La giardiasis Giardiasis An infection of the small intestine caused by the flagellated protozoan giardia. It is spread via contaminated food and water and by direct person-to-person contact. Giardia/Giardiasis es causada por Giardia Giardia A genus of flagellate intestinal eukaryotes parasitic in various vertebrates, including humans. Characteristics include the presence of four pairs of flagella arising from a complicated system of axonemes and cysts that are ellipsoidal to ovoidal in shape. Nitroimidazoles duodenalis (también conocida como G. lamblia G. lamblia A species of parasitic eukaryotes that attaches itself to the intestinal mucosa and feeds on mucous secretions. The organism is roughly pear-shaped and motility is somewhat erratic, with a slow oscillation about the long axis. Giardia/Giardiasis o G. intestinalis G. intestinalis A species of parasitic eukaryotes that attaches itself to the intestinal mucosa and feeds on mucous secretions. The organism is roughly pear-shaped and motility is somewhat erratic, with a slow oscillation about the long axis. Giardia/Giardiasis), un protozoo flagelado que puede infectar el tracto intestinal. La transmisión ocurre más comúnmente a través de la ingestión de quistes en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum agua o alimentos contaminados, o por propagación fecal-oral de persona a persona. La exquistación ocurre en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum el tracto gastrointestinal y los LOS Neisseria trofozoítos se adhieren a la mucosa intestinal a través de un disco adhesivo ventral, lo que provoca malabsorción. El síntoma distintivo de la giardiasis Giardiasis An infection of the small intestine caused by the flagellated protozoan giardia. It is spread via contaminated food and water and by direct person-to-person contact. Giardia/Giardiasis es la esteatorrea maloliente. Los LOS Neisseria pacientes que desarrollan infecciones crónicas pueden experimentar pérdida de peso, retraso del crecimiento y deficiencias vitamínicas como resultado de la malabsorción. El diagnóstico se realiza mediante la detección de organismos de Giardia Giardia A genus of flagellate intestinal eukaryotes parasitic in various vertebrates, including humans. Characteristics include the presence of four pairs of flagella arising from a complicated system of axonemes and cysts that are ellipsoidal to ovoidal in shape. Nitroimidazoles, antígenos o ácido desoxirribonucleico (ADN) en EN Erythema nodosum is an immune-mediated panniculitis (inflammation of the subcutaneous fat) caused by a type IV (delayed-type) hypersensitivity reaction. It commonly manifests in young women as tender, erythematous nodules on the shins. Erythema Nodosum las heces. El manejo incluye tratamiento de soporte y terapia antimicrobiana con tinidazol, metronidazol, nitazoxanida o albendazol. Las medidas de prevención incluyen el lavado adecuado de manos y el tratamiento del agua.
Last updated: Dec 15, 2025
La giardiasis Giardiasis An infection of the small intestine caused by the flagellated protozoan giardia. It is spread via contaminated food and water and by direct person-to-person contact. Giardia/Giardiasis es causada por el protozoo flagelado Giardia Giardia A genus of flagellate intestinal eukaryotes parasitic in various vertebrates, including humans. Characteristics include the presence of four pairs of flagella arising from a complicated system of axonemes and cysts that are ellipsoidal to ovoidal in shape. Nitroimidazoles duodenalis (sinónimos: G. lamblia G. lamblia A species of parasitic eukaryotes that attaches itself to the intestinal mucosa and feeds on mucous secretions. The organism is roughly pear-shaped and motility is somewhat erratic, with a slow oscillation about the long axis. Giardia/Giardiasis, G. intestinalis G. intestinalis A species of parasitic eukaryotes that attaches itself to the intestinal mucosa and feeds on mucous secretions. The organism is roughly pear-shaped and motility is somewhat erratic, with a slow oscillation about the long axis. Giardia/Giardiasis).
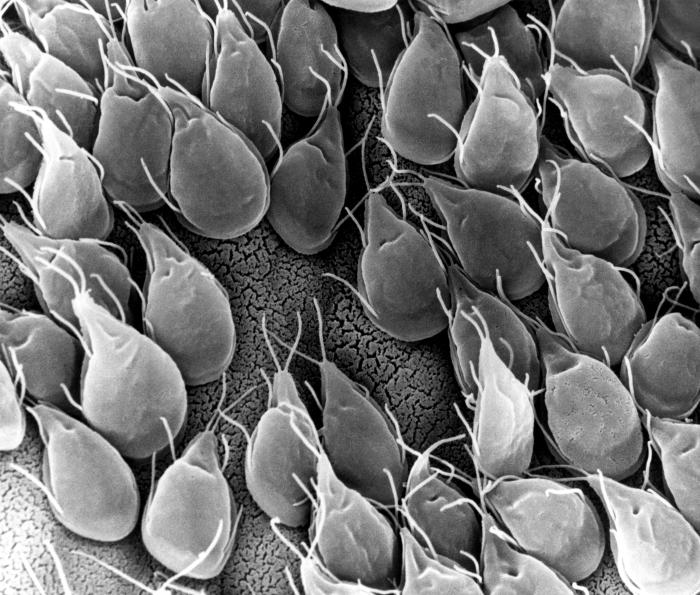
Imagen de microscopio electrónico de barrido de trofozoítos de G. lamblia
Imagen: “SEM” por CDC/Dr. Stan Erlandsen. Licencia: Dominio Público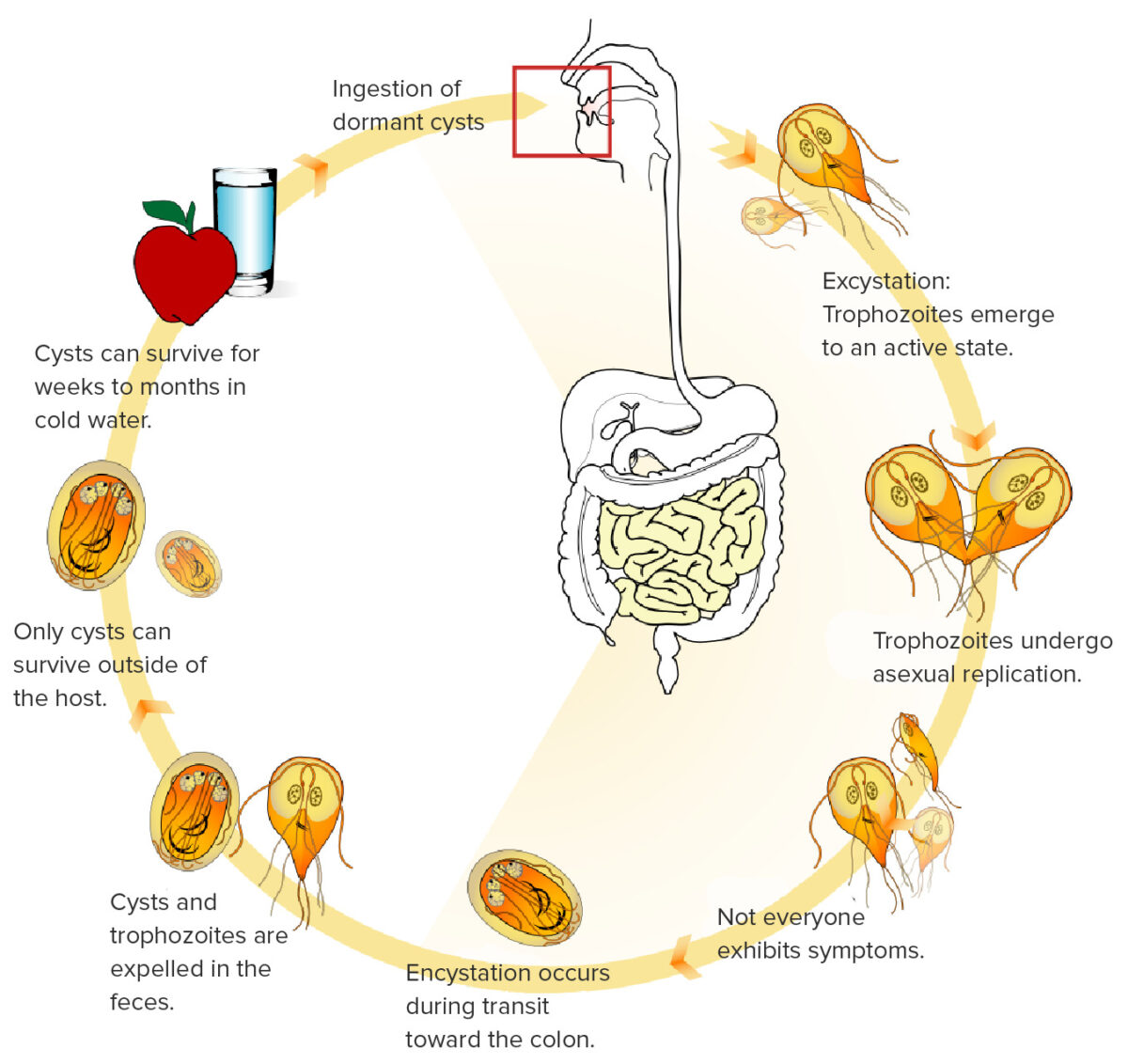
Esta imagen muestra el ciclo de vida de G. lamblia. Los quistes pueden sobrevivir durante largos periodos de tiempo en agua fría y luego ser consumidos inadvertidamente. Una vez consumidos, los quistes se transforman en forma de trofozoíto, se replican e infectan los intestinos. Los trofozoítos se adhieren a las vellosidades intestinales, dando lugar a los síntomas.
Imagen: “Giardia life cycle” por LadyofHats. Licencia: Dominio Público, editada por Lecturio.Aunque algunos pacientes pueden ser asintomáticos, la característica clínica distintiva de la giardiasis Giardiasis An infection of the small intestine caused by the flagellated protozoan giardia. It is spread via contaminated food and water and by direct person-to-person contact. Giardia/Giardiasis es la diarrea malabsortiva.
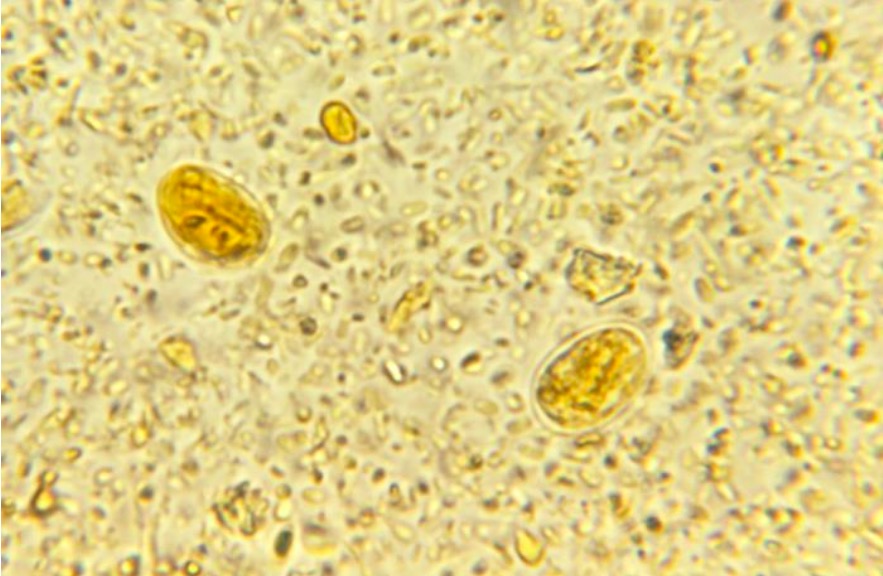
Análisis microscópico de las heces que revela la presencia de 2 quistes de G. lamblia
Imagen: “21085” por CDC. Licencia: Dominio Público| Giardia Giardia A genus of flagellate intestinal eukaryotes parasitic in various vertebrates, including humans. Characteristics include the presence of four pairs of flagella arising from a complicated system of axonemes and cysts that are ellipsoidal to ovoidal in shape. Nitroimidazoles | Leishmania Leishmania Leishmania species are obligate intracellular parasites that are transmitted by an infected sandfly. The disease is endemic to Asia, the Middle East, Africa, the Mediterranean, and South and Central America. Clinical presentation varies, dependent on the pathogenicity of the species and the host’s immune response. Leishmania/Leishmaniasis | Trypanosoma | Trichomonas Trichomonas A genus of parasitic flagellate eukaryotes distinguished by the presence of four anterior flagella, an undulating membrane, and a trailing flagellum. Nitroimidazoles | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Características |
|
|
|
|
| Formas |
|
|
|
|
| Transmisión |
|
|
|
Transmisión sexual |
| Entidad clínica | Giardiasis Giardiasis An infection of the small intestine caused by the flagellated protozoan giardia. It is spread via contaminated food and water and by direct person-to-person contact. Giardia/Giardiasis | Leishmaniasis Leishmaniasis Leishmania species are obligate intracellular parasites that are transmitted by an infected sandfly. The mildest form is cutaneous leishmaniasis (CL), characterized by painless skin ulcers. The mucocutaneous type involves more tissue destruction, causing deformities. Visceral leishmaniasis (VL), the most severe form, presents with hepatosplenomegaly, anemia, thrombocytopenia, and fever. Leishmania/Leishmaniasis |
|
Tricomoniasis |
| Diagnóstico |
|
|
|
|
| Tratamiento |
|
Depende del síndrome clínico:
|
Depende de la enfermedad clínica:
|
|
| Prevención |
|
|
|
|
ELISA: ensayo inmunoabsorbente ligado a enzimas (por sus siglas en inglés)
DFA: ensayo de inmunofluorescencia directa (por sus siglas en inglés)
NAAT: ensayo de amplificación de ácidos nucleicos (por sus siglas en inglés)
PCR: reacción en cadena de la polimerasa (por sus siglas en inglés)
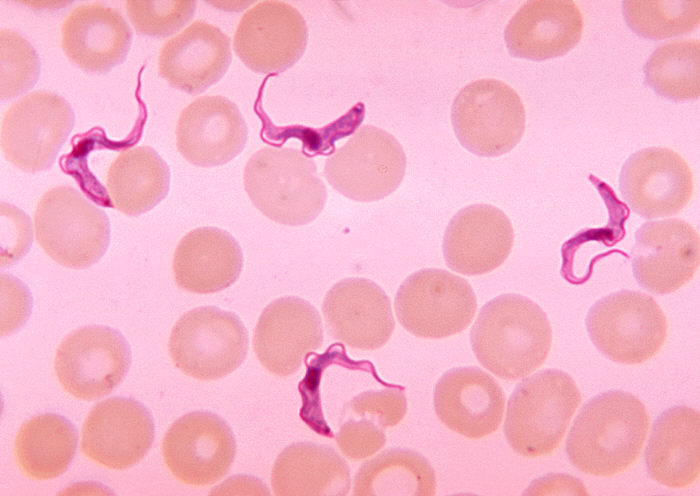
Frotis de sangre que muestra la presencia de tripomastigotes de Trypanosoma
Imagen: “Ms. Michaels forms” por CDC/Dr. Myron G. Schultz. Licencia: Dominio Público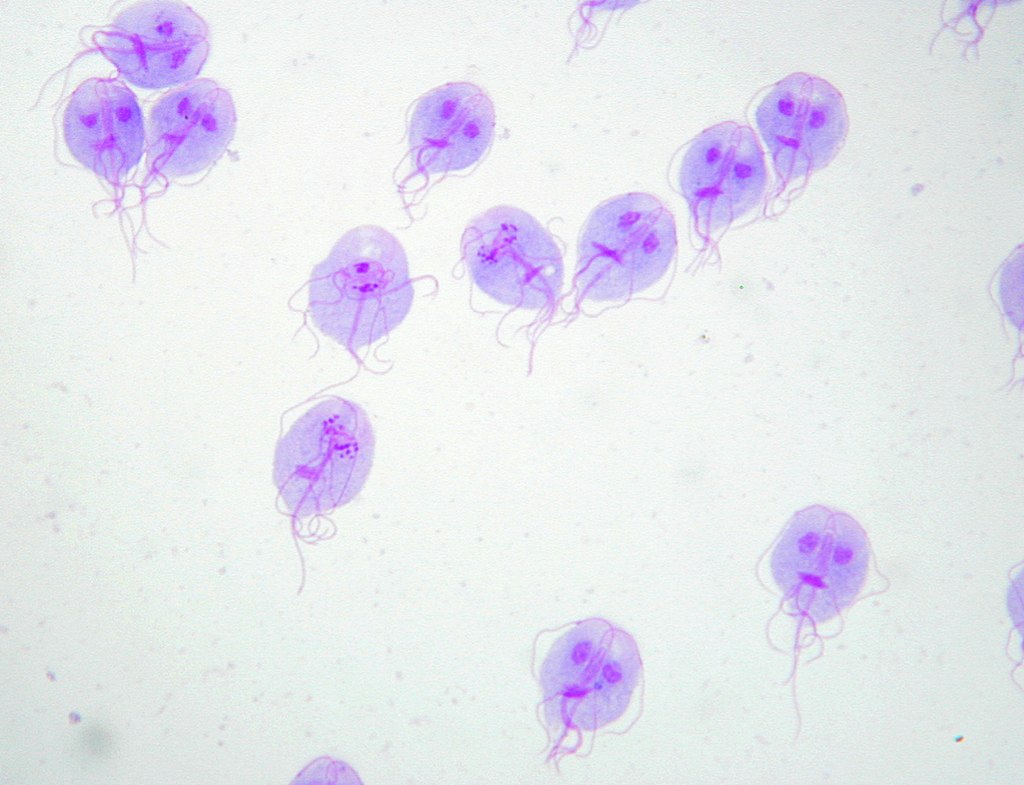
Tinción de Giemsa de trofozoitos de G. lamblia
Imagen: “Trophozoites of Giardia lamblia” por Eva Nohýnková, Department of Tropical Medicine, 1st Faculty of Medicine, Charles University in Prague and Hospital Bulovka, Czech Republic. Licencia: CC BY 4.0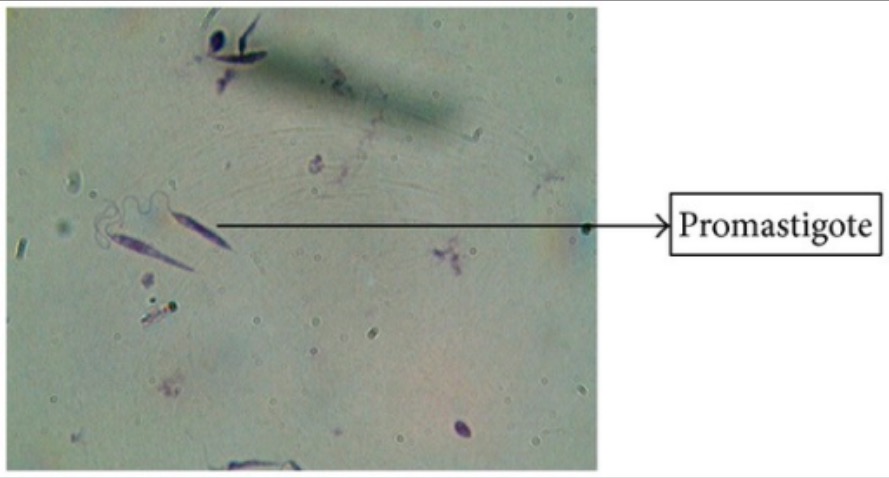
Tinción de Giemsa de promastigotes de Leishmania
Imagen: “Giemsa stain” por Arriyadh Community College, King Saud University, P.O. Box 28095, Riyadh 11437, Saudi Arabia. Licencia: CC BY 3.0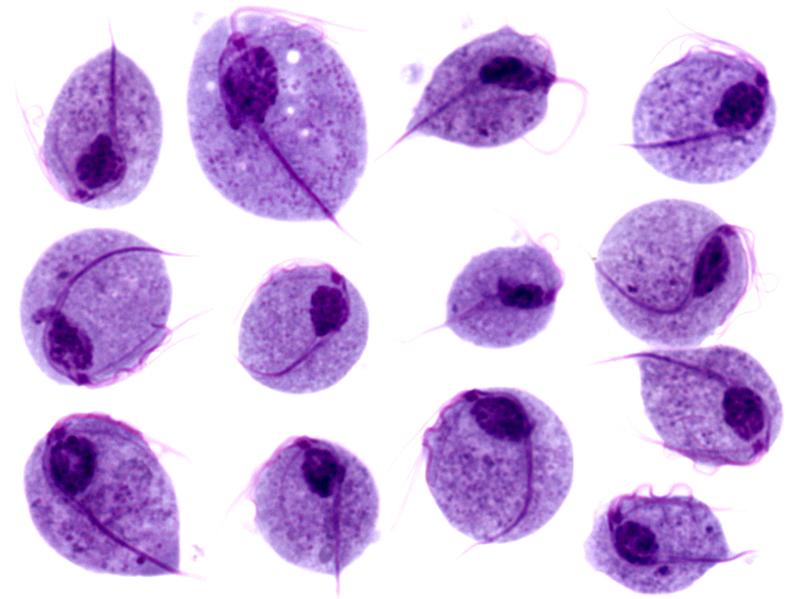
Imágenes microscópicas de trofozoitos de Trichomonas vaginalis
Imagen: “Trichomonas protozoa” por isis325. Licencia: CC BY 2.0.