La glomerulonefritis rápidamente progresiva es un síndrome de enfermedad glomerular grave con pérdida progresiva de la función renal en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum semanas o meses. La glomerulonefritis rápidamente progresiva se asocia con el síndrome nefrótico y es una manifestación de diferentes enfermedades. Histológicamente, las semilunas (la proliferación de células epiteliales y la infiltración de monocitos/macrófagos en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el espacio de Bowman) se encuentran en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum los LOS Neisseria glomérulos y surgen de una lesión inmunológica. Los LOS Neisseria principales mecanismos de lesión inmunológica se clasifican en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum enfermedad anti-membrana basal glomerular (anti-MBG), glomerulonefritis pauciinmune con semilunas y lesión mediada por complejos inmunes. La glomerulonefritis rápidamente progresiva puede manifestarse con hematuria Hematuria Presence of blood in the urine. Renal Cell Carcinoma, proteinuria Proteinuria The presence of proteins in the urine, an indicator of kidney diseases. Nephrotic Syndrome in Children y grados variables de edema Edema Edema is a condition in which excess serous fluid accumulates in the body cavity or interstitial space of connective tissues. Edema is a symptom observed in several medical conditions. It can be categorized into 2 types, namely, peripheral (in the extremities) and internal (in an organ or body cavity). Edema e hipertensión. El diagnóstico se basa en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum la presentación, las pruebas de laboratorio, la imagenología y la biopsia renal. El tratamiento oportuno es esencial porque la glomerulonefritis rápidamente progresiva puede convertirse en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum enfermedad renal en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum etapa terminal en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum un período corto de tiempo. El tratamiento incluye corticosteroides, ciclofosfamida u otros inmunosupresores y plasmaféresis (según la enfermedad subyacente).
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
Glomerulonefritis rápidamente progresiva es un síndrome de enfermedad glomerular grave con pérdida progresiva de la función renal en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum semanas o meses.
La mayoría de los LOS Neisseria casos se deben a una lesión inmunológica de los LOS Neisseria glomérulos. Los LOS Neisseria mecanismos y hallazgos se clasifican en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum:
| Condición | Microscopía de luz | Microscopio fluorescente | Microscopio de electrones |
|---|---|---|---|
| Enfermedad anti-membrana basal glomerular (anti-GBM) |
|
IgG IgG The major immunoglobulin isotype class in normal human serum. There are several isotype subclasses of igg, for example, igg1, igg2a, and igg2b. Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis lineal y C3 |
|
| Lesión mediada por complejos inmunes | IgG IgG The major immunoglobulin isotype class in normal human serum. There are several isotype subclasses of igg, for example, igg1, igg2a, and igg2b. Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis granular, otras inmunoglobulinas y complemento |
|
|
| Glomerulonefritis pauciinmune con medias lunas | Sin depósitos |
|
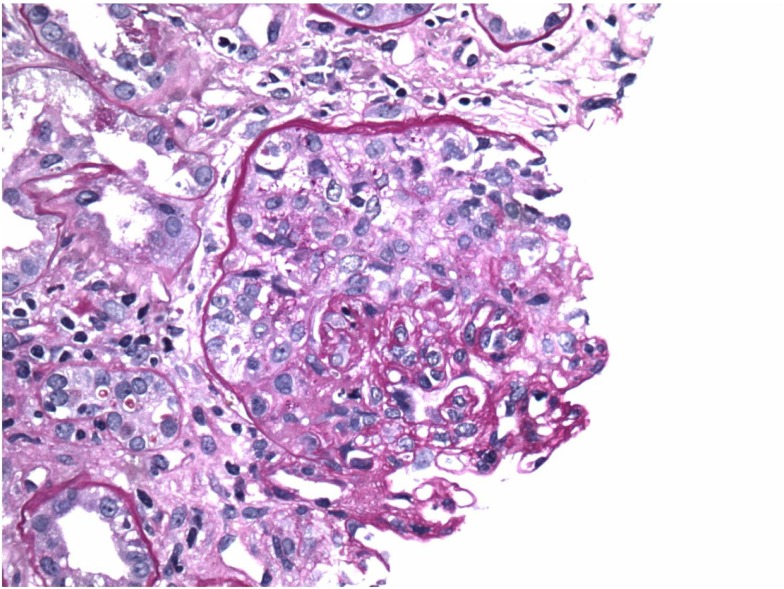
Enfermedad por anticuerpos anti-membrana basal glomerular (anti-GBM): medialunas en microscopía óptica
Imagen: “Crescents on light microscopy” por Mavani G. P., Pommier M., Win S., Michelis M. F., Rosenstock J. Licencia: CC BY 4.0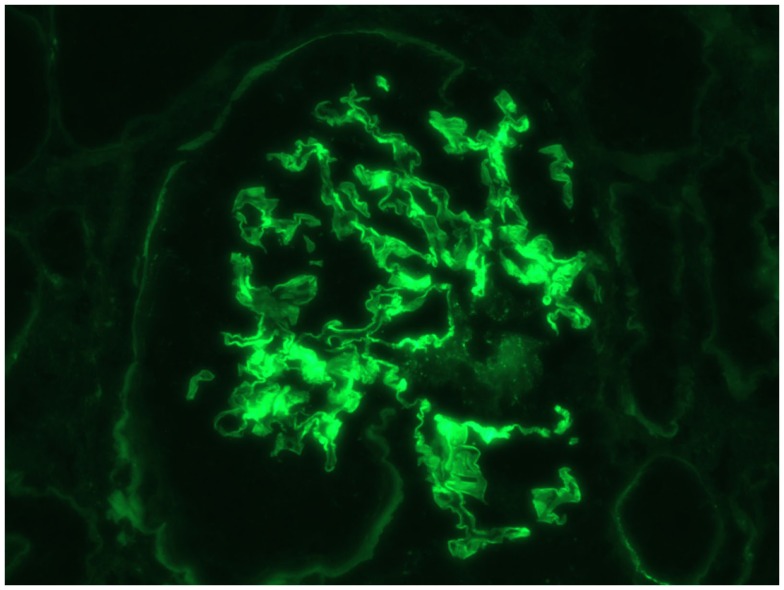
Enfermedad por anticuerpos anti-membrana basal glomerular (anti-GBM): tinción lineal de IgG a la inmunofluorescencia
Imagen: “Immunofluorescence linear staining of IgG” por Mavani G. P., Pommier M., Win S., Michelis M. F., Rosenstock J. Licencia: CC BY 4.0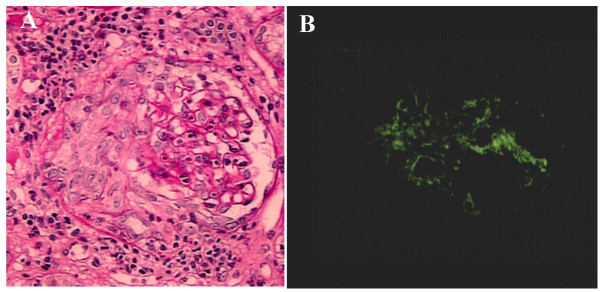
Glomerulonefritis rápidamente progresiva inducida por endocarditis infecciosa en tinción PAS e inmunofluorescencia:
A: PAS que demuestra la formación de media luna circunferencial y celular con nefritis intersticial
B: Inmunofluorescencia que demuestra tinción positiva para C3 en el área mesangial
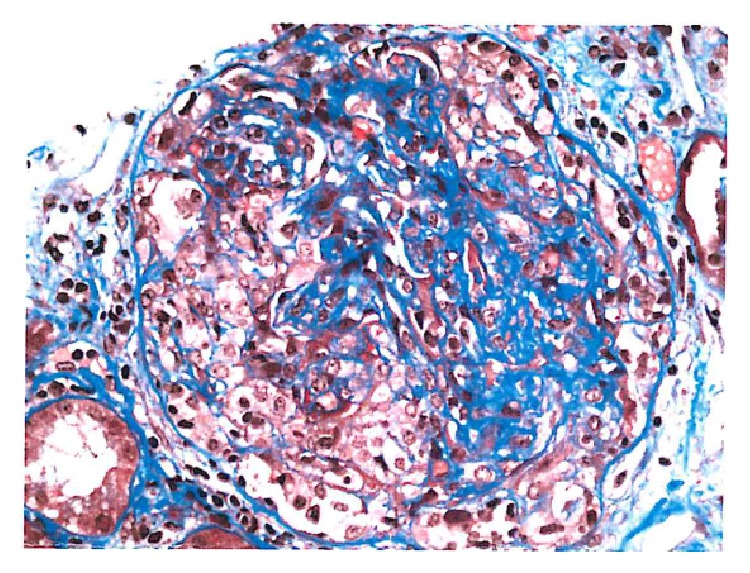
Glomerulonefritis pauciinmune con medialunas que muestra fibrina dentro de las medialunas celulares
Imagen: “Cellular crescent” por Syed R., Rehman A., Valecha G., El-Sayegh S. Licencia: CC BY 3.0