El interferón ( IFN IFN Interferon (IFN) is a cytokine with antiviral properties (it interferes with viral infections) and various roles in immunoregulation. The different types are type I IFN (IFN-ɑ and IFN-β), type II IFN (IFN-ɣ), and type III IFN (IFN-ƛ). Interferons) es una citoquina con propiedades antivirales (interfiere en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum las infecciones víricas) y con diversas funciones en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la inmunorregulación. Los LOS Neisseria diferentes tipos son el IFN IFN Interferon (IFN) is a cytokine with antiviral properties (it interferes with viral infections) and various roles in immunoregulation. The different types are type I IFN (IFN-ɑ and IFN-β), type II IFN (IFN-ɣ), and type III IFN (IFN-ƛ). Interferons de tipo I (IFN-ɑ e IFN-β), el IFN IFN Interferon (IFN) is a cytokine with antiviral properties (it interferes with viral infections) and various roles in immunoregulation. The different types are type I IFN (IFN-ɑ and IFN-β), type II IFN (IFN-ɣ), and type III IFN (IFN-ƛ). Interferons de tipo II (IFN-ɣ) y el IFN IFN Interferon (IFN) is a cytokine with antiviral properties (it interferes with viral infections) and various roles in immunoregulation. The different types are type I IFN (IFN-ɑ and IFN-β), type II IFN (IFN-ɣ), and type III IFN (IFN-ƛ). Interferons de tipo III (IFN-ƛ). Los LOS Neisseria interferones de tipo I han sido ampliamente estudiados; estas proteínas se unen a los LOS Neisseria receptores de la superficie celular cuando son activadas por una infección viral. Tras la estimulación, se activan las vías para producir proteínas (e.g., ribonucleasa) que inhiben la replicación viral. Se forma un estado antiviral Antiviral Antivirals for Hepatitis B tanto en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum las células infectadas como en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum las no infectadas. El interferón de tipo I también tiene propiedades antitumorales. La actividad antiviral Antiviral Antivirals for Hepatitis B del interferón de tipo II (IFN-ɣ) no es tan potente como la del tipo I, pero el IFN- ɣ es crucial en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la activación de los LOS Neisseria macrófagos. IFN-ƛ recientemente descubierto ha HA Hemolytic anemia (HA) is the term given to a large group of anemias that are caused by the premature destruction/hemolysis of circulating red blood cells (RBCs). Hemolysis can occur within (intravascular hemolysis) or outside the blood vessels (extravascular hemolysis). Hemolytic Anemia demostrado tener actividad contra los LOS Neisseria virus Virus Viruses are infectious, obligate intracellular parasites composed of a nucleic acid core surrounded by a protein capsid. Viruses can be either naked (non-enveloped) or enveloped. The classification of viruses is complex and based on many factors, including type and structure of the nucleoid and capsid, the presence of an envelope, the replication cycle, and the host range. Virology intestinales. Con una amplia gama de efectos biológicos, los LOS Neisseria interferones se utilizan en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el tratamiento de enfermedades malignas, infecciones y otras afecciones relacionadas con el sistema inmunológico (e.g., esclerosis múltiple).
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Los LOS Neisseria interferones son un grupo de proteínas pertenecientes a una clase de moléculas de señalización conocidas como citoquinas y son liberadas por múltiples células durante la respuesta inflamatoria.
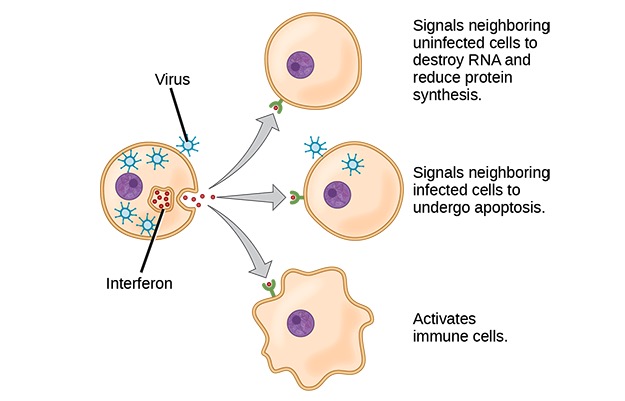
Interferones:
Los interferones son citoquinas que liberan las células infectadas por un virus, los leucocitos y otras células inmunológicas. Para limitar la infección, las respuestas de las células al interferón incluyen; inhibición de la síntesis de proteínas, activación de las células inmunológicas e inducción de la apoptosis.
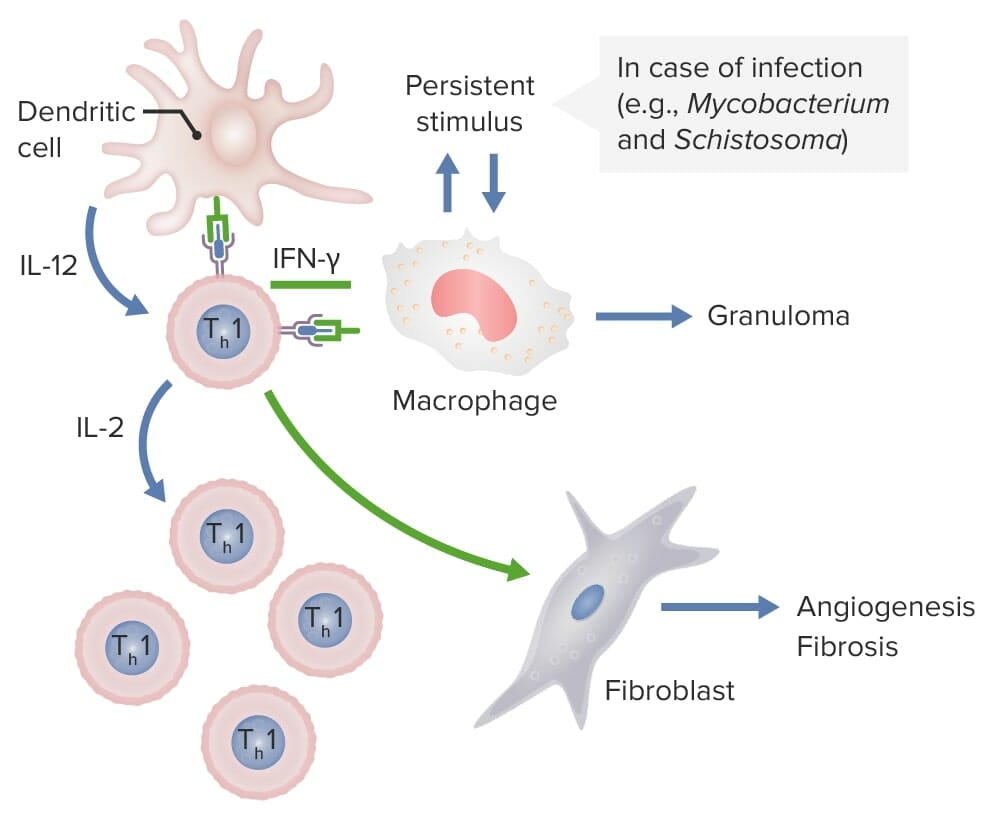
Las células dendríticas liberan IL-12, que activa a los linfocitos T CD4 colaboradores tipo 1 (Th1). Estos linfocitos Th1 producen IL-2, estimulando la producción de más subconjuntos de linfocitos Th1. Los linfocitos Th1 también liberan IFN-γ, que activa macrófagos y activa fibroblastos para causar angiogénesis y fibrosis. Si estos macrófagos son estimulados persistentemente por patógenos como Mycobacterium y Schistosoma, se forman granulomas.
Imagen por Lecturio.| Otra designación | Localización cromosómica | Célula de origen | |
|---|---|---|---|
| IFN-ɑ | Intron-A | 9p22 | Leucocitos |
| IFN-β | IFN-b2 | 9p21 | Fibroblastos |
| IFN-ɣ | Factor activador de macrófagos: inmuno-interferón | 12q14 | Linfocitos, macrófagos, linfocitos NK, células dendríticas |
| IFN-ƛ | IL-28A, IL-28B IL-28A, IL-28B Interferons, IL-29, IFNA14 | 19q13.13 | Células epiteliales |
| Interferón | Enfermedad(es) tratada(s) |
|---|---|
| Interferón-α |
|
| Interferón-β | Esclerosis múltiple |
| Interferón-γ |
|