Pseudomonas Pseudomonas Pseudomonas is a non-lactose-fermenting, gram-negative bacillus that produces pyocyanin, which gives it a characteristic blue-green color. Pseudomonas is found ubiquitously in the environment, as well as in moist reservoirs, such as hospital sinks and respiratory equipment. Pseudomonas es un bacilo gramnegativo que no fermenta lactosa y produce piocianina, que le da un color azul verdoso característico. Pseudomonas Pseudomonas Pseudomonas is a non-lactose-fermenting, gram-negative bacillus that produces pyocyanin, which gives it a characteristic blue-green color. Pseudomonas is found ubiquitously in the environment, as well as in moist reservoirs, such as hospital sinks and respiratory equipment. Pseudomonas se encuentra de forma ubicua en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el medio ambiente, así como en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum reservorios húmedos, como lavabos de hospitales y equipos respiratorios. Pseudomonas Pseudomonas Pseudomonas is a non-lactose-fermenting, gram-negative bacillus that produces pyocyanin, which gives it a characteristic blue-green color. Pseudomonas is found ubiquitously in the environment, as well as in moist reservoirs, such as hospital sinks and respiratory equipment. Pseudomonas tiene un olor dulce, parecido a la uva. La especie clínicamente más relevante es Pseudomonas aeruginosa Pseudomonas aeruginosa A species of gram-negative, aerobic, rod-shaped bacteria commonly isolated from clinical specimens (wound, burn, and urinary tract infections). It is also found widely distributed in soil and water. P. Aeruginosa is a major agent of nosocomial infection. Pseudomonas ( P. aeruginosa P. aeruginosa A species of gram-negative, aerobic, rod-shaped bacteria commonly isolated from clinical specimens (wound, burn, and urinary tract infections). It is also found widely distributed in soil and water. P. Aeruginosa is a major agent of nosocomial infection. Pseudomonas), que tiene una amplia gama de manifestaciones clínicas desde enfermedades benignas, como el oído de nadador y la foliculitis de “jacuzzi”, hasta bacteriemia diseminada y osteomielitis. Los LOS Neisseria factores de riesgo de infecciones incluyen: neutropenia Neutropenia Neutrophils are an important component of the immune system and play a significant role in the eradication of infections. Low numbers of circulating neutrophils, referred to as neutropenia, predispose the body to recurrent infections or sepsis, though patients can also be asymptomatic. Neutropenia, fibrosis Fibrosis Any pathological condition where fibrous connective tissue invades any organ, usually as a consequence of inflammation or other injury. Bronchiolitis Obliterans quística, asplenia Asplenia Asplenia is the absence of splenic tissue or function and can stem from several factors ranging from congenital to iatrogenic. There is a distinction between anatomic asplenia, which is due to the surgical removal of the spleen, and functional asplenia, which is due to a condition that leads to splenic atrophy, infarct, congestion, or infiltrative disease. Asplenia, lesiones por quemaduras y catéteres permanentes/intubación endotraqueal. El tratamiento es principalmente con piperacilina/ tazobactam Tazobactam A penicillanic acid and sulfone derivative and potent beta-lactamase inhibitor that enhances the activity of other anti-bacterial agents against beta-lactamase producing bacteria. Cephalosporins.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
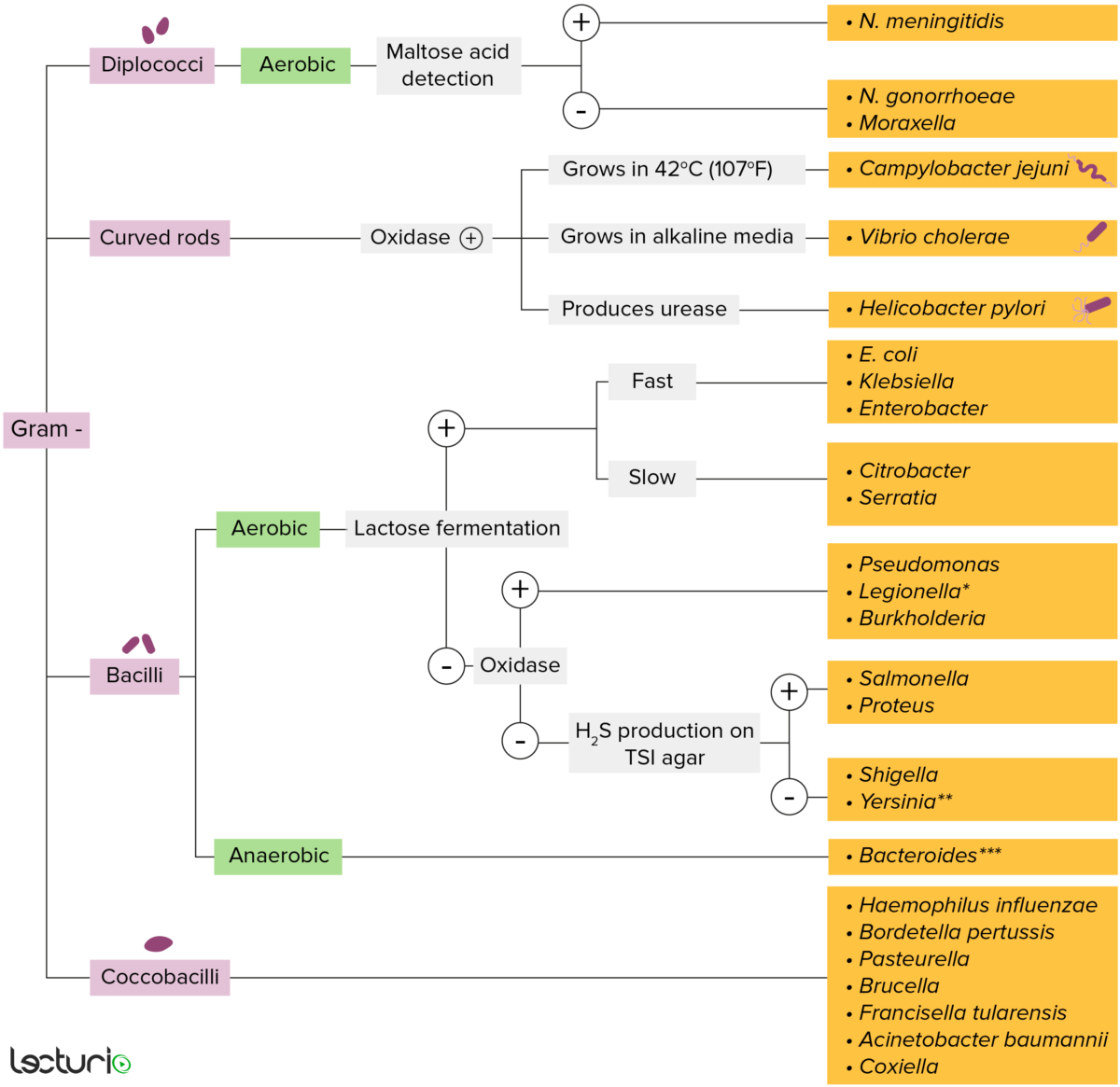
Bacterias gramnegativas:
La mayoría de las bacterias se pueden clasificar de acuerdo a un procedimiento de laboratorio llamado tinción de Gram.
Las bacterias con paredes celulares que tienen una capa delgada de peptidoglicano no retienen la tinción de cristal violeta utilizada en la tinción de Gram. Sin embargo, estas bacterias retienen la contratinción de safranina y, por lo tanto, adoptan un color rojo-rosado en la tinción, lo que las hace gramnegativas. Estas bacterias pueden clasificarse además según su morfología (diplococos, bastones curvos, bacilos y cocobacilos) y su capacidad para crecer en presencia de oxígeno (aeróbicos versus anaeróbicos). Las bacterias se pueden identificar de manera más profunda cultivándolas en medios específicos (agar hierro triple azúcar) donde se pueden identificar sus enzimas (ureasa, oxidasa) y se puede probar su capacidad para fermentar lactosa.
* Se tiñe mal en la tinción de Gram
** Bastón pleomórfico/cocobacilo
*** Requiere medios de transporte especiales
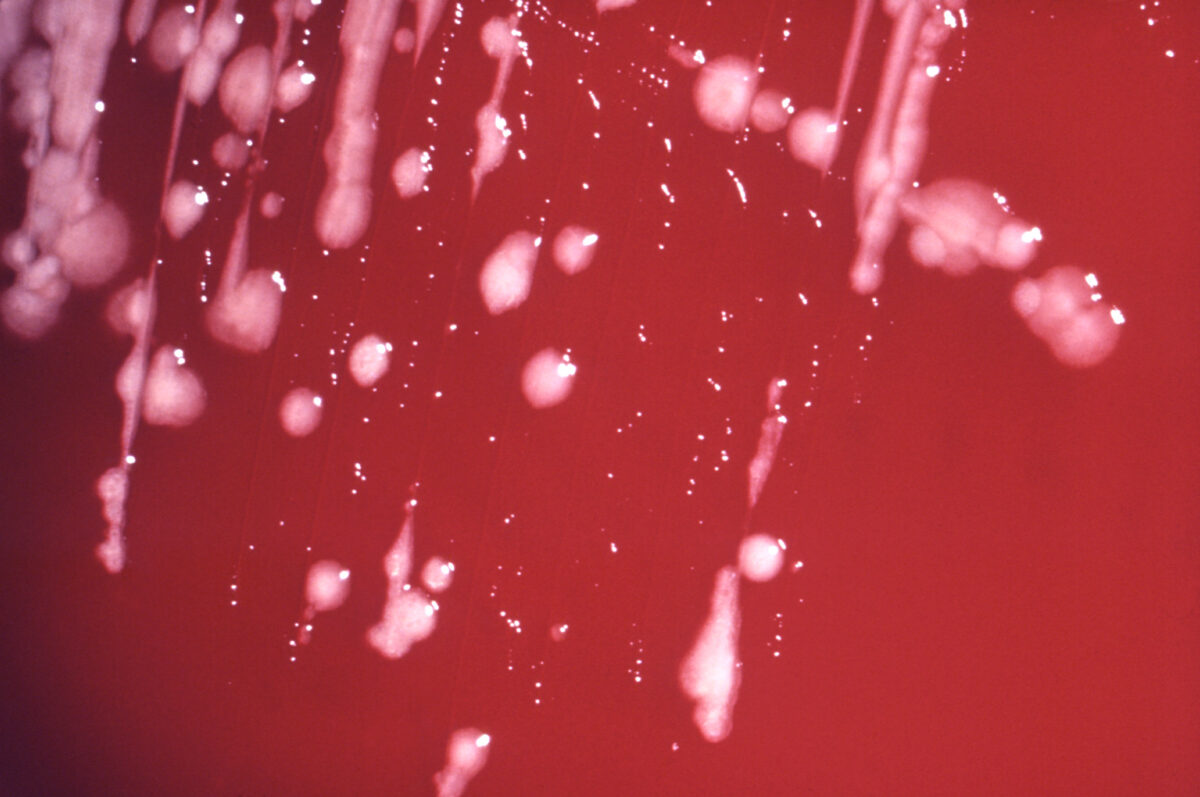

La fotografía muestra el patrón de crecimiento colonial mostrado por la bacteria Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
Imagen: “6688” por CDC/Dr. Teo Hawkins. Licencia: Dominio Público.Reservorio:
Transmisión:
| Factor de virulencia | Efecto |
|---|---|
| Cápsula de polisacárido |
|
| Pili Pili Filamentous or elongated proteinaceous structures which extend from the cell surface in gram-negative bacteria that contain certain types of conjugative plasmid. These pili are the organs associated with genetic transfer and have essential roles in conjugation. Normally, only one or a few pili occur on a given donor cell. This preferred use of ‘pili’ refers to the sexual appendage, to be distinguished from bacterial fimbriae, also known as common pili, which are usually concerned with adhesion. Salmonella |
|
| Fosfolipasa C |
|
| Exotoxina A |
|
| Piocianina |
|
| Sistema de secreción tipo III |
|
| Formación de biopelículas in vivo |
|
| ꞵ-lactamasa y bombas de eflujo |
|
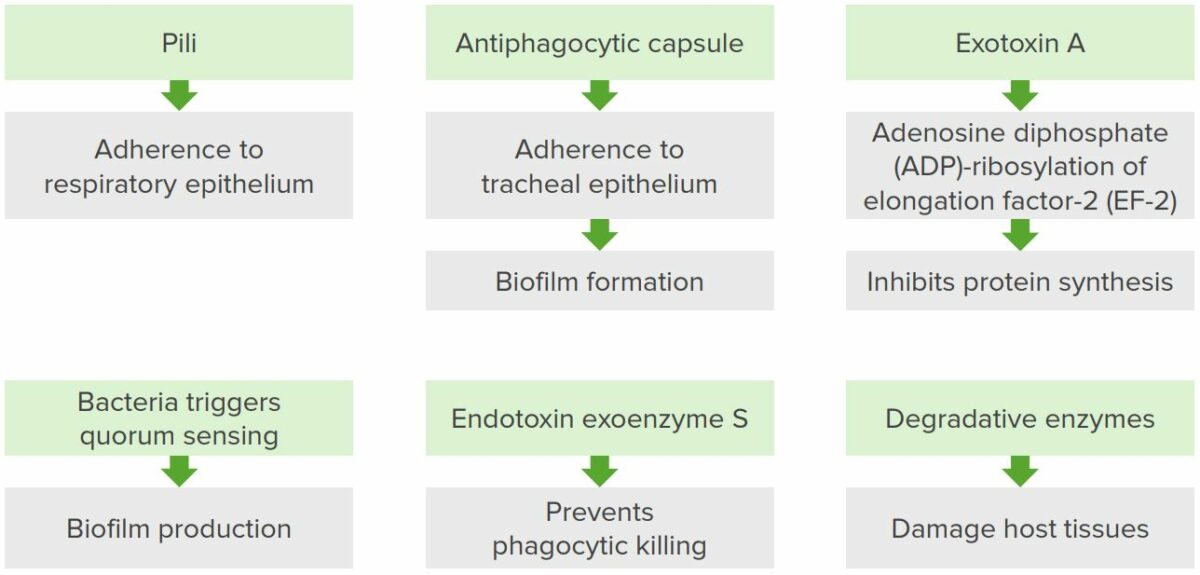
Mecanismos de la patogénesis de Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Imagen por Lecturio.| Tipo de afección | Características |
|---|---|
| Infección del tracto urinario |
|
| Infecciones de heridas por quemadura |
Asociada con lesiones por quemaduras, causando:
|
| Infecciones de oído |
Otitis externa
Otitis externa
Otitis externa (also known as external otitis or swimmer’s ear) is an infection of the external auditory canal that is most often caused by acute bacterial infection and is frequently associated with hot, humid weather and water exposure. Patients commonly present with ear pain, pruritus, discharge, and hearing loss.
Otitis Externa:
|
| Infecciones de la piel |
Ectima gangrenoso:
|
| Infecciones pulmonares |
|
| Infecciones oculares |
Ocurre
en
EN
Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins.
Erythema Nodosum usuarios de lentes de contacto o traumatismo ocular menor:
|
| Infecciones diseminadas |
Ocurre
en
EN
Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins.
Erythema Nodosum huéspedes inmunocomprometidos:
|
| Osteomielitis |
|
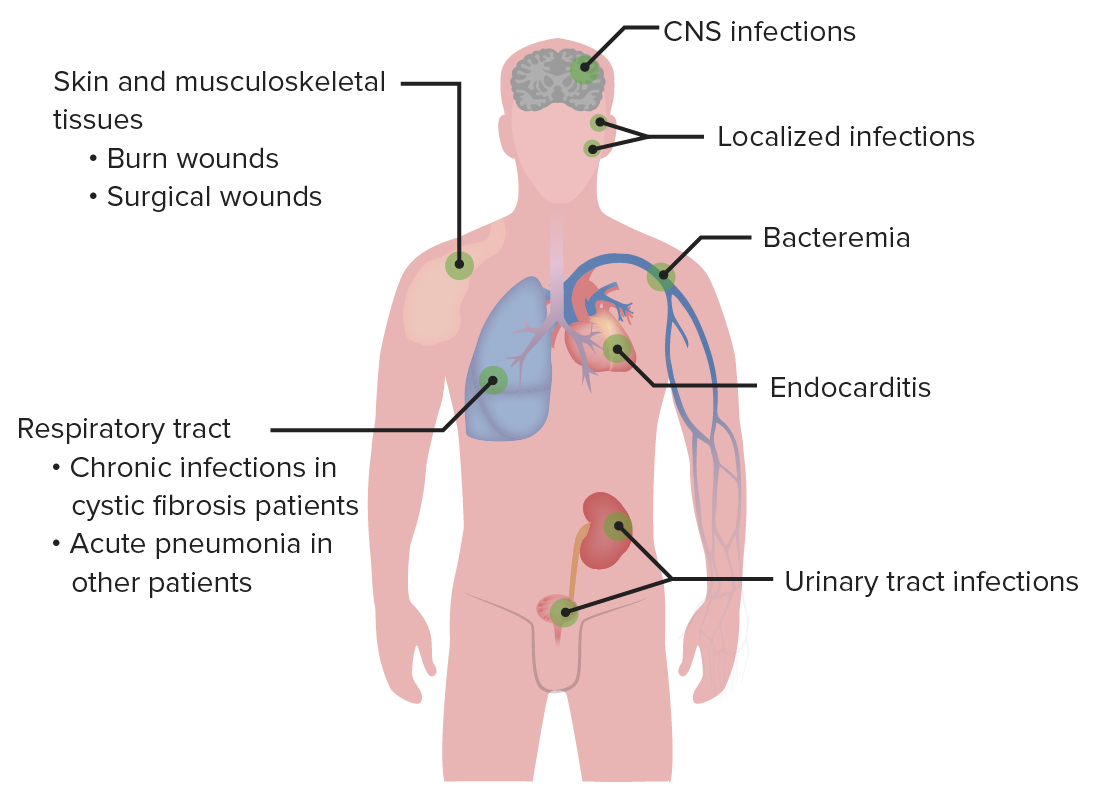
Diagrama de los sitios comunes de infección por Pseudomonas
Imagen por Lecturio.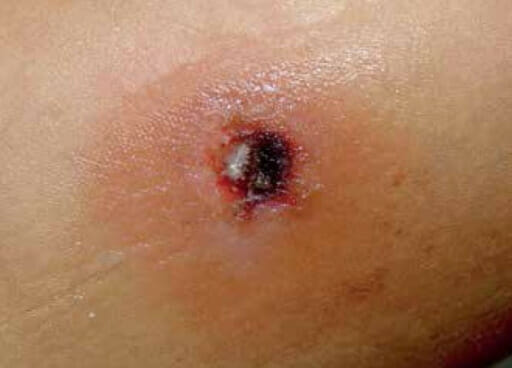
Imagen que muestra un ectima gangrenoso debido a la bacteria Pseudomonas en un niño inmunocomprometido
Imagen: “A single black ulcer in a child with acute lymphocytic leukemia” por Michelangelo Vestita et al. Licencia: CC BY 4.0Para ayudar a recordar los múltiples datos clínicamente relevantes sobre Pseudomonas, use la mnemotecnia “PSEUDOMONAS” ( en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum inglés):