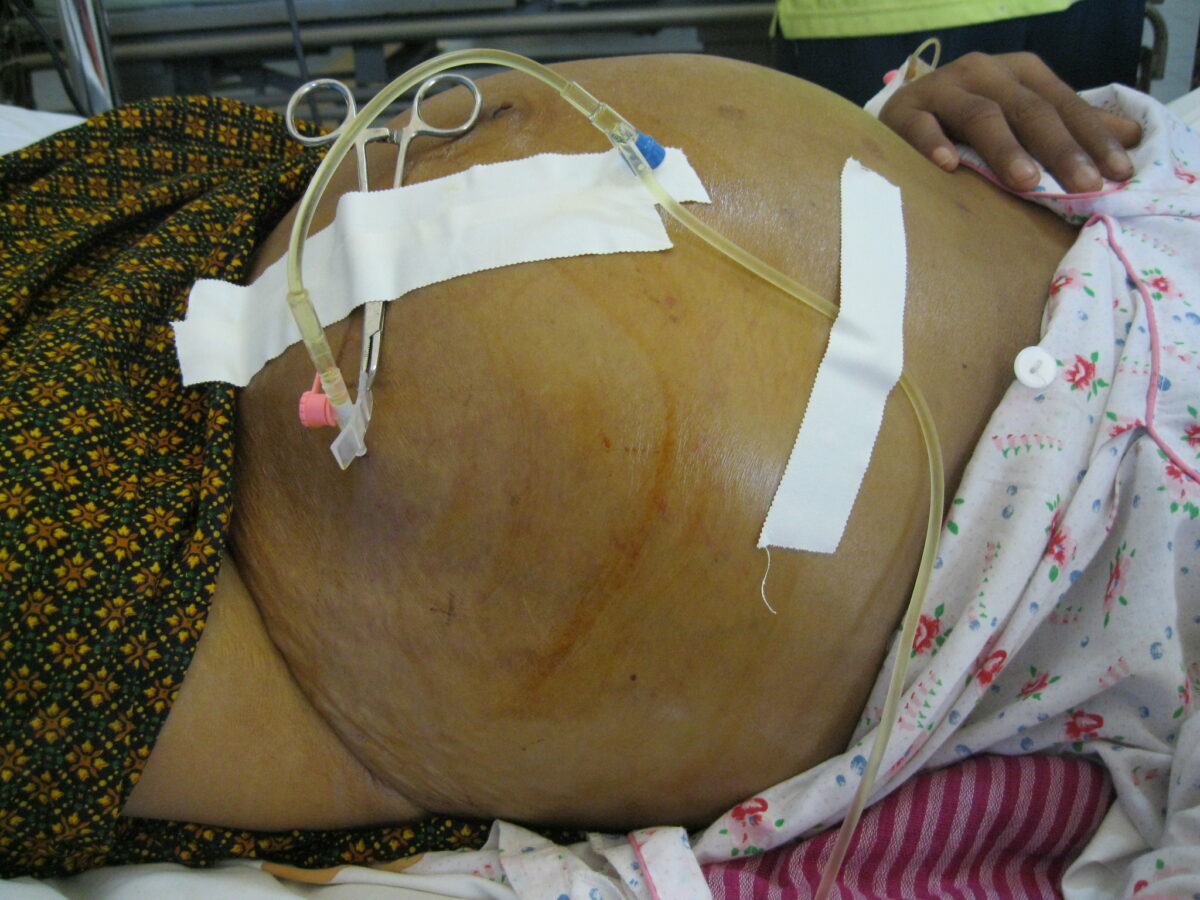
Imagen que muestra a un paciente con ascitis sometido a paracentesis
Imagen: “Draining ascites, secondary to hepatic cirrhosis” por John Campbell. Licencia: Dominio Público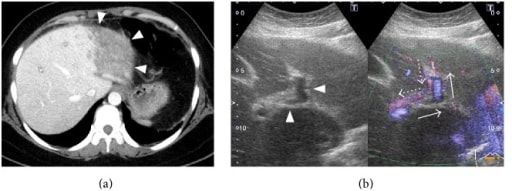
Mujer de 34 años con síndrome antifosfolípido que presenta síndrome de Budd-Chiari agudo.
a) TC dinámica: mal realce del segmento lateral del lóbulo hepático izquierdo (puntas de flecha).
(b) Ultrasonido Doppler de la parte intrahepática de la vena porta: la rama izquierda de la vena porta (puntas de flecha) muestra reflujo (flechas: flujo sanguíneo normal; flechas punteadas: flujo sanguíneo observado en este paciente).
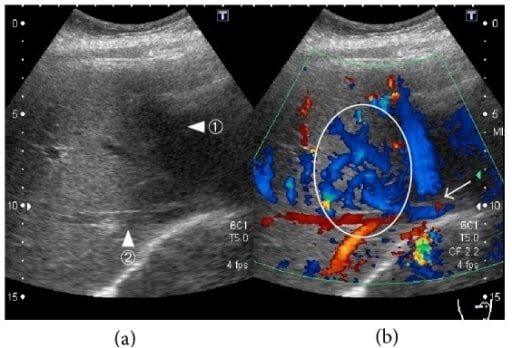
Mujer de 34 años con síndrome de Budd-Chiari agudo (trombosis en vena hepática media e izquierda), ultrasonido Doppler de venas hepáticas:
(a) Vena hepática media (punta de flecha ①) y vena hepática derecha (punta de flecha ②).
(b) El flujo sanguíneo está ausente en partes de la vena hepática media (flecha). Se observa un aumento del flujo sanguíneo en la región que va desde la vena hepática media hasta la vena hepática derecha (círculo).
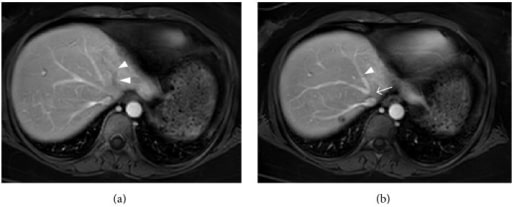
RM con contraste de una mujer de 34 años con síndrome de Budd-Chiari agudo (oclusión de la vena hepática izquierda y media):
(a) No hay captación de contraste en la vena hepática izquierda (punta de flecha).
(b) Se visualiza la vena hepática media (punta de flecha), pero no hay realce en su confluencia con la vena cava inferior (flecha), lo que sugiere obstrucción.