Las especies de Leishmania Leishmania Leishmania species are obligate intracellular parasites that are transmitted by an infected sandfly. The disease is endemic to Asia, the Middle East, Africa, the Mediterranean, and South and Central America. Clinical presentation varies, dependent on the pathogenicity of the species and the host's immune response. Leishmania/Leishmaniasis son parásitos intracelulares obligatorios que se transmiten a través de un flebótomo infectado. La enfermedad es endémica en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum Asia ASIA Spinal Cord Injuries, Oriente Medio, África, el Mediterráneo y América Central y del Sur. La presentación clínica varía dependiendo de la patogenicidad de la especie y de la respuesta inmunitaria del huésped. La forma más leve es la leishmaniasis Leishmaniasis Leishmania species are obligate intracellular parasites that are transmitted by an infected sandfly. The mildest form is cutaneous leishmaniasis (CL), characterized by painless skin ulcers. The mucocutaneous type involves more tissue destruction, causing deformities. Visceral leishmaniasis (VL), the most severe form, presents with hepatosplenomegaly, anemia, thrombocytopenia, and fever. Leishmania/Leishmaniasis cutánea, caracterizada por úlceras cutáneas indoloras. El tipo mucocutáneo implica una mayor destrucción de los LOS Neisseria tejidos, provocando deformidades. La leishmaniasis Leishmaniasis Leishmania species are obligate intracellular parasites that are transmitted by an infected sandfly. The mildest form is cutaneous leishmaniasis (CL), characterized by painless skin ulcers. The mucocutaneous type involves more tissue destruction, causing deformities. Visceral leishmaniasis (VL), the most severe form, presents with hepatosplenomegaly, anemia, thrombocytopenia, and fever. Leishmania/Leishmaniasis visceral, la forma más grave, se presenta con hepatoesplenomegalia, anemia Anemia Anemia is a condition in which individuals have low Hb levels, which can arise from various causes. Anemia is accompanied by a reduced number of RBCs and may manifest with fatigue, shortness of breath, pallor, and weakness. Subtypes are classified by the size of RBCs, chronicity, and etiology. Anemia: Overview and Types, trombocitopenia y fiebre. El tratamiento se basa en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la gravedad clínica y el estado inmunitario del paciente. Algunas lesiones cutáneas se resuelven espontáneamente o requieren una terapia local. La anfotericina B liposomal es el tratamiento sistémico de primera línea preferido para la leishmaniasis Leishmaniasis Leishmania species are obligate intracellular parasites that are transmitted by an infected sandfly. The mildest form is cutaneous leishmaniasis (CL), characterized by painless skin ulcers. The mucocutaneous type involves more tissue destruction, causing deformities. Visceral leishmaniasis (VL), the most severe form, presents with hepatosplenomegaly, anemia, thrombocytopenia, and fever. Leishmania/Leishmaniasis visceral en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum muchas regiones; otras opciones dependen de la geografía y la especie.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
En EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el flebótomo:
En EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria humanos:
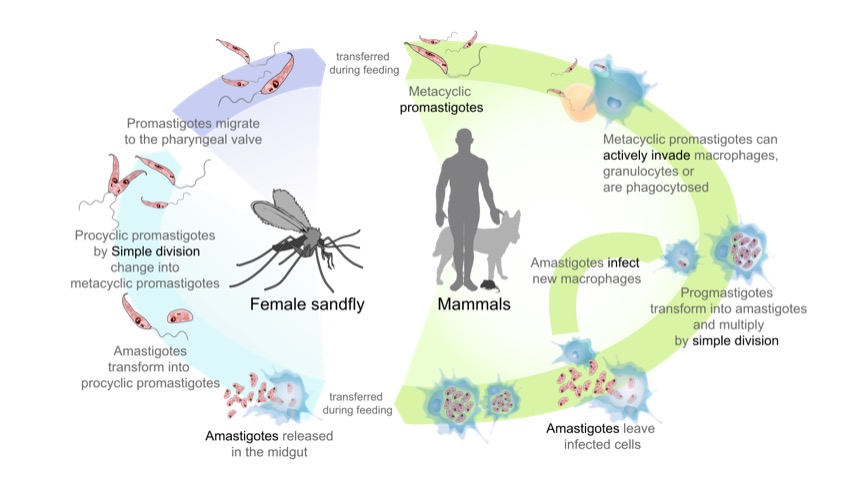
Ciclo de vida de los parásitos del género Leishmania, causantes de la enfermedad de la leishmaniasis:
En el lado izquierdo (empezando por abajo): el flebótomo adquiere amastigotes de un mamífero infectado. Los amastigotes se transforman en promastigotes extracelulares que se multiplican en el intestino medio. Finalmente, los promastigotes migran a la probóscide del flebótomo, listos para ser transferidos a un huésped cuando el flebótomo pique.
En el lado derecho (empezando por arriba): los promastigotes se transfieren a los mamíferos y son fagocitados por los macrófagos. En la célula, los promastigotes se transforman en amastigotes y se multiplican. La célula afectada se rompe y los amastigotes se propagan para infectar otras células.
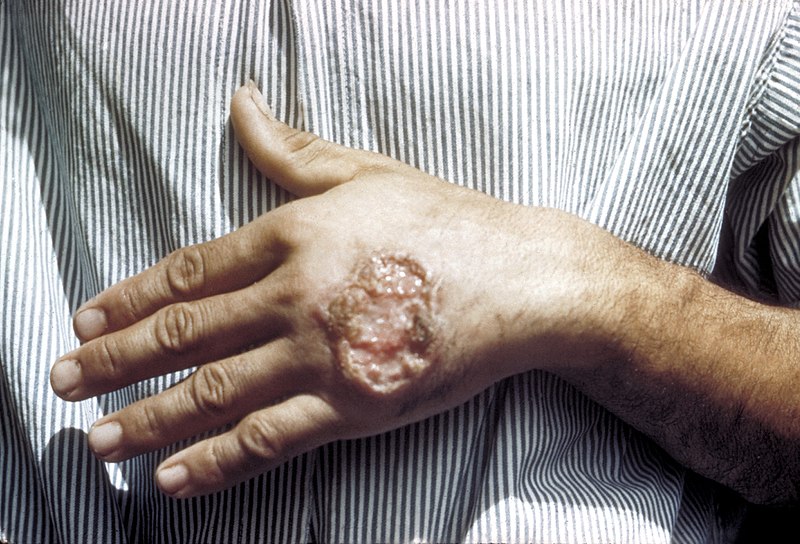
Úlcera cutánea debida a la leishmaniasis observada en la mano de un adulto de América Central
Imagen: “Skin ulcer due to leishmaniasis” por CDC/ Dr. D.S. Martin. Licencia: Dominio Público
Leishmaniasis cutánea difusa o diseminada: se observa en un paciente con síndrome de inmunodeficiencia humana (VIH)
Imagen: “Diffuse or disseminated cutaneous leishmaniasis” por Rotterdam Centre for Tropical Medicine, Rotterdam, The Netherlands. Licencia: CC BY 4.0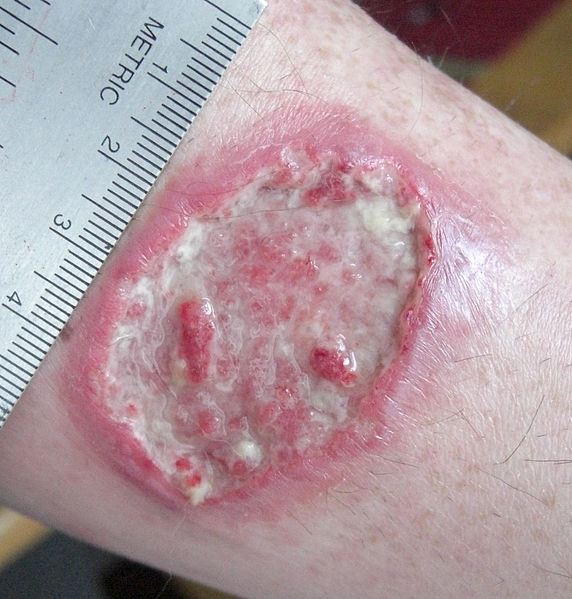
Leishmaniasis cutánea: úlcera de leishmaniasis en el antebrazo izquierdo
Imagen: “Leishmaniasis ulcer on left forearm” por Layne Harris. Licencia: Dominio Público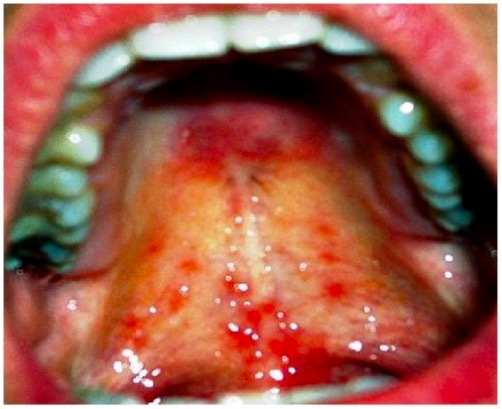
Leishmaniasis mucocutánea: lesiones mucosas dolorosas en el paladar
Imagen: “Healing of lesion” por Department of Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery, E.S.I.C Dental College & Hospital, Rohini, Delhi 110089, India. Licencia: CC BY 3.0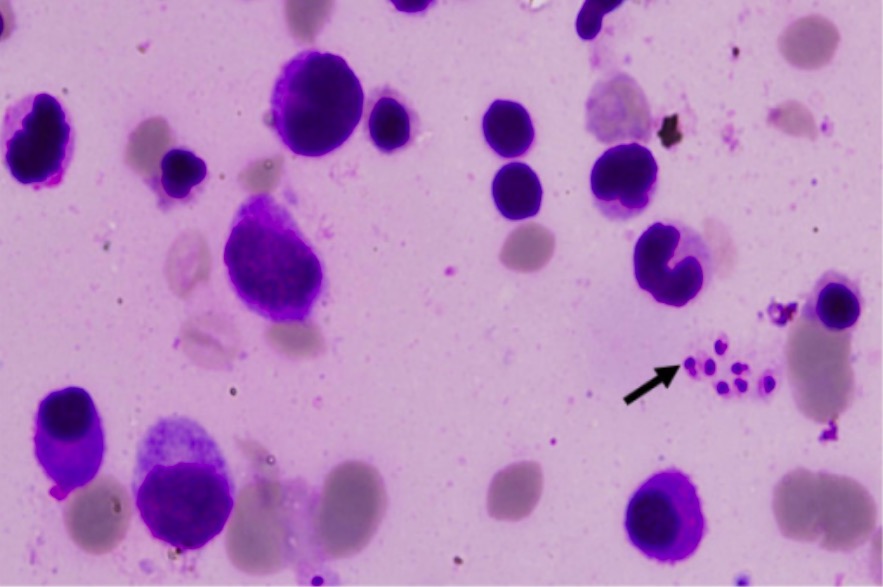
Leishmaniasis visceral: muestra de médula ósea que muestran los cuerpos de Leishman-Donovan (flecha)
Imagen: “Leishman-Donovan bodies” por Department of Medicine, Maulana Azad Medical College, Bahadur Shah Zafar Marg, New Delhi, 110002, India. Licencia: CC BY 2.0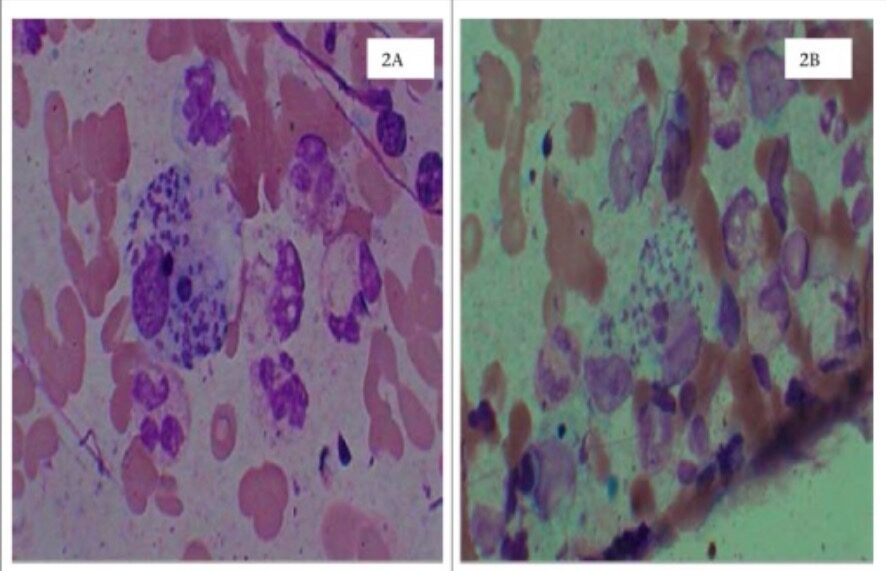
Leishmaniasis cutánea
2A: raspados dérmicos en tinción de Wright que muestran cuerpos de Leishman-Donovan (amastigotes) en el macrófago
2B: raspados dérmicos en la tinción de Leishman
| Giardia Giardia A genus of flagellate intestinal eukaryotes parasitic in various vertebrates, including humans. Characteristics include the presence of four pairs of flagella arising from a complicated system of axonemes and cysts that are ellipsoidal to ovoidal in shape. Nitroimidazoles | Leishmania Leishmania Leishmania species are obligate intracellular parasites that are transmitted by an infected sandfly. The disease is endemic to Asia, the Middle East, Africa, the Mediterranean, and South and Central America. Clinical presentation varies, dependent on the pathogenicity of the species and the host’s immune response. Leishmania/Leishmaniasis | Trypanosoma | Trichomonas Trichomonas A genus of parasitic flagellate eukaryotes distinguished by the presence of four anterior flagella, an undulating membrane, and a trailing flagellum. Nitroimidazoles | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Características |
|
|
|
|
| Formas |
|
|
|
|
| Transmisión |
|
|
|
Transmisión sexual |
| Entidad clínica | Giardiasis Giardiasis An infection of the small intestine caused by the flagellated protozoan giardia. It is spread via contaminated food and water and by direct person-to-person contact. Giardia/Giardiasis | Leishmaniasis Leishmaniasis Leishmania species are obligate intracellular parasites that are transmitted by an infected sandfly. The mildest form is cutaneous leishmaniasis (CL), characterized by painless skin ulcers. The mucocutaneous type involves more tissue destruction, causing deformities. Visceral leishmaniasis (VL), the most severe form, presents with hepatosplenomegaly, anemia, thrombocytopenia, and fever. Leishmania/Leishmaniasis |
|
Tricomoniasis |
| Diagnóstico |
|
|
|
|
| Tratamiento |
|
Depende del síndrome clínico:
|
Depende de la enfermedad clínica:
|
|
| Prevención |
|
|
|
|
ELISA: ensayo inmunoabsorbente ligado a enzimas (por sus siglas en inglés)
DFA: ensayo de inmunofluorescencia directa (por sus siglas en inglés)
NAAT: ensayo de amplificación de ácidos nucleicos (por sus siglas en inglés)
PCR: reacción en cadena de la polimerasa (por sus siglas en inglés)
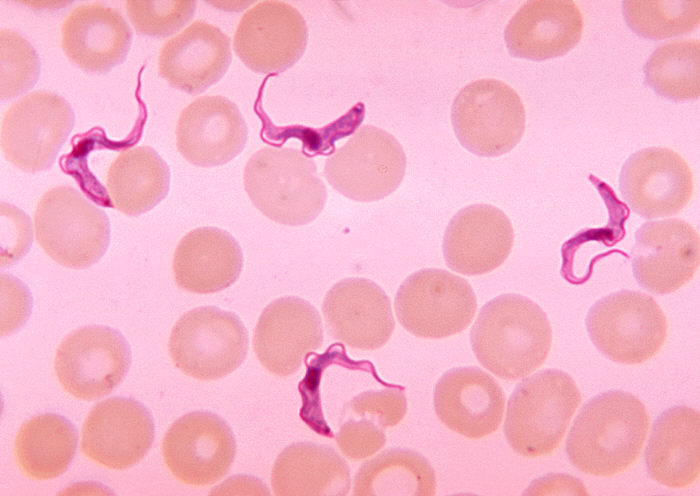
Frotis de sangre que muestra la presencia de tripomastigotes de Trypanosoma
Imagen: “Ms. Michaels forms” por CDC/Dr. Myron G. Schultz. Licencia: Dominio Público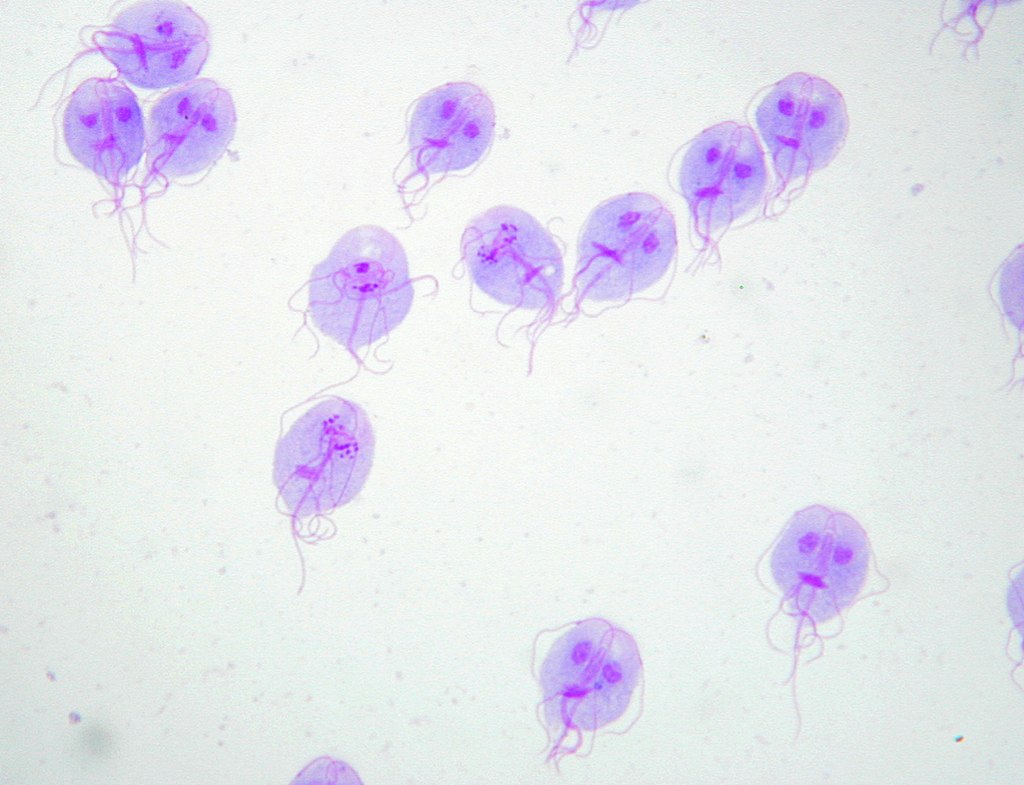
Tinción de Giemsa de trofozoitos de Giardia lamblia
Imagen: “Trophozoites of Giardia lamblia” por Eva Nohýnková, Department of Tropical Medicine, 1st Faculty of Medicine, Charles University in Prague and Hospital Bulovka, Czech Republic. Licencia: CC BY 4.0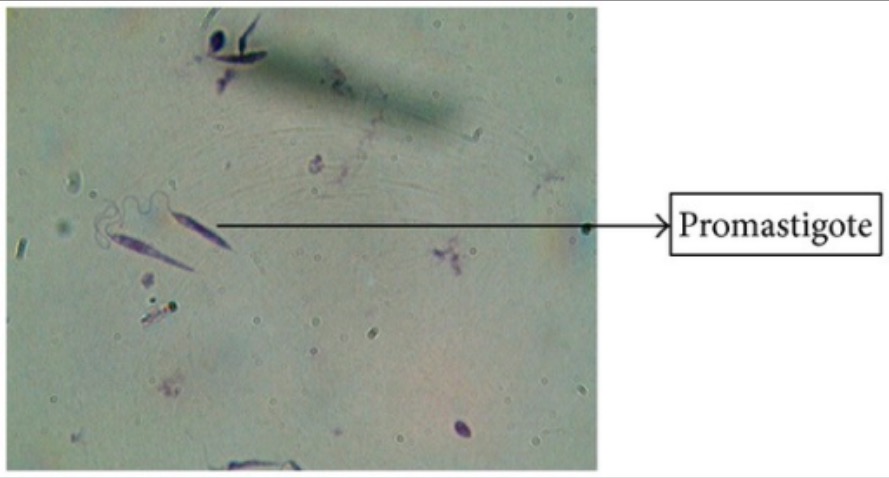
Tinción de Giemsa de promastigotes de Leishmania
Imagen: “Giemsa stain” por Arriyadh Community College, King Saud University, P.O. Box 28095, Riyadh 11437, Saudi Arabia. Licencia: CC BY 3.0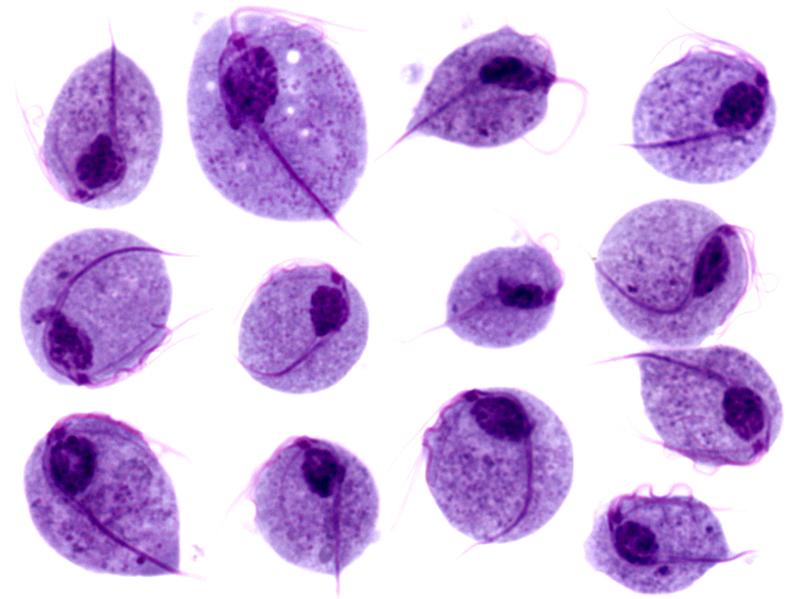
Imágenes microscópicas de trofozoítos de Trichomonas vaginalis
Imagen: “Trichomonas protozoa” por isis325. Licencia: CC BY 2.0.