La hepatitis autoinmune (HAI) es una enfermedad hepática inflamatoria crónica cada vez más reconocida, con una incidencia global en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum aumento. La presentación clínica varía desde casos asintomáticos hasta síntomas de insuficiencia hepática aguda (ictericia, dolor Dolor Inflammation en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el cuadrante superior derecho del abdomen). El diagnóstico se basa en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum hallazgos serológicos característicos, niveles elevados de IgG IgG The major immunoglobulin isotype class in normal human serum. There are several isotype subclasses of igg, for example, igg1, igg2a, and igg2b. Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis y evidencia histológica de hepatitis de interfase. El consenso reciente se aleja de marcadores tradicionales como la emperipolesis y las rosetas. El reconocimiento temprano es crucial dado el alto riesgo de mortalidad sin tratamiento. El tratamiento estándar con corticosteroides y azatioprina logra una respuesta bioquímica completa en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la mayoría de los LOS Neisseria pacientes. Los LOS Neisseria síndromes de solapamiento presentan desafíos diagnósticos y terapéuticos adicionales que requieren atención especializada.
Last updated: Jun 3, 2025
Epidemiología
Etiología
Asociada con otras afecciones autoinmunes (e.g., tiroiditis de Hashimoto, enfermedad de Graves, diabetes Diabetes Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a metabolic disease characterized by hyperglycemia and dysfunction of the regulation of glucose metabolism by insulin. Type 1 DM is diagnosed mostly in children and young adults as the result of autoimmune destruction of β cells in the pancreas and the resulting lack of insulin. Type 2 DM has a significant association with obesity and is characterized by insulin resistance. Diabetes Mellitus mellitus, artritis reumatoide, enfermedad celíaca, síndrome de Sjogren)
La hepatitis autoinmune es un diagnóstico diferencial para cualquier paciente que presente al AL Amyloidosis menos uno de los LOS Neisseria siguientes:
La hepatitis autoinmune es un diagnóstico de exclusión, por lo que el primer paso es descartar una infección viral, medicamentos, causas metabólicas o genéticas.
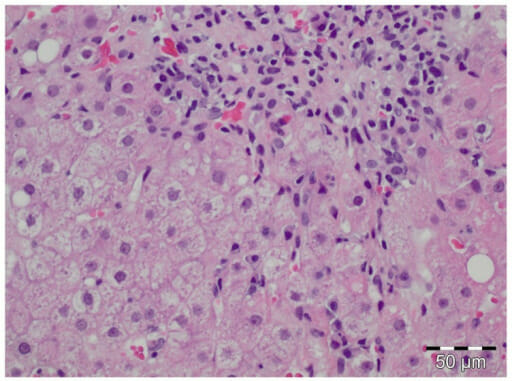
Histología de la hepatitis autoinmune en un individuo con infección aguda por virus de la hepatitis E
Imagen: “pone-0085330-g002” por Sven Pischke et al. Licencia: CC BY 4.0Las siguientes condiciones son diagnósticos diferenciales de la hepatitis autoinmune:
La hepatitis autoinmune puede solaparse con otras enfermedades hepáticas autoinmunes, lo que genera desafíos diagnósticos y terapéuticos: